不能重载的运算符有 . 和 .* 和 ?: 和 :: 和 sizeof
友元函数和成员函数的使用场合:一般情况下,建议一元运算符使用成员函数,二元运算符使用友元函数
1、运算符的操作需要修改类对象的状态,则使用成员函数。如需要做左值操作数的运算符(如 =,+=,++)
2、运算时,有数和对象的混合运算时,必须使用友元
3、二元运算符中,第一个操作数为非对象时,必须使用友元函数。如输入输出运算符 << 和 >>
4、当一个重载运算符是成员函数时,this 绑定到左侧运算对象。成员运算符函数的显式形参比运算对象的数量少一个
5、可以直接调用一个重载的运算符函数,如 operator+(data1, data2), data1.operator(data2)
6、当运算符作用于内置类型对象时,我们无法改变运算符的含义
具体规则如下:
|
运算符 |
建议使用 |
|
所有一元运算符 |
成员函数 |
|
= ( ) [ ] -> |
必须是成员函数 |
|
+= -= /= *= ^= &= != %= >>= <<= , 似乎带等号的都在这里了. |
成员函数 |
|
所有其它二元运算符, 例如: –,+,*,/ |
友元函数 |
|
<< >> |
必须是友元函数 |
参数和返回值:
当参数不会被改变,一般按 const 引用来传递(若是使用成员函数重载,函数也为 const).对于返回数值的决定:
1) 如果返回值可能出现在 = 号左边, 则只能作为左值, 返回非 const 引用。
2) 如果返回值只能出现在 = 号右边, 则只需作为右值, 返回 const 型引用或者 const 型值。
3) 如果返回值既可能出现在 = 号左边或者右边, 则其返回值须作为左值, 返回非 const 引用。
以上内容摘自:blog.csdn.net/insistgogo/article/details/6626952
重载 -> 运算符:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class strptr{ 5 // friend std::string* operator->(const strptr&); 6 7 private: 8 std::string *ptr; 9 10 public: 11 strptr(string *s) : ptr(s) {} 12 strptr() = default; 13 std::string* operator->(){//注意这里返回的是一个指针,而非对象本身 14 return ptr; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 // std::string* operator->(const strptr &it){ 19 // return it.ptr; 20 // } 21 22 int main(void){ 23 string s = "hello"; 24 strptr str(&s); 25 cout << str->size() << endl; 26 return 0; 27 }
我们可以发现 -> 运算符只能作为成员函数重载,如果作为友元函数重载的话会报错:
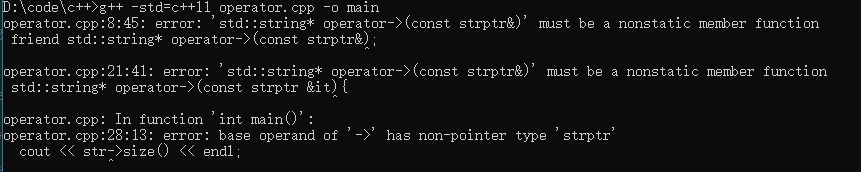
str->size() 等价于 ptr.operator->()->size(); 等价于 ptr->size();
这是由 C++ 标准规定的,对于 ptr->mem 根据 ptr 类型的不同,操作符 -> 的解释也不同:
当 ptr 的类型是内置指针类型时,等价于 (*ptr).mem;
当 ptr 的类型是类时,等价于ptr.operator->()->mem;//从这里也可以看出 -> 重载必须是成员函数
你会发现这是一个递归的解释,对于 ptr->mem 会递归成:
(*(ptr.operator->().operator->().….operator->())).mem
重载 +/- 运算符:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 friend const gel operator+(const gel&, const gel&); 6 // friend gel operator-(const gel&, const gel&); 7 8 private: 9 int x; 10 11 public: 12 gel(int a) : x(a){} 13 gel() = default; 14 ~gel(){} 15 16 // const gel operator+(const gel &b) const{ 17 // gel c = *this; 18 // c.x += b.x; 19 // return c; 20 // } 21 22 const gel operator-(const gel &b) const{//返回的是右值,所以可以返回const值 23 gel c = *this; 24 c.x -= b.x; 25 return c;//c是一个局部对象,不能返回引用 26 } 27 28 29 void print(ostream &os) const{ 30 os << x << endl; 31 } 32 }; 33 34 const gel operator+(const gel &a, const gel &b){ 35 gel c = a;//为了不改变*this,即加数本身 36 c.x += b.x; 37 return c; 38 } 39 40 // gel operator-(const gel &a, const gel &b){ 41 // gel c = a; 42 // c.x -= b.x; 43 // return c; 44 // } 45 46 int main(void){ 47 gel a(1), b(2); 48 gel c = a + b;//正确,调用友元函数 49 c.print(cout);//3 50 51 a = c - b;//正确,调用成员函数 52 a.print(cout);//1 53 54 c = a + 1;//正确,先执行转换构造函数将1转换成gel类类型,再执行加法 55 c.print(cout);//2 56 57 c = 1 + a;//正确,先执行转换构造函数将1转换成gel类类型,再执行加法 58 c.print(cout);//2 59 60 a = c - 1;//正确,先执行转换构造函数将1转换成gel类类型,再执行减法 61 a.print(cout);//1 62 63 // a = 3 - c;//错误,-是gel类成员函数重载,其第一个操作数必须是gel类对象 64 return 0; 65 }
注意:
重载 +/- 函数作为成员函数时不能有两个显示的形参,因为 +/- 是二元运算符,而 this 也算是一个形参,如果再传两个形参进去的话就有三个形参了
重载成类的成员函数的话在使用重载后的运算符时需要满足其第一个操作数为类的对象,因此在混合运算时应该将其重载为友元函数
重载 *// 运算符:
与 +/- 运算符的重载基本一样:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 friend const gel operator/(const gel&, const gel&); 6 7 private: 8 int x; 9 10 public: 11 gel(int a) : x(a){} 12 gel(void) : gel(0){} 13 ~gel(){} 14 15 const gel operator*(const gel &b) const{ 16 gel c = *this;//最好不要改变两个乘数本身 17 c.x *= b.x; 18 return c; 19 } 20 21 ostream& print(ostream &os){ 22 os << this->x << endl; 23 } 24 }; 25 26 const gel operator/(const gel &a, const gel &b){ 27 gel c = a; 28 c.x /= b.x; 29 return c; 30 } 31 32 int main(void){ 33 gel a(1), b(2); 34 gel c = a * b;//正确,执行成员函数 35 c.print(cout);//2 36 37 c = b / a;//正确,执行友元函数 38 c.print(cout);//2 39 40 c = a * 3;//正确,先通过转换构造函数将3转换成gel类对象,再进行*运算 41 c.print(cout);//3 42 43 // c = 3 * a;//错误,成员函数重载的第一个操作数必须是类的对象 44 45 c = 3 / a;//正确,先通过转换构造函数将3转换成gel类对象,再进行/运算 46 c.print(cout);//3 47 48 c = b / 1;//正确,先通过转换构造函数将1转换成gel类对象,再进行/运算 49 c.print(cout);//2 50 return 0; 51 }
注意:
重载 *// 函数作为成员函数时不能有两个显示的形参,因为 *// 是二元运算符,而 this 也算是一个形参,如果再传两个形参进去的话就有三个形参了
重载成类的成员函数的话在使用重载后的运算符时需要满足其第一个操作数为类的对象,因此在混合运算时应该将其重载为友元函数
重载 ++/-- 运算符:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 friend void print(ostream&, const gel&); 6 friend gel& operator--(gel&); 7 friend const gel operator--(gel&, int); 8 9 private: 10 int x; 11 12 public: 13 gel(int a) : x(a){}; 14 gel() = default; 15 ~gel(){} 16 17 gel& operator++(){ 18 ++x; 19 return *this; 20 } 21 const gel operator++(int){//这里不能返回引用 22 const gel cmp = *this; 23 ++x; 24 return cmp; 25 } 26 // gel& operator--(){ 27 // --x; 28 // return *this; 29 // } 30 // const gel operator--(int){//不能返回引用 31 // const gel cmp = *this; 32 // --x; 33 // return cmp; 34 // } 35 36 }; 37 38 gel& operator--(gel &it){ 39 --it.x; 40 return it; 41 } 42 43 const gel operator--(gel &it, int){//不能返回引用 44 const gel cmp = it; 45 --it.x; 46 return cmp; 47 } 48 49 void print(ostream &os, const gel &it){ 50 os << it.x << std::endl; 51 } 52 53 int main(void){ 54 gel a(10); 55 print(cout, ++a);//11 56 print(cout, a++);//11 57 print(cout, a);//12 58 print(cout, --a);//11 59 print(cout, a--);//11 60 print(cout, a);//10 61 return 0; 62 }
注意:
需要用一个占位符(虚参数)区分前后缀运算
后置时不要返回引用,不然会返回一个局部对象引用
重载 [] 运算符:

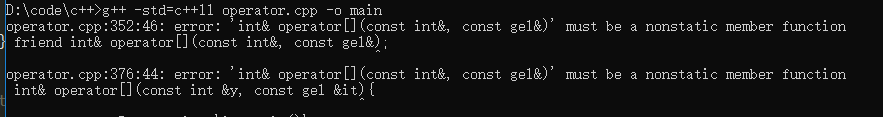
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 // friend int& operator[](const int&, const gel&); 6 7 private: 8 int x[5]; 9 10 public: 11 gel(){ 12 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 13 x[i] = i; 14 } 15 } 16 ~gel(){} 17 18 int& operator[](const int &y){//[]重载必须是一个非静态成员函数 19 static int t = 0; 20 if(y < 5 && y >= 0) return x[y]; 21 else { 22 cout << "out of arange!" << endl; 23 return t; 24 } 25 } 26 27 }; 28 29 // int& operator[](const int &y, const gel &it){ 30 // static int t = 0; 31 // if(y < 5 && y >= 0) return x[y]; 32 // else { 33 // cout << "out of arange!" << endl; 34 // return t; 35 // } 36 // } 37 38 int main(void){ 39 gel a; 40 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 41 cout << a[i] << " "; 42 } 43 cout << endl; 44 a[0] = 10;//重载返回的是左值 45 cout << a[0] << endl;//10 46 return 0; 47 }
我们可以发现 [] 只能作为成员函数重载,如果重载为友元函数的话会报错:
注意:
从上面的代码我们可以发现 [] 重载必须是一个非静态成员函数
但是上面的代码任然有一个 bug:我们对 [] 的重载是非 const 的,不能被 const 对象调用
我们可以通过基于 const 的重载来解决这个问题:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 private: 6 int x[5]; 7 8 public: 9 gel(){ 10 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 11 x[i] = i; 12 } 13 } 14 ~gel(){} 15 16 int& operator[](const int &y){ 17 static int tmp = do_operator(y); 18 return tmp; 19 } 20 21 const int& operator[](const int &y) const{//这里返回值是const值,是右值 22 static const int tmp = do_operator(y); 23 return tmp; 24 } 25 26 27 private: 28 const int& do_operator(const int &y) const{ 29 static int t = 0; 30 if(y < 5 && y >= 0) return x[y]; 31 else { 32 cout << "out of arange!" << endl; 33 return t; 34 } 35 } 36 37 }; 38 39 int main(void){ 40 gel a; 41 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 42 cout << a[i] << " "; 43 } 44 cout << endl; 45 a[0] = 10;//对非const对象重载返回的是左值 46 cout << a[0] << endl; 47 48 const gel b; 49 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 50 cout << b[i] << " "; 51 } 52 cout << endl; 53 return 0; 54 }
重载 () 运算符:

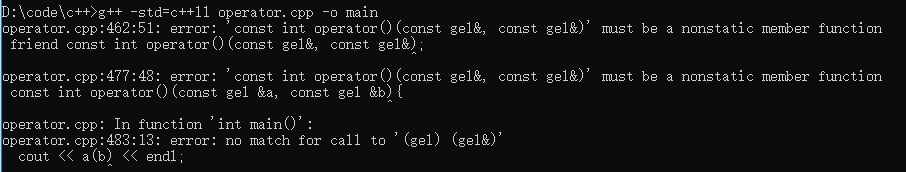
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 // friend const int operator()(const gel&, const gel&); 6 7 private: 8 int x; 9 10 public: 11 gel(int a) : x(a){} 12 gel() : gel(0){} 13 ~gel(){} 14 15 const int operator()(const gel &it) const{ 16 return (x + it.x); 17 } 18 }; 19 20 // const int operator()(const gel &a, const gel &b){ 21 // return a.x + b.x; 22 // } 23 24 int main(void){ 25 gel a(1), b(2); 26 cout << a(b) << endl;//3 27 return 0; 28 }
我们可以发现 () 只能作为非静态成员函数重载,如果重载为友元函数的话会报错:
重载运算符 () 的目的:对象 () 类似于函数名 (x),更加符合习惯
语法:
重载方式:只能使用成员函数重载
重载后还可以继续重载
函数名:operator( )(参数表)
参数表:参数随意,具体根据实际情况而定。
函数调用:显式调用:Obj(x)
隐式调用:obj.operator( )(x)
返回类型:
1、返回成员的实际类型随意,具体由程序员根据函数体定义
2、因为返回值只能做右值,只读,应该使用返回值为const类型
重载 >>/<<运算符:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&, const gel&); 6 friend istream& operator>>(istream&, gel&); 7 8 private: 9 int x, y; 10 11 public: 12 gel(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b){} 13 gel(int a) : gel(a, 0){} 14 gel() : gel(0, 0){} 15 ~gel(){} 16 }; 17 18 ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, const gel &it){ 19 os << it.x << " " << it.y; 20 return os; 21 } 22 23 istream& operator>>(istream &is, gel &it){ 24 is >> it.x >> it.y; 25 return is; 26 } 27 28 int main(void){ 29 gel a(1, 2); 30 cin >> a; 31 cout << a << endl; 32 }
注意:
在重载输出输入运算符的时候,只能采用全局函数的方式(因为我们不能在 ostream 和 istream 类中编写成员函数),这里才是友元函数真正的应用场景。
成员函数要求是有对象调用,则第一个参数必须是类的对象,但是 << 和 >> 第一个参数是流的对象引用。故不能使用成员函数:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 // friend ostream& operator<<(const gel&, ostream&); 6 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&, const gel&); 7 8 private: 9 int x, y; 10 11 public: 12 gel(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b){} 13 gel(int a) : gel(a, 0){} 14 gel(void) : gel(0, 0){} 15 ~gel(){} 16 }; 17 18 // ostream& operator<<(const gel &it, ostream &os){ 19 // os << it.x << " " << it.y; 20 // return os; 21 // } 22 23 ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, const gel &it){ 24 os << it.x << " " << it.y; 25 return os; 26 } 27 28 int main(void){ 29 gel a(1, 2); 30 cout << a << endl; 31 return 0; 32 }
通过这个例子可以发现 << 运算符的第一个参数必须是流的对象引用
我们可以发现不加 cout << a << endl; 着个语句的话这个代码是正确的,再结合前面的东西,我们可以得出这个语句错误的原因:
将 << 重载成 gel 类的成员函数,其第一个参数必须是 gel 类的对象,即要求 << 是右结合的 (a 在 << 右边嘛),而 << 本身是要求左结合的。此处矛盾所以是错误的
那么我们可以尝试着将 cout << a << endl; 改成既满足 << 是左结合的,又满足 << 的第一个参数是 a:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class gel{ 5 private: 6 int x, y; 7 8 public: 9 gel(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b){} 10 gel(int a) : gel(a, 0){} 11 gel(void) : gel(0, 0){} 12 ~gel(){} 13 14 ostream& operator<<(ostream &os){ 15 os << this->x << " " << this->y; 16 return os; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 int main(void){ 21 gel a(1, 2); 22 // cout << a << endl; 23 //我们可以发现不加这个语句的话这个代码是正确的,再结合前面的东西,我们可以得出这个语句错误的原因: 24 //将<<重载成gel类的成员函数,其第一个参数必须是gel类的对象,即要求<<是右结合的(a在<<右边嘛),而<<本身是要求左结合的.此处矛盾所以是错误的 25 //那么我们可以尝试着将cout << a << endl;改成既满足<<是左结合的,又满足<<的第一个参数是a 26 a.operator << (cout) << endl;//此处cout必须加括号,将opetator<<当成一个a类的成员函数,后面接着的当然是参数列表啦,cout是实参.又因为其返回的是一个cout流,所以后面可以接其它输出内容 27 return 0; 28 }
当然通常我们没必要把代码写成这样~
重载 = 运算符:

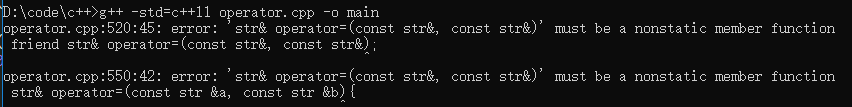
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class str{ 8 // friend str& operator=(const str&, const str&); 9 10 private: 11 int id; 12 char *name; 13 14 public: 15 str(int id_, const char *name_) : id(id_){ 16 name = new char[strlen(name_) + 1]; 17 strcpy(name, name_); 18 } 19 str(int id_) : str(id_, ""){} 20 str(const char *name_) : str(0, name_){} 21 ~str(){ delete name; } 22 23 ostream& print(ostream &os) const{ 24 os << id << " " << name << endl; 25 } 26 27 str& operator=(const str &it){//返回左值,如果不返回str&的话将不能用连等 28 if(this != &it){//如果目标字符串的地址不同的话执行拷贝操作 29 if(name != NULL) delete name; 30 id = it.id; 31 name = new char[strlen(it.name) + 1]; 32 strcpy(name, it.name); 33 } 34 return *this; 35 } 36 }; 37 38 // str& operator=(const str &a, const str &b){ 39 // if(&a != &b){ 40 // if(a.name != NULL) delete a.name; 41 // a.id = b.id; 42 // a.name = new char[strlen(b.name) + 1]; 43 // strcpy(a.name, b.name); 44 // } 45 // return *this; 46 // } 47 48 int main(void){ 49 str a(1, "hello world"), b(2, "jj fu jj"); 50 a.print(cout);//1 hello world 51 a = b; 52 a.print(cout);//2 jj fu jj 53 54 a = "ajsdfkls";//先通过转换构造函数将"ajsdfkls"转换成str对象,然后再执行赋值操作 55 a.print(cout);//0 ajsdfkls 56 return 0; 57 }
我们可以发现 = 只能作为成员函数重载,如果重载为友元函数的话会报错:
注意:
我们最好将返回类型写成 str&,不然将不能用连等~
要避免自赋值,即地址相同的两个对象相互赋值:
1.为了效率。显然,自己给自己赋值完全是毫无意义的无用功,特别地,对于基类数据成员间的赋值,还会调用基类的赋值运算符重载函数,开销是很大的。如果我们一旦判定是自赋值,就立即 return *this,会避免对其它函数的调用。
2.如果类的数据成员中含有指针,自赋值有时会导致灾难性的后果。对于指针间的赋值(注意这里指的是指针所指内容间的赋值,这里假设用 _p 给 p 赋值),先要将 p 所指向的空间 delete 掉(为什么要这么做呢?因为指针 p 所指的空间通常是 new 来的,如果在为 p 重新分配空间前没有将p原来的空间 delete 掉,会造成内存泄露),然后再为 p 重新分配空间,将 _p 所指的内容拷贝到 p 所指的空间。如果是自赋值,那么 p 和 _p 是同一指针,在赋值操作前对 p 的 delete 操作,将导致 p 所指的数据同时被销毁。那么重新赋值时,拿什么来赋?
所以,对于赋值运算符重载函数,一定要先检查是否是自赋值,如果是,直接return *this。
