一 Introduction to tf2
本部分是关于tf2简单介绍,比如tf2能做什么,并使用一个turtlesim的例子来显示tf2在多机器人中的一些能力.同时也包括一些工具的使用,比如tf2_echo, view_frames, and rviz.
1.安装Demo
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-turtle-tf2 ros-$ROS_DISTRO-tf2-tools ros-$ROS_DISTRO-tf
2.Running the Demo
$ roslaunch turtle_tf2 turtle_tf2_demo.launch
看到下面两个turtles,如下
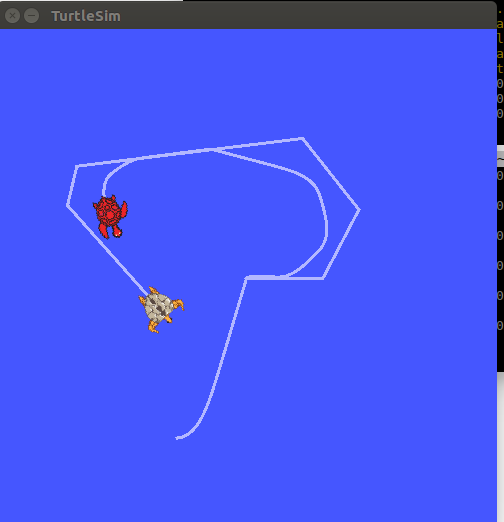
在启动的界面使用方向键来控制中间的turtle运动,会看到另外一个turtle跟随运动.
3.上面都做了什么呢?
在这个demo里面使用tf2库来创建了三个坐标系:世界坐标系,turtle1坐标系,turtle2坐标系.
本教程使用了一个tf2 的broadcaster来发布turtle的坐标系,以及一个tf2 的listener来计算两个turtles坐标系之间的差异.然后移动一个turtle来跟随另一个运动.
4.tf2 工具
4.1 使用view_frames
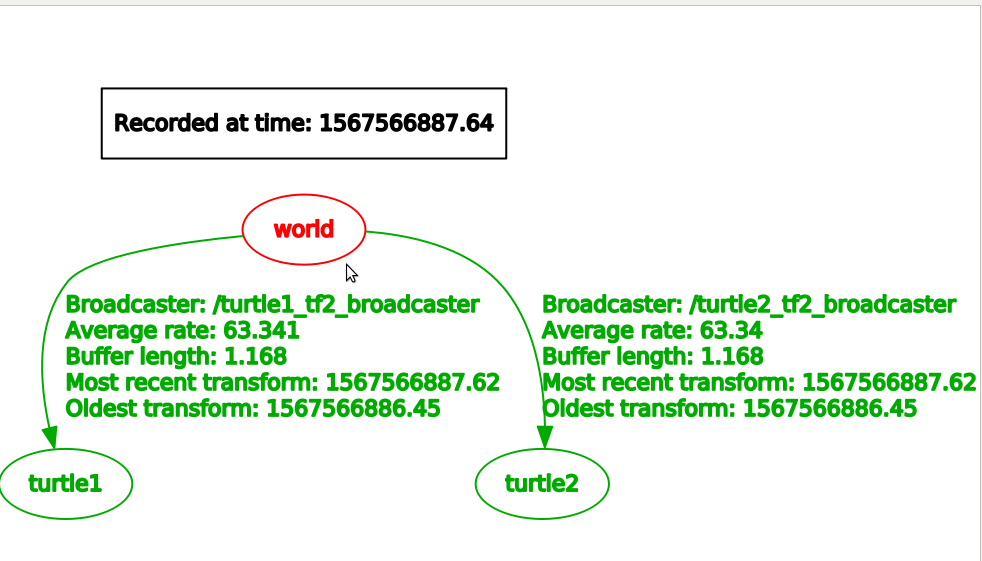
view_frames创建一个由tf2在ROS中发布的坐标系图标.
$ rosrun tf2_tools view_frames.py
有一个tf2的listener来监听ROS中发布的frames,然后画出由坐标系组成的树型结构:
$ evince frames.pdf
4.2 使用tf_echo
tf_echo得出在ROS中任意两个坐标系之间的transform.
rosrun tf tf_echo [reference_frame] [target_frame]
对于本demo中turtle2相对于trutle1坐标系的一个变换等同于如下:
 :
:
$ rosrun tf tf_echo turtle1 turtle2
二 写代码实现一个tf2的静态broadcaster
1.创建一个包learning_tf2
$ catkin_create_pkg learning_tf2 tf2 tf2_ros roscpp rospy turtlesim
2.怎样来broadcast一个transforms
怎样broadcast坐标系到tf2中.在本例中将broadcast变化中的turtles的坐标系.
创建文件,包的src/static_turtle_tf2_broadcaster.cpp

#include <ros/ros.h> #include <tf2_ros/static_transform_broadcaster.h> #include <geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h> #include <cstdio> #include <tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h> std::string static_turtle_name; int main(int argc, char** argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "my_static_tf2_broadcaster"); if(argc != 8) { ROS_ERROR("Invalid number of parameters usage: static_turtle_tf2_broadcaster child_frame_name x y z roll pitch yaw "); return -1; } if(strcmp(argv[1], "world") == 0) { ROS_ERROR("Your static turtle name cannot be 'world' "); return -1; } static_turtle_name = argv[1]; static tf2_ros::StaticTransformBroadcaster static_broadcaster; geometry_msgs::TransformStamped static_transformStamped; static_transformStamped.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); static_transformStamped.header.frame_id ="world"; static_transformStamped.child_frame_id = static_turtle_name; static_transformStamped.transform.translation.x = atof(argv[2]); static_transformStamped.transform.translation.y = atof(argv[3]); static_transformStamped.transform.translation.z = atof(argv[4]); tf2::Quaternion quat; quat.setRPY(atof(argv[5]), atof(argv[6]), atof(argv[7])); static_transformStamped.transform.rotation.x = quat.x(); static_transformStamped.transform.rotation.y = quat.y(); static_transformStamped.transform.rotation.z = quat.z(); static_transformStamped.transform.rotation.w = quat.w(); static_broadcaster.sendTransform(static_transformStamped); ROS_INFO("Spinning until killed publishing %s to world",static_turtle_name.c_str()); ros::spin(); return 0; }
修改CMakeLists.txt文件

add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}_node src/static_turtle_tf2_broadcaster.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}_node
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
)
然后运行之

$ rosrun learning_tf2 static_turtle_tf2_broadcaster mystaticturtle 0 0 1 0 0 0
rostopic echo /tf_static transforms: - header: seq: 0 stamp: secs: 1567585822 nsecs: 250673262 frame_id: "world" child_frame_id: "mystaticturtle" transform: translation: x: 0.0 y: 0.0 z: 1.0 rotation: x: 0.0 y: 0.0 z: 0.0 w: 1.0 ---
3.发布静态transform的合适方法
在实际的机器人开发使用中,基本不会使用上面的方式来发布静态tf,应该使用一个可执行节点static_transform_publisher来执行,其要么在命令行执行,要么在launch文件中执行.
static_transform_publisher x y z yaw pitch roll frame_id child_frame_id Publish a static coordinate transform to tf2 using an x/y/z offset in meters and yaw/pitch/roll in radians. (yaw is rotation about Z, pitch is rotation about Y, and roll is rotation about X). static_transform_publisher x y z qx qy qz qw frame_id child_frame_id Publish a static coordinate transform to tf2 using an x/y/z offset in meters and quaternion.
比如
<launch>
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="link1_broadcaster" args="1 0 0 0 0 0 1 link1_parent link1" />
</launch>
Unlike in tf, there is no period argument, and a latched topic is used.
