Redis过期键删除
在Redis中使用server.dbnum来控制Redis实例包含的DB数量,每个RedisDB结构如下:
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
其中使用*dict字典来存放该DB的所有键,使用*expires字典来存放该DB下所有设置过期时间的键,*expires字典存放的value是对应Key的过期时间( UNIX时间戳)。
Redis提供三种过期删除策略:
- 定时删除,在设置键过期时同时设置一个定时器,定时器到期后立即删除该键。优点是能保证键在过期后能立即被删除,缺点是定时器会消耗过多CPU资源。
- 惰性删除,在每次请求键时判断该键是否已过期,如果过期则删除该键。优点是消耗CPU资源较少,缺点是删除操作实时性较低,存在过期键长时间未被删除的情况。
- 定期删除,通过定时任务进行触发,遍历所有RedisDB,并从每个RedisDB的
*expires字典随机获取已设置过期的键,找出已过期的键并进行删除。
在实际生成环境中,主要采用惰性删除策略+定期删除策略来对已过期的键进行清理。
惰性删除策略
惰性删除主要依赖于函数expireIfNeeded来完成,在进行lookupKeyRead、lookupKeyWrite、dbRandomKey等操作时,都会调用expireIfNeeded来检查键是否过期。
/* This function is called when we are going to perform some operation
* in a given key, but such key may be already logically expired even if
* it still exists in the database. The main way this function is called
* is via lookupKey*() family of functions.
*
* The behavior of the function depends on the replication role of the
* instance, because slave instances do not expire keys, they wait
* for DELs from the master for consistency matters. However even
* slaves will try to have a coherent return value for the function,
* so that read commands executed in the slave side will be able to
* behave like if the key is expired even if still present (because the
* master has yet to propagate the DEL).
*
* In masters as a side effect of finding a key which is expired, such
* key will be evicted from the database. Also this may trigger the
* propagation of a DEL/UNLINK command in AOF / replication stream.
*
* The return value of the function is 0 if the key is still valid,
* otherwise the function returns 1 if the key is expired. */
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
/* If we are running in the context of a slave, instead of
* evicting the expired key from the database, we return ASAP:
* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
*
* Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
* we think the key is expired at this time. */
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
/* Delete the key */
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",key,db->id);
return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
主动删除策略
主动删除策略主要依赖activeExpireCycleTryExpire函数来实现单个键的删除,通过activeExpireCycle和expireSlaveKeys来分别清理主实例和从实例上的过期键。
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Incremental collection of expired keys.
*
* When keys are accessed they are expired on-access. However we need a
* mechanism in order to ensure keys are eventually removed when expired even
* if no access is performed on them.
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Helper function for the activeExpireCycle() function.
* This function will try to expire the key that is stored in the hash table
* entry 'de' of the 'expires' hash table of a Redis database.
*
* If the key is found to be expired, it is removed from the database and
* 1 is returned. Otherwise no operation is performed and 0 is returned.
*
* When a key is expired, server.stat_expiredkeys is incremented.
*
* The parameter 'now' is the current time in milliseconds as is passed
* to the function to avoid too many gettimeofday() syscalls. */
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
if (now > t) {
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_expire)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",keyobj,db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
函数activeExpireCycle提供两者工作模式:
- ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST,快速过期模式,执行的时间不会长过 EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒(默认1ms),且在EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒之内不会再重新执行。
- ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW,正常过期模式,执行时间上限为:1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100,其中ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC默认值为25,server.hz默认值为10,默认为25ms。
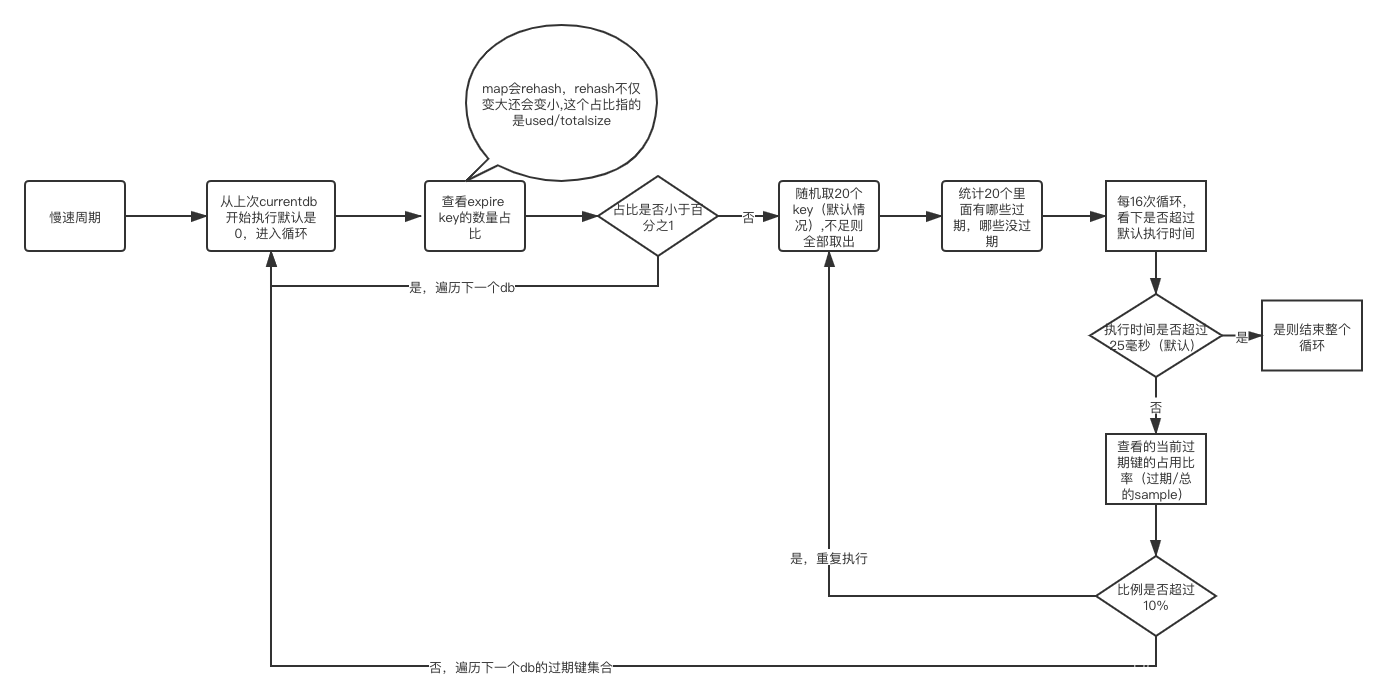
/* Try to expire a few timed out keys. The algorithm used is adaptive and
* will use few CPU cycles if there are few expiring keys, otherwise
* it will get more aggressive to avoid that too much memory is used by
* keys that can be removed from the keyspace.
*
* 函数尝试删除数据库中已经过期的键。
* 当带有过期时间的键比较少时,函数运行得比较保守,
* 如果带有过期时间的键比较多,那么函数会以更积极的方式来删除过期键,
* 从而可能地释放被过期键占用的内存。
*
* No more than REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL databases are tested at every
* iteration.
*
* 每次循环中被测试的数据库数目不会超过 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL 。
* REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL 在代码中已经写死为16,不可以配置。
*
* This kind of call is used when Redis detects that timelimit_exit is
* true, so there is more work to do, and we do it more incrementally from
* the beforeSleep() function of the event loop.
*
* 如果 timelimit_exit 为真,那么说明还有更多删除工作要做,
* 那么在 beforeSleep() 函数调用时,程序会再次执行这个函数。
*
* Expire cycle type:
*
* 过期循环的类型:
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST the function will try to run a
* "fast" expire cycle that takes no longer than EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION
* microseconds, and is not repeated again before the same amount of time.
*
* 如果循环的类型为 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST ,
* 那么函数会以“快速过期”模式执行,
* 执行的时间不会长过 EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒,
* 并且在 EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒之内不会再重新执行。
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW, that normal expire cycle is
* executed, where the time limit is a percentage of the REDIS_HZ period
* as specified by the REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_TIME_PERC define.
*
* 如果循环的类型为 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW ,
* 那么函数会以“正常过期”模式执行,
* 函数的执行时限为 REDIS_HS 常量的一个百分比,
* 这个百分比由 REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_TIME_PERC 定义。
*/
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* This function has some global state in order to continue the work
* incrementally across calls. */
// 静态变量,用来累积函数连续执行时的数据
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */
unsigned int j, iteration = 0;
// 默认每次处理的数据库数量
unsigned int dbs_per_call = REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
// 函数开始的时间
long long start = ustime(), timelimit;
// 快速模式
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exited
* for time limt. Also don't repeat a fast cycle for the same period
* as the fast cycle total duration itself. */
// 如果上次函数没有触发 timelimit_exit ,那么不执行处理
if (!timelimit_exit) return;
// 如果距离上次执行未够一定时间,那么不执行处理
if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*2) return;
// 运行到这里,说明执行快速处理,记录当前时间
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
/* We usually should test REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with
* two exceptions:
*
* 一般情况下,函数只处理 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL 个数据库,
* 除非:
*
* 1) Don't test more DBs than we have.
* 当前数据库的数量小于 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL
* 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs
* in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want
* expired keys to use memory for too much time.
* 如果上次处理遇到了时间上限,那么这次需要对所有数据库进行扫描,
* 这可以避免过多的过期键占用空间
*/
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* We can use at max ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC percentage of CPU time
* per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of
* server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of
* microseconds we can spend in this function. */
// 函数处理的微秒时间上限
// ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 默认为 25 ,也即是 25 % 的 CPU 时间
timelimit = 1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
// 如果是运行在快速模式之下
// 那么最多只能运行 FAST_DURATION 微秒
// 默认值为 1000 (微秒)
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* in microseconds. */
// 遍历数据库
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
int expired;
// 指向要处理的数据库
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
/* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time
* in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to
* distribute the time evenly across DBs. */
// 为 DB 计数器加一,如果进入 do 循环之后因为超时而跳出
// 那么下次会直接从下个 DB 开始处理
current_db++;
/* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle more than 25%
* of the keys were expired. */
do {
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
/* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */
// 获取数据库中带过期时间的键的数量
// 如果该数量为 0 ,直接跳过这个数据库
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
// 获取数据库中键值对的数量
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
// 当前时间
now = mstime();
/* When there are less than 1% filled slots getting random
* keys is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...
* The dictionary will be resized asap. */
// 这个数据库的使用率低于 1% ,扫描起来太费力了(大部分都会 MISS)
// 跳过,等待字典收缩程序运行
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
/* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys
* with an expire set, checking for expired ones.
*
* 样本计数器
*/
// 已处理过期键计数器
expired = 0;
// 键的总 TTL 计数器
ttl_sum = 0;
// 总共处理的键计数器
ttl_samples = 0;
// 每次最多只能检查 LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP 个键, ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP 已经写死为20
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
// 开始遍历数据库
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
// 从 expires 中随机取出一个带过期时间的键
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
// 计算 TTL
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
// 如果键已经过期,那么删除它,并将 expired 计数器增一
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl < 0) ttl = 0;
// 累积键的 TTL
ttl_sum += ttl;
// 累积处理键的个数
ttl_samples++;
}
/* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */
// 为这个数据库更新平均 TTL 统计数据
if (ttl_samples) {
// 计算当前平均值
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
// 如果这是第一次设置数据库平均 TTL ,那么进行初始化
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
/* Smooth the value averaging with the previous one. */
// 取数据库的上次平均 TTL 和今次平均 TTL 的平均值
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl+avg_ttl)/2;
}
/* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to
* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the
* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */
// 我们不能用太长时间处理过期键,
// 所以这个函数执行一定时间之后就要返回
// 更新遍历次数
iteration++;
// 每遍历 16 次执行一次
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0 && /* check once every 16 iterations. */
(ustime()-start) > timelimit)
{
// 如果遍历次数正好是 16 的倍数
// 并且遍历的时间超过了 timelimit
// 那么断开 timelimit_exit
timelimit_exit = 1;
}
// 已经超时了,返回
if (timelimit_exit) return;
/* We don't repeat the cycle if there are less than 25% of keys
* found expired in the current DB. */
// 如果已删除的过期键占当前总数据库带过期时间的键数量的 25 %
// 那么不再遍历
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);
}
}
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW(正常过期模式)使用serverCron-->databasesCron来调用,其执行频率由参数redisServer.hz来控制,默认值为10,即每秒执行10次。
/* This function handles 'background' operations we are required to do
* incrementally in Redis databases, such as active key expiring, resizing,
* rehashing. */
void databasesCron(void) {
/* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves
* as master will synthesize DELs for us. */
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (server.masterhost == NULL) {
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
}
/* This is our timer interrupt, called server.hz times per second.
* Here is where we do a number of things that need to be done asynchronously.
* For instance:
*
* - Active expired keys collection (it is also performed in a lazy way on
* lookup).
* - Software watchdog.
* - Update some statistic.
* - Incremental rehashing of the DBs hash tables.
* - Triggering BGSAVE / AOF rewrite, and handling of terminated children.
* - Clients timeout of different kinds.
* - Replication reconnection.
* - Many more...
*
* Everything directly called here will be called server.hz times per second,
* so in order to throttle execution of things we want to do less frequently
* a macro is used: run_with_period(milliseconds) { .... }
*/
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
......
/* We need to do a few operations on clients asynchronously. */
clientsCron();
/* Handle background operations on Redis databases. */
databasesCron();
......
}
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST(快速过期模式)在函数beforeSleep中调用,beforeSleep函数在main函数中绑定到server.el(aeEventLoop)循环事件上。快速过期模式执行频率较高,但单次执行事件较短(最多1ms)。
/* This function gets called every time Redis is entering the
* main loop of the event driven library, that is, before to sleep
* for ready file descriptors. */
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
UNUSED(eventLoop);
/* Call the Redis Cluster before sleep function. Note that this function
* may change the state of Redis Cluster (from ok to fail or vice versa),
* so it's a good idea to call it before serving the unblocked clients
* later in this function. */
if (server.cluster_enabled) clusterBeforeSleep();
/* Run a fast expire cycle (the called function will return
* ASAP if a fast cycle is not needed). */
if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL)
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST);
}
在定期清理策略中,主要还是依赖ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW--正常过期模式来清理数据。