基础数据类型(四类八种 ) 不能为null。
整数型 byte 取值范围2的8次方
short 取值范围2的16次方
int 取值范围2的32次方 一般用int
long 取值范围2的64次方
浮点型 :浮点型记录小数点的数据类型,一般用double。
float 4个字节
double 8个字节
布尔型
boolean(true false)
字符型
char(可以是一个字母,也可以是一个汉字)
基础数据类型全部存到栈空间,所以不能为空。
引用类型:String s="abc",
所有的类、数组、接口
运算符 字符串连接字符串需要注意的地方:在输出的时候,只要有一个参数是字符串,整个输出结果都是字符串。
异或运算符:转换成二进制的形式来对比每一位数,不一样的为1,一样的为0;
类型转换的优先级:double float long int chcar short byte
char short byte进行运算的时候,取值默认为int
隐式转换(低--》高) 显示转换(高--》低)
例如:int a=5;b=3.4;
a+=b a的值为8; 用+=赋值的时候有一个隐式的自动转换
byte a=(byte)200 这个为显示转换 也成称为强制转换。
public class textJava3{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 3;
int c = 5 - (a--); 2
boolean b = a == c; true
b = b && (a < c--) ? false : true; a=2,c=2 true c赋值后自减1
int d = b ? 7 : 9; 7
int e = d - 3; 4 (*错了)
c *= 3; 3
int f = ((++e == c) ? 25 : 35) + (++a); 38
System.out.println("f的值:" + f);
}
class text7
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b, c;
a = c = 8; // a=8,c=8
System.out.println("a的值"+a);
System.out.println("c的值"+c);
b = a++; // b=8,a=9,c=8
System.out.println("b的值"+b);
System.out.println("a的值"+a);
System.out.println("c的值"+c);
short d = 3; // d=3
System.out.println("d的值"+d);
long e1 = d++ + a; // e1=12
System.out.println("e1的值"+e1);
long e2 = d++ + a++; // e2=13
System.out.println("e2的值"+e2);
boolean b1 = false;
boolean b2 = !b1; // true
System.out.println("b2的值"+b2);
float g = b2 ? a : b; // 10
System.out.println("g的值"+g);
double h = g -= 1; // 9.0
System.out.println("h的值"+h);
boolean b3 = g == 10; // false
System.out.println("b3的值"+b3);
char s = b3 ? 'a' : 'b'; // b
System.out.println("s的值"+s);
int i = 2 * s; // 196 这里s=b b代表的是编码值 *错了
System.out.println("i的值"+i);
前加加 后加加 前减减 后减减 即使在外边加了括号 不会影响运算顺序
前加加:将一个整型变量进行前加加,程序先将变量加一,然后在进行计算;
后加加:将一个整型变量进行后加加,程序会先进行就算,计算完以后,再将变量加一
前减减:将一个整型变量进行前减减,程序会先将变量值减一,在进行计算;
后减减:将一个整型变量进行后减减,程序会先进行计算,计算完以后再将变量减一
分支和循环
if(){
}
if(){
}else{
}
if(){
}else if(){
}
if(){
}else if(){
}else
switch(a){
case 1
...
break
case 2
...
break
case 3
...
break
}
if和switch的区别
循环
for( int i=0; i<10; i++){
...
}
while(循环条件){
}
do{
}while(); 这个循环至少循环一次。
if 跟switch的区别
if
1、对具体的值进行判断
2、对区间判断。
3、对运算结果是布尔类型的表达式进行判断
switch
对具体的值进行判断
值得个数通常是固定的
对于几个固定的值判断建议使用switch语句,因为switch语句会将具体的答案一次性都加载到内存,效率相对高
如果判断的具体数值不多,而且符合byte、short、int、char这四种类型。虽然两个语句都可以使用,建议使用switch语句。因为效率稍高
其他情况:对区间判断,对结果为boolean类型判断,使用if,if的使用范围更广。
import java.util.Scanner;
class siji
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份。。");
String str=s.nextLine();
int month=Integer.parseInt(str);
/*if(month>=2&&month<=4){
System.out.println("春天了");
}else if(month>=5&&month<=7){
System.out.println("注意防暑");
}else if(month>=8&&month<=10){
System.out.println("秋风瑟瑟");
}else{
System.out.println("雪花飘飘");
}*/
switch(month){
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
System.out.println("春天了");
break;
case 5:
case 6:
case 7:
System.out.println("注意防暑");
break;
case 8:
case 9:
case 10:
System.out.println("秋风瑟瑟");
break;
case 11:
case 12:
case 1:
System.out.println("雪花飘飘");}
}
}
在选择分支较多时,选用switch...case结构会提高程序的效率,但switch不足的地方在于只能处理字符或者数字类型的变量,if...else结构更加灵活一些,if...else结构可以用于判断表达式是否成立,比如if(a+b>c),if...else的应用范围更广,switch...case结构在某些情况下可以替代if...else结构。
for循环与while循环,当不能明确要循环的次数的时候选择while循环。
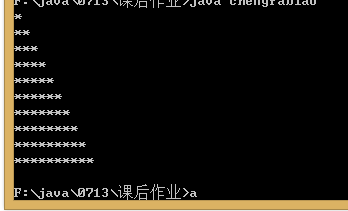
class chengfabiao{
public static void main(String[] args){
for( int i=0; i<10; i++){
for(int j=0; j<i; j++){
System.out.print("*");}
System.out.println("*");}
class chengfabiao{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=0; //初始化条件
while (i<100){ //循环条件
System.out.println(i); //循环体
i++;//迭代条件
}}
}