- 题意:
每次给一个n。求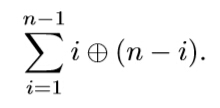
(2≤n<10500)
- 分析:
先说一下自己的想法,假设将n换成二进制数,也就一两千位左右,那么一位一位处理是能够接受的。将0-n写成二进制形式后,显然全部数某一个二进制位是有一个循环节的。那么我们就能够从这里入手直接求解
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static BigInteger zero = BigInteger.ZERO;
public static BigInteger one = BigInteger.ONE;
public static BigInteger two = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
public static BigInteger three = BigInteger.valueOf(3);
public static BigInteger four = BigInteger.valueOf(4);
public static BigInteger six = BigInteger.valueOf(6);
public static BigInteger Down(BigInteger now, BigInteger L) {
BigInteger mid = now.divide(L).multiply(L).add(L.shiftRight(1));
if (now.subtract(mid).signum() < 0)
return mid;
return mid.add(L.shiftRight(1));
}
public static BigInteger Up(BigInteger now, BigInteger L) {
BigInteger start = now.divide(L).multiply(L);
BigInteger mid = start.add(L.shiftRight(1));
if (now.subtract(mid).signum() < 0)
return start.subtract(one);
return mid.subtract(one);
}
public static int getValue(BigInteger now, BigInteger L) {
BigInteger mid = now.divide(L).multiply(L).add(L.shiftRight(1));
if (now.subtract(mid).signum() < 0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
public static BigInteger solve(BigInteger nl, BigInteger nr, BigInteger gl, BigInteger L) {
BigInteger ret = zero, step = Down(nl, L).subtract(nl), t = nr.subtract(Up(nr, L));
if (step.subtract(t).signum() > 0)
step = t;
while (nl.add(step).subtract(gl).signum() <= 0) {
if ((getValue(nl, L) ^ getValue(nr, L)) == 1)
ret = ret.add(step);
nl = nl.add(step); nr = nr.subtract(step);
step = Down(nl, L).subtract(nl); t = nr.subtract(Up(nr, L));
if (step.subtract(t).signum() > 0)
step = t;
}
if (gl.subtract(nl).add(one).signum() >= 0 && (getValue(nl, L) ^ getValue(nr, L)) == 1)
ret = ret.add(gl.subtract(nl).add(one));
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger n, L, tans, nl, ans;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while (cin.hasNext()) {
n = cin.nextBigInteger();
L = two;
ans = zero;
while (L.subtract(n.shiftLeft(1)).signum() <= 0)//(L <= n * 2)
{
tans = zero;
if (n.divide(L).shiftRight(1).signum() > 0) {
tans = solve(zero, n, L.subtract(one), L);
}
nl = n.divide(L).shiftRight(1).multiply(L);
tans = n.divide(L).shiftRight(1).multiply(tans).add(solve(nl, n.subtract(nl), n.subtract(one).shiftRight(1), L));
ans = ans.add(tans.multiply(L));
L = L.shiftLeft(1);
}
System.out.println(ans.subtract(n.shiftLeft(1)));
}
}
}学习一下题解的方法。关键在于:(2 * k) ^ x = (2 * k + 1) ^ x
之后就学习一下题解的公式化简方法了

import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
static BigInteger n, ret;
static BigInteger one = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
static BigInteger two = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
static BigInteger four = BigInteger.valueOf(4);
static BigInteger six = BigInteger.valueOf(6);
static HashMap<BigInteger, BigInteger> mp = new HashMap<BigInteger, BigInteger>();
public static BigInteger fun(BigInteger n) {
if (n.equals(BigInteger.ZERO) || n.equals(BigInteger.ONE))
return BigInteger.ZERO;
if (mp.containsKey(n))
return mp.get(n);
BigInteger k = n.shiftRight(1);
if (n.testBit(0)) {
ret = four.multiply(fun(k)).add(six.multiply(k));
mp.put(n, ret);
return ret;
}
else {
ret = (fun(k).add(fun(k.subtract(one))).add(k.shiftLeft(1)).subtract(two)).shiftLeft(1);
mp.put(n, ret);
return ret;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while (cin.hasNext()) {
n = cin.nextBigInteger();
mp.clear();
System.out.println(fun(n));
}
}
}