管道概念
进程间通信工具, 把数据从一端输出到另一端
如 ps –ef | grep pts
相当于 1: ps –ef > tmpfile 2: grep pts < tmpfile
半双工通信
无名管道(直接称之为管道), 只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程间通信。
命名管道 , 可以用于所有进程间通信
管道创建
<unistd.h>
int pipe( int fds[2] )
成功返回 0 , 失败返回 -1
fds[0] 用于读取, fds[1] 用于写入
思路:
管道(单向)创建流程 (父进程发送信息到子进程)
1: 创建管道 pipe() 获取管道 fds[0] (读取), fds[1] (写入)
2: 创建子进程 fork() 子进程继承 fds[0], fds[1]
3: 父进程关闭读取功能 close(fds[0])
4: 子进程关闭写入功能 close(fds[1])
5:父进程写信息到 fds[1]
6:子进程读信息从 fds[0]
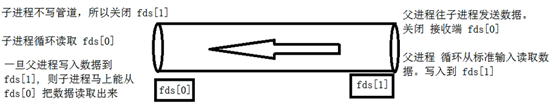
单向管道
例子: 父进程发送消息到子进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void testSinglePipe()
{
int fds[2];
pid_t pid;
char buf[128]={0};
//-1 crete pipe fail
if(pipe(fds))
{
perror("fail pipe!");
return ;
}
//printf("fds[%d,%d] ",fds[0],fds[1]);
// 0 sucess
pid=fork();
//-1 fail
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fail fork!");
return ;
}
//child process
else if(pid==0)
{
printf("child pid:[%d] ",getpid());
//ban write in child
close(fds[1]);
while(1)
{
usleep(100);
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
//read message from parent
read(fds[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("child receive:%s ",buf);
}
close(fds[0]);
return ;
}
//parent process
else
{
//printf("parent pid:[%d]",getpid());
//ban read in parent
close(fds[0]);
while(1)
{
usleep(100);
//==printf()
//fprintf(stderr,"parent send:");
write(STDOUT_FILENO,""parent send:"",strlen("parent send:"));
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
//scanf()
read(STDIN_FILENO,buf,sizeof(buf));
//scanf("%s",buf);
//send message to child
write(fds[1],buf,strlen(buf));
}
close(fds[1]);
return ;
}
}
read(STDIN_FILENO,buf,sizeof(buf))和scanf("%s",buf)的好坏:
scanf("%s",buf),对方无法一次性接受有空格的字符。如:hello world,就会被分成两部分显示child receive:hello child receive:world.
read(STDIN_FILENO,buf,sizeof(buf)),对方可以一次性接受所有字符。但是回车键也会被打印出来。因此child receive:hello world每一次后面都空白多一行。
双向管道
创建两个管道,分别用于两个进程的输入和输出。
思路与单向管道一致,但要区别父子进程的读或写的关闭。
例子:父进程发送字符串给子进程,子进程处理完毕后(转大写),返回给父进程输出
void testDoublePipe()
{
int fdsA[2]; //parent->child
int fdsB[2]; //child->parent
pid_t pid;
char recv[128]={0};
char send[128]={0};
//-1 fail
if(pipe(fdsA)||pipe(fdsB))
{
perror("fail pipe!");
return ;
}
// 0 sucess
pid=fork();
//-1 fail
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fail fork!");
return ;
}
//child
else if(pid==0)
{
printf("child pid:[%d] ",getpid());
//ban write of child
close(fdsA[1]);
//ban read of parent
close(fdsB[0]);
while(1)
{
usleep(100);
memset(recv,0,sizeof(recv));
//recv message from parent
read(fdsA[0],recv,sizeof(recv));
printf("child receive:%s ",recv);
//change from lower to upper
int i=0;
for(;i<strlen(recv);i++)
{
send[i]=toupper(recv[i]);
}
send[i]='�';
//send message to parent
write(fdsB[1],send,strlen(send));
}
close(fdsA[1]);
close(fdsB[0]);
return ;
}
//parent
else
{
//printf("parent pid:[%d]",getpid());
//ban read of parent
close(fdsA[0]);
//ban write of child
close(fdsB[1]);
while(1)
{
usleep(100);
//==printf()
//fprintf(stderr,"parent send:");
write(STDOUT_FILENO,"parent send:",strlen("parent send:"));
memset(send,0,sizeof(send));
//==scanf()
read(STDIN_FILENO,send,sizeof(send));
//scanf("%s",buf);
//send message to child
write(fdsA[1],send,strlen(send));
//teturn message from child
read(fdsB[0],recv,sizeof(recv));
printf("child return:%s ",recv);
}
close(fdsA[1]);
close(fdsB[0]);
return ;
}
}
理清双向管道,关闭问题:
int fdsA[2]; //parent->child
int fdsB[2]; //child->parent
[1] 写权限,[0]读权限
对于父进程:
int fdsA[2]; parent->child
从父进程到子进程,父进程只能写,因此把读权限关闭,close(fdsA[0])
int fdsB[2]; child->parent
从父进程到子进程,父进程只能读,因此把写权限关闭,close(fdsB[1])
同理,对于子进程:
int fdsA[2]; parent->child
从子进程到父进程,子进程只能读,因此把写权限关闭,close(fdsA[1])
int fdsB[2]; child->parent
从子进程到父进程,子进程只能写,因此把读权限关闭,close(fdsB[0])