2021-05-15 19:18:59
A*就不赘述,比较关键的地方需要注意。
下边内容参考自:
- 高飞--深蓝学院
- pathfinding.js
- https://www.redblobgames.com/
1.关于admisible
一个一定要明白的概念,就是admissible。
定义:h <= h*,则h就是admissible heuristic。其中h*到终点最小的真实cost。
只要h是admissible,那A*结果一定是最优的,否则就是次优的(换来的是计算速度提升)。
2.三种heuristic
先介绍代码中会用到的eigen中的几种范数,老是记不住:
- squaredNorm(): 等价于vector自身点积,即所有元素平方和。
- norm(): 返回squaredNorm()的开方根,注意不管是几维的vector,都是开平方根。
- lpNorm< p >(): p取Infinity,就表示L∞范数,p取1就表示L1范数,p取2就表示L2范数
范数的概念:
- 1范数:即向量元素绝对值之和
- 2范数:Euclid范数(欧几里得范数,常用计算向量长度),即向量元素绝对值的平方和再开方
- ∞范数:即所有向量元素绝对值中的最大值
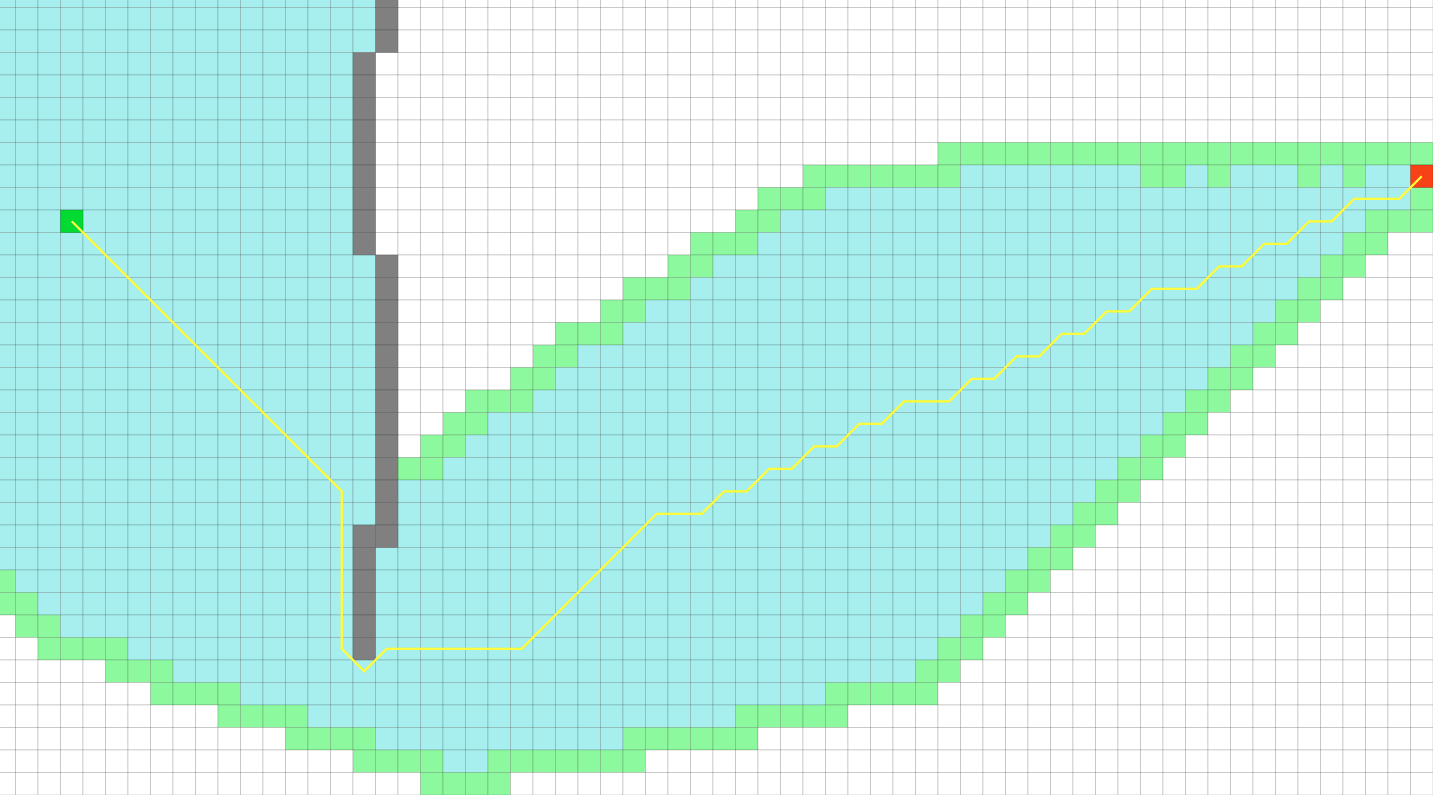
2.1 Euclidean Distance
double Astar::getEuclHeu(Eigen::Vector3d x1, Eigen::Vector3d x2) { return tie_breaker_ * (x2 - x1).norm(); //norm = sqrt(squaredNorm()) }
理想结果是(PathFinding.js) VS 实际结果,正确!

2.2 Manhattan Distance
引用:
在该网站的介绍中,有一个系数D,该如何理解。
文中定义D:两个相邻栅格之间的最小距离。
我的理解:这里之所以有D,是因为node是用的栅格索引,而不是物理上的位置,所以需要D,而我代码中,用的就是物理上的坐标,所以不需要D
function heuristic(node) = dx = abs(node.x - goal.x) dy = abs(node.y - goal.y) return D * (dx + dy)
double Astar::getManhHeu(Eigen::Vector3d x1, Eigen::Vector3d x2) { double dx = fabs(x1(0) - x2(0)); double dy = fabs(x1(1) - x2(1));return tie_breaker_ * (dx + dy); }
理想结果是(PathFinding.js) VS 实际结果,正确!
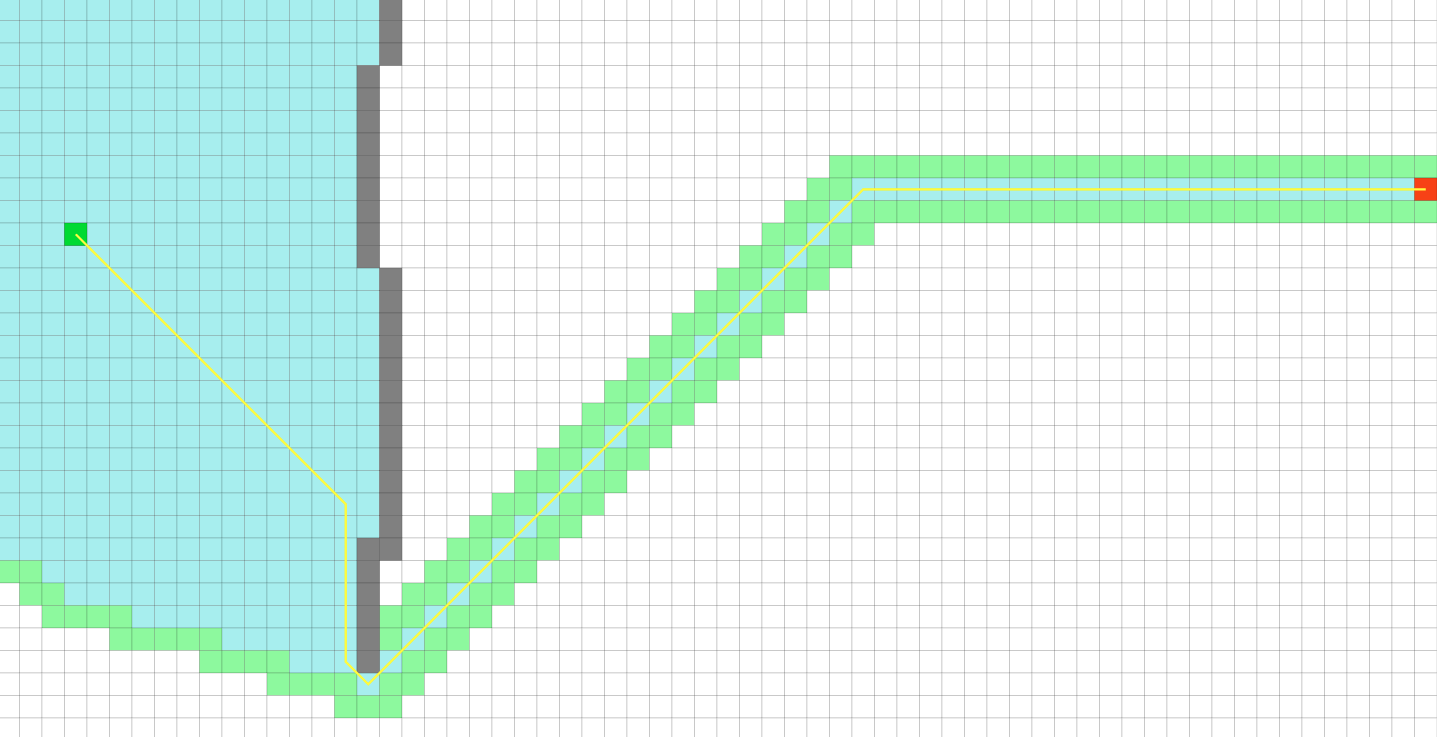

2.3 Diagonal Distance
引用:
如果曼哈顿需要上移4,右移4,共8*D,(D代表两个栅格的距离)
那Diagonal需要斜着移动4*D2。(D2代表一个栅格的对角线距离)
When D = 1 and D2 = 1, this is called the Chebyshev distance. When D = 1 and D2 = sqrt(2), this is called the octile distance.
我这里采用octile distance。
function heuristic(node) = dx = abs(node.x - goal.x) dy = abs(node.y - goal.y) return D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy)
代码里是不是有问题,没起作用呢?确实有问题,代码中对应sqrt(2)是D2,2是2*D,很明显我把栅格间距认为是1了,
但其实应该用自己的栅格地图的间距才行,我这里用的是0.05, 也就是说一个栅格的边长是0.05米。
double Astar::getDiagHeu(Eigen::Vector3d x1, Eigen::Vector3d x2) { double dx = fabs(x1(0) - x2(0)); double dy = fabs(x1(1) - x2(1)); double h = (dx + dy) + 0.05 * (sqrt(2) - 2) * min(dx, dy); //double h = (dx + dy) + (sqrt(2) - 2) * min(dx, dy); return tie_breaker_ * h; }
理想结果是(PathFinding.js) VS 实际结果,正确!
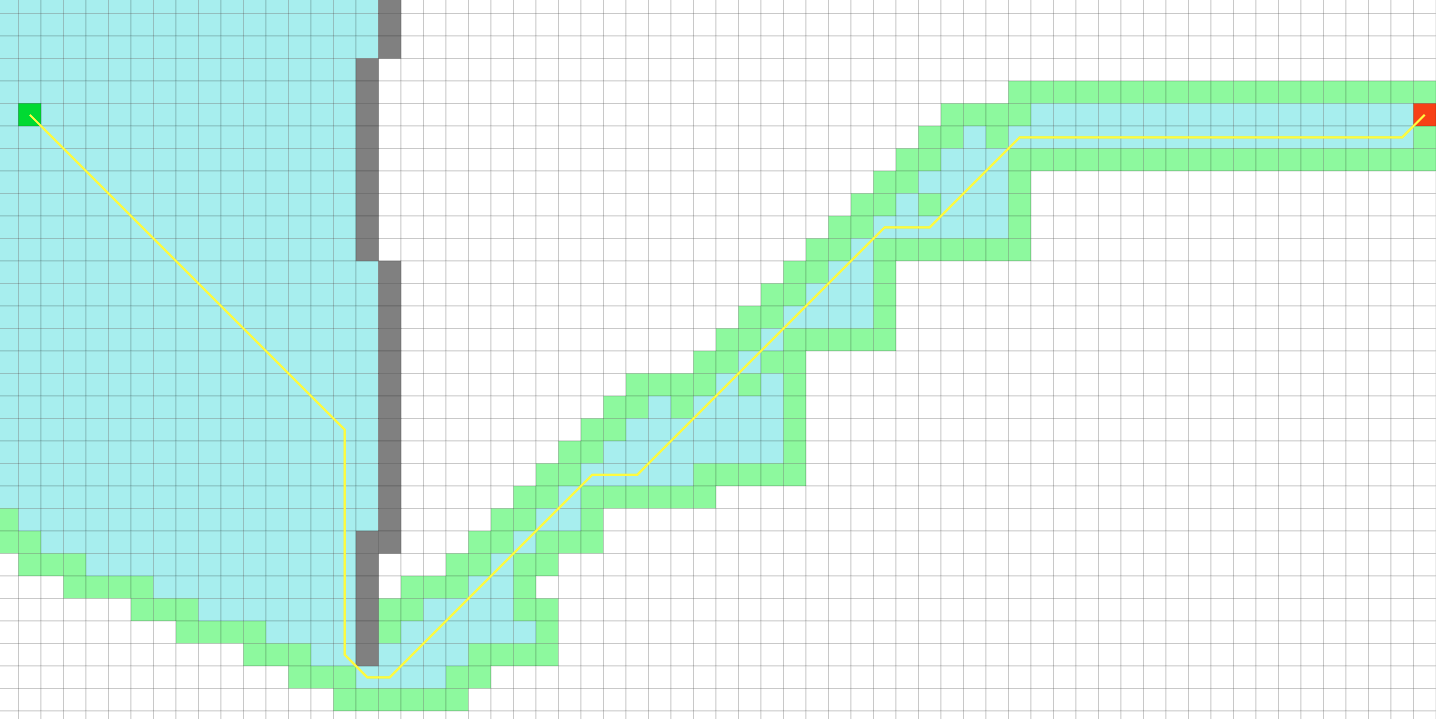
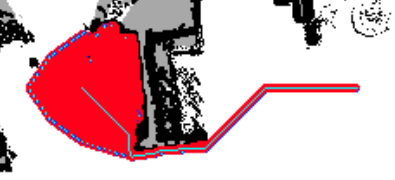
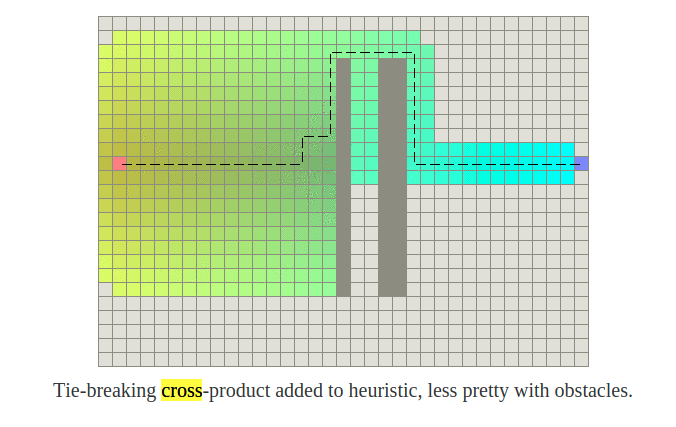
2.4 其他
下边这个启发值,可以使得路径尽量保持起点到终点连接的直线,对于洗地车来说,是比较合适的,但是代码里哪里有问题,没起作用。
double Astar::getCrossHeu(Eigen::Vector3d s, Eigen::Vector3d c, Eigen::Vector3d e) { double dx1 = (c(0) - e(0)); double dy1 = (c(1) - e(1)); double dx2 = (s(0) - e(0)); double dy2 = (s(1) - e(1)); double cross = fabs(dx1*dy2 - dx2*dy1); double h = (c-e).norm(); h = h + cross*0.001; return h; //norm = sqrt(squaredNorm()) }
dx1 = current.x - goal.x dy1 = current.y - goal.y dx2 = start.x - goal.x dy2 = start.y - goal.y cross = abs(dx1*dy2 - dx2*dy1) heuristic += cross*0.001
理想效果是这样的:
2.4 如何选用
引用http://theory.stanford.edu/~amitp/GameProgramming/Heuristics.html#heuristics-for-grid-maps中的内容:
四联通地图,用曼哈顿;
八联通地图,用对角线距离;
任意方向联通,用欧氏距离;
- On a square grid that allows 4 directions of movement, use Manhattan distance (L1).
- On a square grid that allows 8 directions of movement, use Diagonal distance (L∞).
- On a square grid that allows any direction of movement, you might or might not want Euclidean distance (L2). If A* is finding paths on the grid but you are allowing movement not on the grid, you may want to consider other representations of the map.
- On a hexagon grid that allows 6 directions of movement, use Manhattan distance adapted to hexagonal grids.
3.tie break
tie_break在代码里怎么不起作用呢??
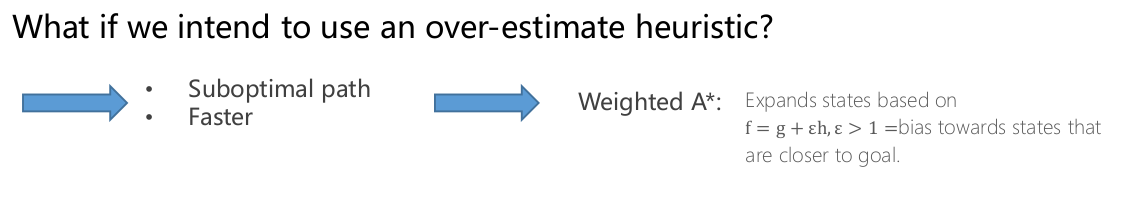
4. over-estimate heuristic
如果将a*用于lattice中计算启发值,那速度绝对要非常快才行,所以感觉次有解是很有必要的;
但是尝试过将h调大,有可能使得轨迹曲曲折折,这里应该需要cost function调整了。