1,最小标准随机数生成器Linear congruential generator(LCG):

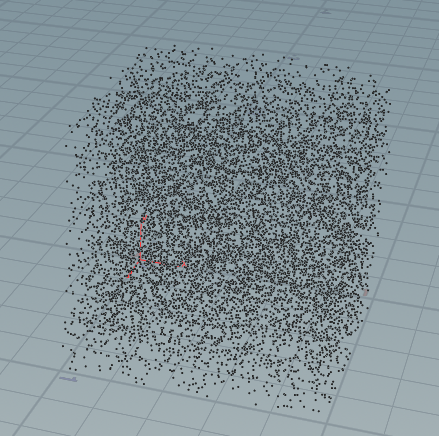
如图所示:感觉随机度很高。书中这个随机周期很高了,绝对够用。

void gen_points(int npts;float ptpos[]) { int m = pow(2,31) - 1; int a = 16807; int b = 45454; int seed = 1412133; float ui = 0.0f; for(int i=0;i<npts*3;i++){ seed = (a * seed + b) % m; ui = float(seed) / float(m); //printf("%f ,%f ",ui,seed); append(ptpos,ui); } } float pts[]; int np = 10000; // generation random points gen_points(np,pts); for(int i=0;i<np;i++) { float x = pts[i*3]; float y = pts[i*3+1]; float z = pts[i*3+2]; addpoint(geoself(),set(x,y,z)); }
2,随机游走random walk:

int np = 100; float w = 0 ; float scale = 0.1; for(int i=0;i<np;i++) { // add main point int add_ptnum = addpoint(geoself(),set(i*scale,w,0)); if (rand(i*10000)> (1.0/2.0) ) { // up w += 1.0f * scale; } else{ // down w -= 1.0f* scale; } }

3,布朗运动brownian motion
不改变期望,也不改变方差.............

int np = 100; float w = 0 ; float scale = 1; // substeps movement! int substeps = 6; float substep_scale = 1 / sqrt(substeps); for(int i=0;i<np;i++) { for(int j =0;j<substeps;j++) { // add main point int add_ptnum = addpoint(geoself(),set( (i*substeps + j)*scale/substeps,w,0)); if (rand(i*10+j*1000)> (1.0/2.0f) ) { // up w += 1.0f * scale * substep_scale; } else{ // down w -= 1.0f* scale * substep_scale; } } }
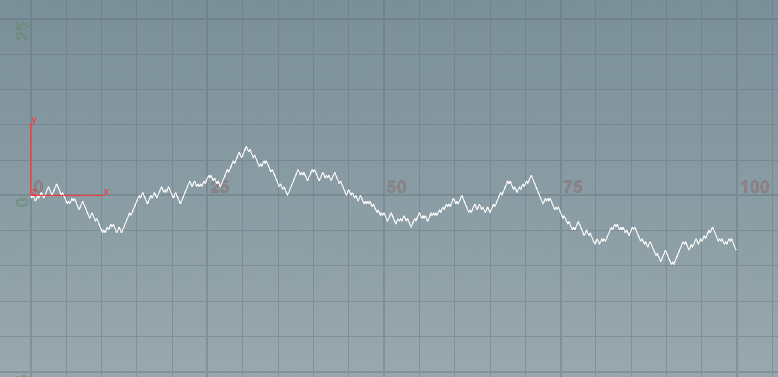
然后书中给了 用randn生成正态分布,模拟布朗运动,在houdini随便对应个rand

int k = 100; float dt = 1.0/24.000f; float sqdelt = sqrt(dt); float b = 0; for (int i=0;i<k;i++) { addpoint(geoself(),set(i,b,0)); b = b + sqdelt * fit(rand(i),0,1,-5,5); }
单位方块的采样点:
1,抖动采样

int n = 10; for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ float x = (i + rand(i*500+j*500))/n; float y = (j + rand(j*5000+i*1000000))/n; addpoint(geoself(),set(x,y,0)); } }
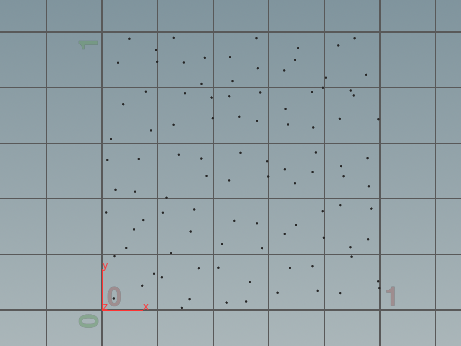
抗锯齿 抖动采样:
注释的部分就是像素中心发射一根光线:
但是这个引来一个问题,这个方法肯定不能并发,因为书中讲的random方法,不是线程安全。应该把houdini的rand()方法做出来。
void RT_World::render() { // INIT our PPMIO PPMIO *imageIo = new PPMIO; PPMIO::WriteParam imageIoParam; // imageIoParam.width = vp.hres; imageIoParam.height = vp.vres; imageIoParam.maxPixelValue = 255; // IO will save ascii type for easy reading imageIoParam.imageIOType = PPMIO::ASCII_P3_TYPE; imageIoParam.imageType = PPMIO::RGB_TYPE; // IO image buffer; PPMIO::RGB *data = new PPMIO::RGB[vp.hres*vp.hres]; // RT_RGB pixel_color; RT_Ray ray; double zw = 100; ray.d = RT_VEC_3D({ 0,0,-1 }); RT_VEC_2D sample_point; // unit square sample point RT_VEC_2D pixel_pos; // pixel pos with sample point RT_Log_StdOut("Start Rendering"); for (int r = 0; r < vp.vres; r++) { // loop the row for (int c = 0; c < vp.hres; c++) { // loop the column pixel_color = black_color; //double x = vp.size * (c - 0.5 *(vp.hres - 1.0)); //double y = vp.size * (r - 0.5 *(vp.vres - 1.0)); //cout << "rendering pixel x/y: " << x << "/" << y << endl; //ray.o = RT_VEC_3D({ x,y,zw }); //pixel_color = tracer_ptr->trace_ray(ray); //cout << "trace ptr get color->" << pixel_color << endl; // for samples for (int i = 0; i < vp.num_samples; i++) { sample_point = vp.sampler_ptr->sample_unit_square(); pixel_pos[0] = vp.size * (c - 0.5*vp.hres + sample_point[0]); pixel_pos[1] = vp.size * (r - 0.5*vp.vres + sample_point[1]); ray.o = RT_VEC_3D({ pixel_pos[0],pixel_pos[1],RT_SCALAR(zw) }); pixel_color += tracer_ptr->trace_ray(ray); } pixel_color /= vp.num_samples; // because our ray born from Cartesian coordinates // we need trans to our image coord int row = (vp.vres-1) - r; int column = c; // our pixel_color is 0~1 , we need convert to RGB 0~255 space //cout << "current set x y :" << row << "|" << column << endl; int index = row * vp.hres + column; PPMIO::RGB indexRGB; indexRGB.R = unsigned char(pixel_color[0] * 255); indexRGB.G = unsigned char(pixel_color[1] * 255); indexRGB.B = unsigned char(pixel_color[2] * 255); data[index] = indexRGB; } } imageIo->writeImage("c:/test_aa.ppm", data, imageIoParam); delete imageIo; delete []data; RT_Log_StdOut("End Rendering"); }
2,比较有意思的,相邻像素随机在 采样集合 采取不同的 samples:

inline int rand_int(void) { return(rand()); } void unit_test_random_ray() { int num_samples = 25; int num_sets = 10; int count = 0; int jump = 0; // per ray has unique own jump cout << "construct samples:" << num_samples << "with num_set:" << num_sets << endl; for (int ray = 0; ray < 5; ray++) { cout << "sending the ray id:" << ray << endl; // loop 25 times,get 25 points for (int i = 0; i < num_samples; i++) { if (count % num_samples == 0) { jump = (rand_int() % num_sets) * num_samples; cout << "set jump init:" << jump << endl; } // 25 samples position index we get: cout <<"cout index:" << count <<" RND:" << jump + (count++ % num_samples) << endl; } } }
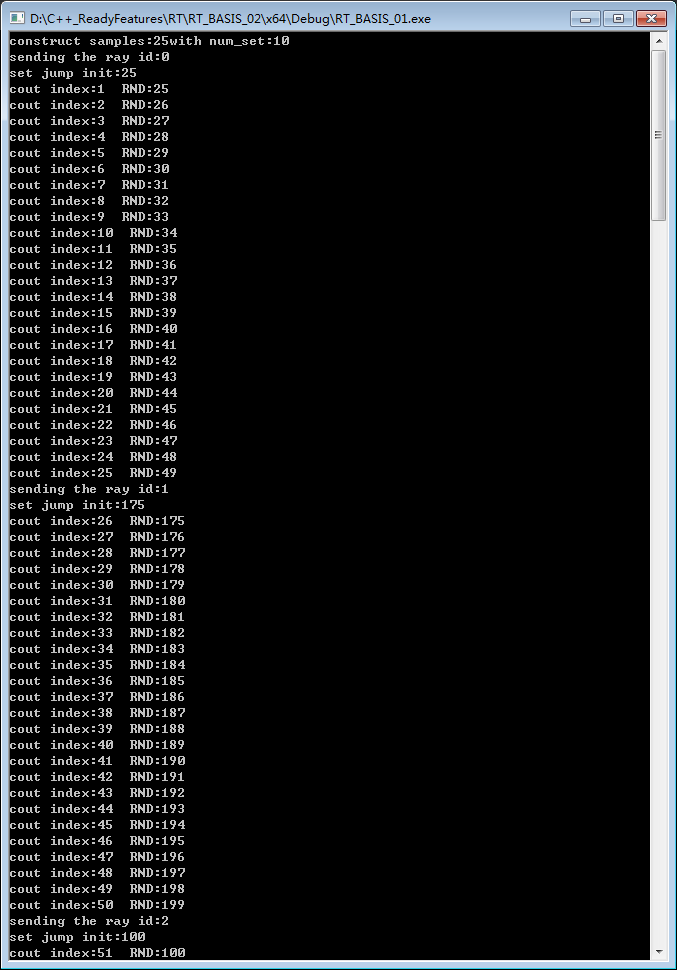
而且在set里面访问连续的samples,还可以把这些连续的打乱访问。

void unit_test_random_ray2() { int num_samples = 25; int num_sets = 10; int count = 0; int jump = 0; vector<int> shuffled_indices; // set up shuffle_indices vector <int> indices; for (int i = 0; i < num_samples; i++) { indices.push_back(i); } for (int p = 0; p < num_sets; p++) { random_shuffle(indices.begin(), indices.end()); for (int j = 0; j < num_samples; j++) { shuffled_indices.push_back(indices[j]); } } // per ray has unique own jump cout << "construct samples:" << num_samples << "with num_set:" << num_sets << endl; for (int ray = 0; ray < 5; ray++) { cout << "sending the ray id:" << ray << endl; // loop 25 times,get 25 points for (int i = 0; i < num_samples; i++) { if (count % num_samples == 0) { jump = (rand_int() % num_sets) * num_samples; cout << "set jump init:" << jump << endl; } // 25 samples position index we get: cout << "cout index:" << count << " RND:" << jump + shuffled_indices[jump+(count++ % num_samples)] << endl; } } }

例如书中给的图是用的第一种方式访问,反射有明显的水波纹.第二种就改善这个问题:


3,圆采样映射。
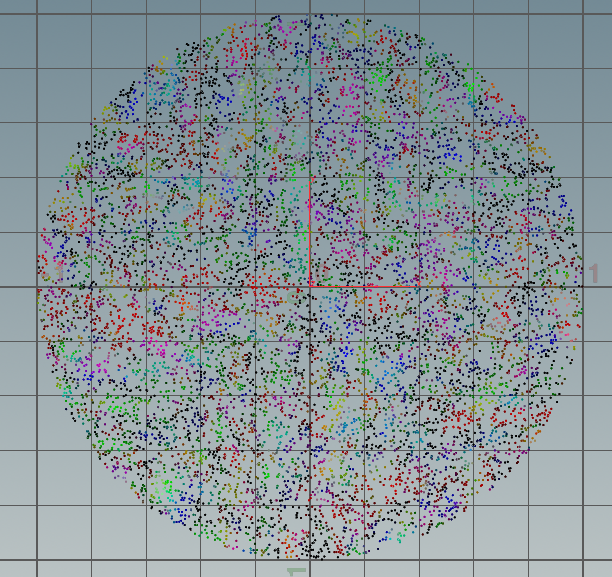
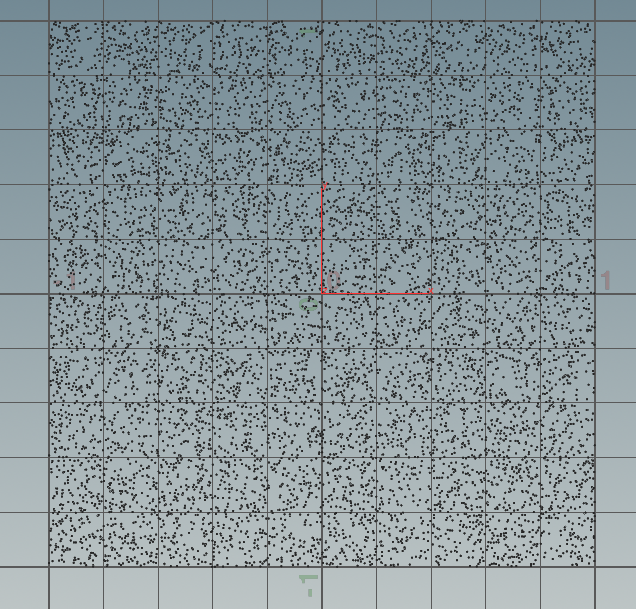


float r = 0; float phi = 0; if(@P.x > -@P.y) { if(@P.x > @P.y) { r = @P.x; phi = @P.y / @P.x; } else { r= @P.y; phi = 2 - @P.x / @P.y; } } else{ if(@P.x < @P.y) { r = -@P.x; phi = 4 + @P.y/@P.x; } else{ r = -@P.y ; if(@P.y != 0.0){ phi = 6 - @P.x / @P.y; } else phi = 0.0; } } phi *= 3.1415926/4.0; @P.x = r * cos(phi); @P.y = r * sin(phi);
4,(书里是8.4章)采样与轴对齐透视,也就是当eye点z轴有数值,然后定义在视线方向有个距离d

void RT_World::render_perspective_zw() { // INIT our PPMIO PPMIO *imageIo = new PPMIO; PPMIO::WriteParam imageIoParam; // imageIoParam.width = vp.hres; imageIoParam.height = vp.vres; imageIoParam.maxPixelValue = 255; // IO will save ascii type for easy reading imageIoParam.imageIOType = PPMIO::ASCII_P3_TYPE; imageIoParam.imageType = PPMIO::RGB_TYPE; std::cout << "Start Construct Image buffer data "; // IO image buffer; PPMIO::RGB *data = new PPMIO::RGB[vp.hres*vp.hres]; std::cout << "End Construct Image buffer data "; // RT_RGB pixel_color; RT_Ray ray; RT_SCALAR eye = 100; // view point RT_SCALAR d = 20; // distance view point to ViewPlane! ray.o = RT_VEC_3D({0.0,0.0,eye}); RT_VEC_2D sample_point; // unit square sample point RT_VEC_2D pixel_pos; // pixel pos with sample point RT_Log_StdOut("Start Rendering"); for (int r = 0; r < vp.vres; r++) { // loop the row for (int c = 0; c < vp.hres; c++) { // loop the column pixel_color = black_color; // for samples for (int i = 0; i < vp.num_samples; i++) { sample_point = vp.sampler_ptr->sample_unit_square(); pixel_pos[0] = vp.size * (c - 0.5*vp.hres + sample_point[0]); pixel_pos[1] = vp.size * (r - 0.5*vp.vres + sample_point[1]); // cal ray direction ray.d = RT_VEC_3D({ pixel_pos[0] - ray.o[0],pixel_pos[1] - ray.o[1],-d }); ray.d.normalize(); //ray.o = RT_VEC_3D({ pixel_pos[0],pixel_pos[1],RT_SCALAR(zw) }); pixel_color += tracer_ptr->trace_ray(ray); } pixel_color /= vp.num_samples; // because our ray born from Cartesian coordinates // we need trans to our image coord int row = (vp.vres - 1) - r; int column = c; // our pixel_color is 0~1 , we need convert to RGB 0~255 space //cout << "current set x y :" << row << "|" << column << endl; int index = row * vp.hres + column; PPMIO::RGB indexRGB; indexRGB.R = unsigned char(pixel_color[0] * 255); indexRGB.G = unsigned char(pixel_color[1] * 255); indexRGB.B = unsigned char(pixel_color[2] * 255); data[index] = indexRGB; } } imageIo->writeImage("c:/test_aa_pzw_e100_d_100.ppm", data, imageIoParam); delete imageIo; delete[]data; RT_Log_StdOut("End Rendering"); }
参考
<<数值分析>>
<<RayTracing from ground up>>
<<Fundamentals of computer graphics>>
