网络流练习日志
前言:
教练说 (Csp) 之前要学会网络流基础,在暑假培训的时候,学长过来讲了一些。
但由于年代太过久远(大雾),现在发现几乎快忘了。
所以刷(水)几道题来牢固一下。
P1402 酒店之王
题目描述
XX 酒店的老板想成为酒店之王,本着这种希望,第一步要将酒店变得人性化。由于很多来住店的旅客有自己喜好的房间色调、阳光等,也有自己所爱的菜,但是该酒店只有 (p) 间房间,一天只有固定的 (q) 道不同的菜,每个房间只能住一位客人,每道菜也只能给一位客人食用。
有一天来了 (n) 个客人,每个客人说出了自己喜欢哪些房间,喜欢哪道菜。但是很不幸,可能做不到让所有顾客满意(满意的条件是住进喜欢的房间且吃到喜欢的菜)。
要怎么分配,能使最多顾客满意呢?
输入格式
第一行给出三个整数,分别表示表示 (n,p,q)。
之后 (n) 行,每行 (p) 个整数,只可能是 (0) 或 (1),第 (i) 行第 (j) 个数表示第 (i) 个人喜不喜欢第 (j) 个房间((1) 表示喜欢, (0) 表示不喜欢)。
之后 (n) 行,每行 (q) 个整数,只可能是 (0) 或 (1),第 (i) 行第 (j) 个数表示第 (i) 个 人喜不喜欢第 (j) 道菜((1) 表示喜欢, (0) 表示不喜欢)。
输出格式
最大的顾客满意数。
比较经典的网络流匹配模型。
首先,我们先开两个点分别为超级源以及超级汇。
对于每道菜由于他只能用一次,所以我们从源点到每道菜连一条容量为 (1) 的边。
同理,每间房也只能用一次,我们把每间房向汇点连一条容量为 (1) 的边
对于每个客人呢,我们只需要把他和他喜欢的菜和房间分别连一条容量为 (1) 的边。
把图建出来具体长这样。
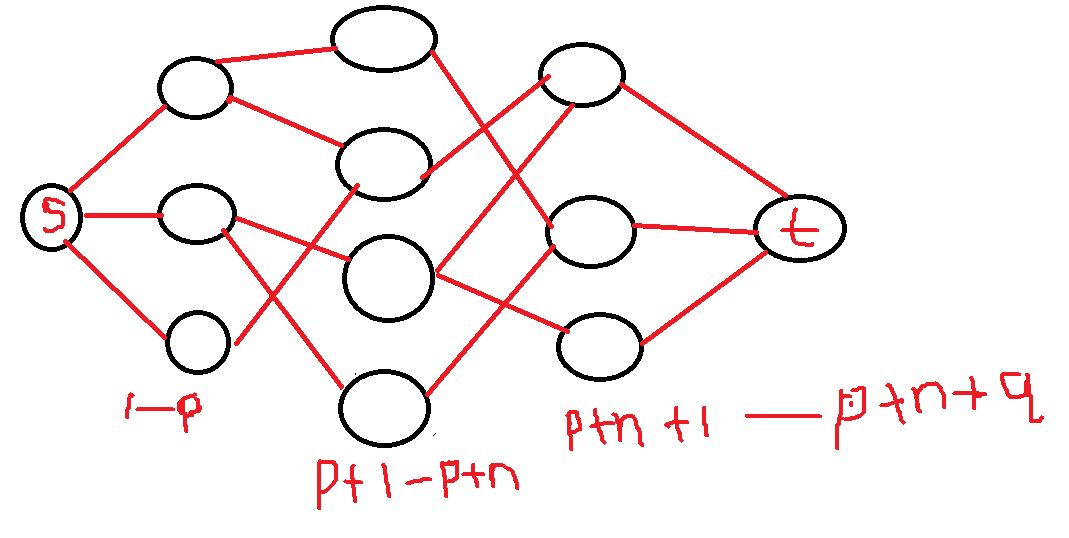
电脑上画图太难弄了,就这么凑合着看吧 QAQ.
(1-p) 表示每道菜, (p+1-p+n) 表示每个人, (p+n+1-p+n+q) 表示每间房
但当你在用这张图跑最大流的时候是没问题的,但有一种情况会把你卡的死死地。
例如下面这张图(直接从题解里面扒了一张,自己画的太难看了):
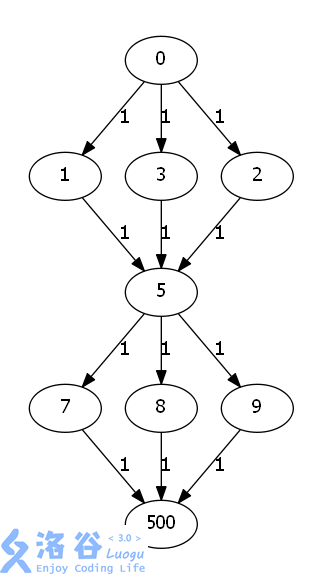
你跑出来的答案是 (3) ,但正确答案却是 (1) ,这是因为你増广之后五号节点的反向边边权会增加 (1) ,这样五号这个点还可以和其他的节点再次构成增广路。
相当于你五号点这个人被我们重复用了多次,(影分身之术???)
这当然是我们不能接受的,那我们怎么办呢?
我们可以把五号点拆成两个点,一个只接受入流,一个向外面出流,这两个点之间连一条容量为 (1) 的边,表示这个点只能用一次。
你也可以理解为用这个点来限流。那上面那张图就可以转化为:
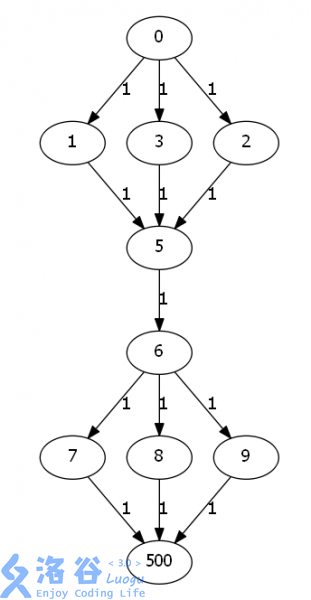
这样我们的正确性就可以保证了,剩下的就是 (Dinic) 的模板了
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 2147483647;
const int N = 510;
int n,p,q,ans,flow,tot = 1,s,t,x;//tot 初值一定要赋为1
int dep[N],head[N];
struct node
{
int to,net,w;
}e[100010];
void add(int x,int y,int w)
{
e[++tot].to = y;
e[tot].w = w;
e[tot].net = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s = s * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
bool bfs()//分层
{
queue<int> q;
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
q.push(s); dep[s] = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && !dep[to])
{
q.push(to);
dep[to] = dep[x] + 1;
if(to == t) return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int x,int flow)//增广
{
if(x == t) return flow;
int rest = flow;
for(int i = head[x]; i && rest; i = e[i].net)//rest是一个优化,如果到当前点的流为0,那么就不用往下增广了
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && dep[to] == dep[x] + 1)
{
int k = dinic(to,min(e[i].w,rest));//向下增广
if(!k) dep[to] = 0;//优化,如果这个点后面不能再增广下去,那么直接把他踢出去分层图就可以
e[i].w -= k;
e[i^1].w += k;
rest -= k;
}
}
return flow - rest;
}
int main()
{
n = read(); p = read(); q = read();
s = 0; t = n*2 + p + q + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i++) add(s,i,1), add(i,s,0);//源点向每一道菜连一条边
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) add(n*2+p+i,t,1), add(t,n*2+p+i,0);//每一间房向汇点连边
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= p; j++)
{
x = read();
if(x == 1)
{
add(j,i+p,1);//每个人向他喜欢的房间连边
add(i+p,j,0);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= q; j++)
{
x = read();
if(x == 1)
{
add(i+n+p,n*2+p+j,1);//每个人向他喜欢的房连边
add(n*2+p+j,i+n+p,0);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
add(i+p,i+n+p,1);//拆点
add(i+n+p,i+p,0);
}
int flow = 0;
while(bfs())
{
while(flow = dinic(s,inf)) ans += flow;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
P2891 [USACO07OPEN]Dining G
题目描述
有 (F) 种食物和 (D) 种饮料,每种食物或饮料只能供一头牛享用,且每头牛只享用一种食物和一种饮料。
现在有 (n) 头牛,每头牛都有自己喜欢的食物种类列表和饮料种类列表,问最多能使几头牛同时享用到自己喜欢的食物和饮料。(1 <= f <= 100, 1 <= d <= 100, 1 <= n <= 100)
双倍经验,和上道题一模一样。
把源点向每种食物连一条容量为 (1) 的边,每种饮料向汇点连一条容量为 (1) 的边,每头牛向他喜欢的食物和饮料连边。
在把每条牛拆点表示每头牛只能选一次即可。
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 2147483647;
const int N = 510;
int n,a,b,s,t,ans,tot = 1;
int head[N],dep[N];
struct node
{
int to,net,w;
}e[100010];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s = s * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
void add(int x,int y,int w)
{
e[++tot].w = w;
e[tot].to = y;
e[tot].net = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
bool bfs()
{
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
queue<int> q;
q.push(s); dep[s] = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && !dep[to])
{
q.push(to);
dep[to] = dep[x] + e[i].w;
if(to == t) return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int x,int flow)//dinic模板
{
if(x == t) return flow;
int rest = flow;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && dep[to] == dep[x] + 1)
{
int k = dinic(to,min(rest,e[i].w));
if(!k) dep[to] = 0;
e[i].w -= k;
e[i^1].w += k;
rest -= k;
}
}
return flow - rest;
}
int main()
{
n = read(); a = read(); b = read();
s = 0; t = 2*n+a+b+1;
int flow = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= a; i++) add(s,i,1), add(i,s,0);
for(int i = 1; i <= b; i++) add(a+n*2+i,t,1), add(t,a+n*2+i,0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int num1 = read(), num2 = read(), x;
for(int j = 1; j <= num1; j++)
{
x = read();
add(x,a+i,1); add(a+i,x,0);
}
for(int j = 1; j <= num2; j++)
{
x = read();
add(a+n+i,a+2*n+x,1); add(a+2*n+x,a+n+i,0);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
add(a+i,a+i+n,1); add(a+i+n,a+i,0);
}
while(bfs())
{
while(flow = dinic(s,inf)) ans += flow;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
P1231 教辅的组成
三倍经验(大雾)
题目描述
蒟蒻 HansBug 在一本语文书里面发现了一本答案,然而他却明明记得这书应该还包含一份练习题。然而出现在他眼前的书多得数不胜数,其中有书,有答案,有
练习册。已知一个完整的书册均应该包含且仅包含一本书、一本练习册和一份答案,然而现在全都乱做了一团。许多书上面的字迹都已经模糊了,然而 HansBug
还是可以大致判断这是一本书还是练习册或答案,并且能够大致知道一本书和答案以及一本书和练习册的对应关系(即仅仅知道某书和某答案、某书和某练习册有
可能相对应,除此以外的均不可能对应)。既然如此,HansBug 想知道在这样的情况下,最多可能同时组合成多少个完整的书册。
和上面那两道题差不多,都是配对问题。
题目中要求我们每本书都要配对一本练习册和答案。且每本书只能用一次(废话)
从源点向每个练习册连一条容量为 (1) 的边,在从每本答案向汇点连一条容量为 (1) 的边。
再把每本书拆点,向他配对的练习册以及答案连一条容量为 (1) 的边。
剩下的跑一边 (dinic) 模板就可以。
一般来说 (dinic) 的复杂度是 (O(VE^2)) 的,但一般跑不满,所以就放心的用吧,一般没人会卡你的。
还有就是数组要开大些(别问我是怎么知道的,血的教训)
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 2147483647;
const int N = 50010;
int n,m1,m2,p,q,x,y,ans,s,t,tot = 1;
int head[N],dep[N];
struct node
{
int to,net,w;
}e[1000010];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s = s * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
void add(int x,int y,int w)
{
e[++tot].w = w;
e[tot].to = y;
e[tot].net = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
bool bfs()
{
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
queue<int> q;
q.push(s); dep[s] = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && !dep[to])
{
q.push(to);
dep[to] = dep[x] + 1;
if(to == t) return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int x,int flow)
{
if(x == t) return flow;
int rest = flow;
for(int i = head[x]; i && rest; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w && dep[to] == dep[x] + 1)
{
int k = dinic(to,min(e[i].w,rest));
if(!k) dep[to] = 0;
e[i].w -= k;
e[i^1].w += k;
rest -= k;
}
}
return flow - rest;
}
int main()
{
n = read(); p = read(); q = read();
s = 0, t = n*2+p+q+1;
m1 = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i++) add(s,i,1), add(i,s,0);
for(int i = 1; i <= m1; i++)
{
x = read(); y = read();
add(y,x+p,1); add(x+p,y,0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
add(i+p,i+n+p,1), add(i+n+p,i+p,0);
}
m2 = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m2; i++)
{
x = read(); y = read();
add(n+p+x,n*2+p+y,1); add(n*2+p+y,n+p+x,0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++)
{
add(n*2+p+i,t,1), add(t,n*2+p+i,0);
}
int flow = 0;
while(bfs())
{
while(flow = dinic(s,inf)) ans += flow;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}