首先,我们要推一个柿子。
\(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} a[i]\)
把a[i]用差分数组表示出来,就可以写成
\(\displaystyle\sum_{i = 1}^{n}\sum_{j=1}^{i} d[i]\)
我们考虑一下,每个d[i]出现的次数是一定的。
那我们可以换一下枚举顺序,先枚举d[i]在枚举他出现的次数,就可以变成
\(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i]\times (n-i+1)\)
再把后面的(n-i+1)拆成(n+1) - i
就可以变成\(\displaystyle\sum_{i = 1}^{n} d[i] \times (n+1) - d[i] \times i\)
也就是 \(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] \times (n+1)\) - \(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] \times i\)
然后我们可以把前面的(n+1)提出来变成
\((n+1)\times \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] - \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] \times i\)
后面的两个前缀和就可以用树状数组来维护,这样树状数组就可以支持区间修改和区间查询。
求[l,r]的区间和可以用[1,r]的区间和减去[1,l-1]的区间和来求出来
总柿子:
\(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i\)
= \(\displaystyle\sum_{i = 1}^{n}\displaystyle\sum_{j=1}^{i} d_i\)
= \(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d_i\times (n-i+1)\)
= \(\displaystyle\sum_{i = 1}^{n} d_i \times (n+1) - d_i \times i\)
= \(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d_i \times (n+1)\) - \(\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d_i \times i\)
= \((n+1)\times \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] - \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{n} d[i] \times i\)
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int n,m,opt,x,y,z,tmp;
int d[1000100],tr[1000010],a[1000010];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s = s * 10+ch -'0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
int lowbit(int x){return x & (-x);}
void chenge(int x,int val)
{
for(; x <= n; x += lowbit(x))
{
d[x] += val;
}
}
void modify(int x,int val)
{
for(; x <= n; x += lowbit(x))
{
tr[x] += val;
}
}
int ask(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for(; x>=1; x -= lowbit(x))
{
ans += d[x];
}
return ans;
}
int query(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for(; x>=1; x -= lowbit(x))
{
ans += tr[x];
}
return ans;
}
signed main()
{
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
a[i] = read();
tmp = a[i] - a[i-1];
chenge(i,tmp); modify(i,tmp * i);
}
while(m--)
{
opt = read(); x = read(); y = read();
if(opt == 1)
{
z = read();
chenge(x,z); chenge(y+1,-z);
modify(x,x * z); modify(y+1,-(y+1) * z);
}
if(opt == 2)
{
int sum1 = (x) * ask(x-1) - query(x-1);
int sum2 = (y+1) * ask(y) - query(y);
printf("%lld\n",sum2-sum1);
}
}
return 0;
}
二维树状数组
二维树状数组其实和一维的差不多。
你可以形象的理解为先对每一行求一个树状数组,在用树状数组的方式把他们加起来。
D1 单点修改,区间查询:
操作1就是普通的单点修改,直接在原来的循环里面再套一层循环每一行的树状数组就可以了。
操作2的话比较麻烦,我们考虑一下容斥原理。
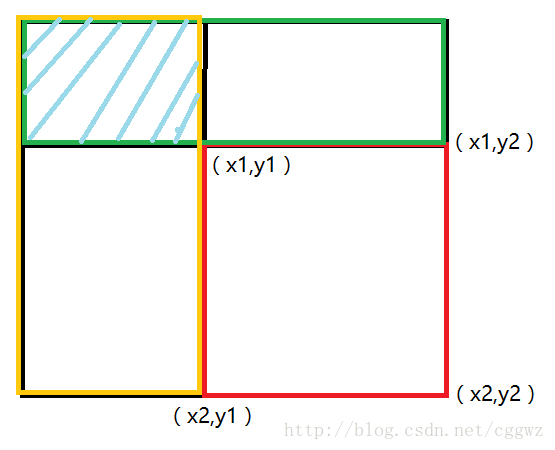
我们可以用整个矩形的面积减去绿色矩形的面积减去黄色矩形的面积,在加上阴影部分的面积。
已就是
ask(c,x2,y2) - ask(c,x1-1,y2) - ask(c,x2,y1-1) + ask(x,x1-1,y1-1)
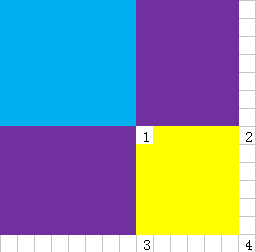
下面这张图可能会更形象些
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,m,opt,x,y,c,t,val,x1,x2,y1,y2;
int tr[110][310][310],a[310][310];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s =s * 10+ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
int lowbit(int x){return x & -x;}
void chenge(int now,int x,int y,int val)
{
for(int i = x; i <= n; i += lowbit(i))//修改最外面的树状数组
{
for(int j = y; j <= m; j += lowbit(j))//修改每一行的树状数组
{
tr[now][i][j] += val;
}
}
}
int ask(int now,int x,int y)
{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i))
{
for(int j = y; j; j -= lowbit(j))
{
ans += tr[now][i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
a[i][j] = read();//对每个元素都开一个树状数组
chenge(a[i][j],i,j,1);
}
}
t = read();
while(t--)
{
opt = read();
if(opt == 1)
{
x = read(); y = read(); val = read();
int t = a[x][y];
chenge(t,x,y,-1);//把原来的数减1
chenge(val,x,y,1);//现在的数加1
a[x][y] = val;//记录一下当前的数
}
else
{
x1 = read(); x2 = read(); y1 = read(); y2 = read(); c = read();
int ans = ask(c,x2,y2) + ask(c,x1-1,y1-1) - ask(c,x1-1,y2) - ask(c,x2,y1-1);//区间查询
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
至于二维树状数组的其他操作,蒟蒻我还没学会,暂且先咕着吧QAQ。
树状数组求逆序对
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
char ch;
int n,tr[1000010],b[1000010],a[50][100010],num[30],cnt[30];
long long ans;
int lowbit(int x){return x & -x;}
void chenge(int x,int val)
{
for(; x <= n; x += lowbit(x)) tr[x] += val;
}
int ask(int x)
{
int res = 0;
for(; x >= 1; x -= lowbit(x)) res += tr[x];
return res;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin>>ch;
a[ch-'A'][++num[ch-'A']] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin>>ch;
b[i] = a[ch-'A'][++cnt[ch-'A']];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
chenge(b[i],1);
ans += i - ask(b[i]);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}