之前文章有写到vue构造函数的实例化过程,只是对vue实例做了个粗略的描述,并没有说明vue组件实例化的过程。本文主要对vue组件的实例化过程做一些简要的描述。
组件的实例化与vue构造函数的实例化,大部分是类似的,vue的实例可以当做一个根组件,普通组件的实例化可以当做子组件。真实的DOM是一个树形结构,虚拟DOM本质只是真实DOM的抽象,也是一个树形结构。简单来说,整个vue工程的实例化过程如下:
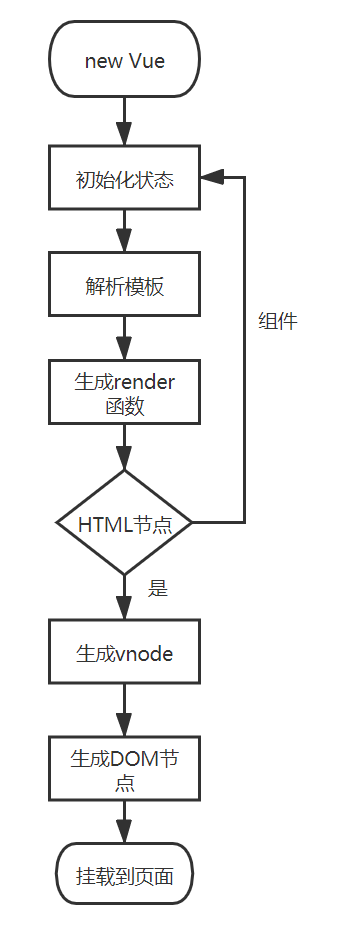
如上图所示,在调用render函数时,会依次调用createElement方法,createElement方法的代码如下,主要作用就是生成vnode。
export function _createElement ( context: Component, tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object, data?: VNodeData, children?: any, normalizationType?: number ): VNode | Array<VNode> { if (isDef(data) && isDef((data: any).__ob__)) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Avoid using observed data object as vnode data: ${JSON.stringify(data)} ` + 'Always create fresh vnode data objects in each render!', context ) return createEmptyVNode() } // object syntax in v-bind if (isDef(data) && isDef(data.is)) { tag = data.is } if (!tag) { // in case of component :is set to falsy value return createEmptyVNode() } // warn against non-primitive key if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isDef(data) && isDef(data.key) && !isPrimitive(data.key) ) { if (!__WEEX__ || !('@binding' in data.key)) { warn( 'Avoid using non-primitive value as key, ' + 'use string/number value instead.', context ) } } // support single function children as default scoped slot if (Array.isArray(children) && typeof children[0] === 'function' ) { data = data || {} data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] } children.length = 0 } // 组件格式化 if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) { children = normalizeChildren(children) } else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) { children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children) } let vnode, ns if (typeof tag === 'string') { let Ctor ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag) // 普通的HTML标签 if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) { // platform built-in elements if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isDef(data) && isDef(data.nativeOn)) { warn( `The .native modifier for v-on is only valid on components but it was used on <${tag}>.`, context ) } // 创建一个普通的DOM节点 vnode = new VNode( config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) { // component // 创建组件 vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag) } else { // unknown or unlisted namespaced elements // check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its // parent normalizes children vnode = new VNode( tag, data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } } else { // direct component options / constructor vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children) } if (Array.isArray(vnode)) { return vnode } else if (isDef(vnode)) { if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns) if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data) return vnode } else { return createEmptyVNode() } }
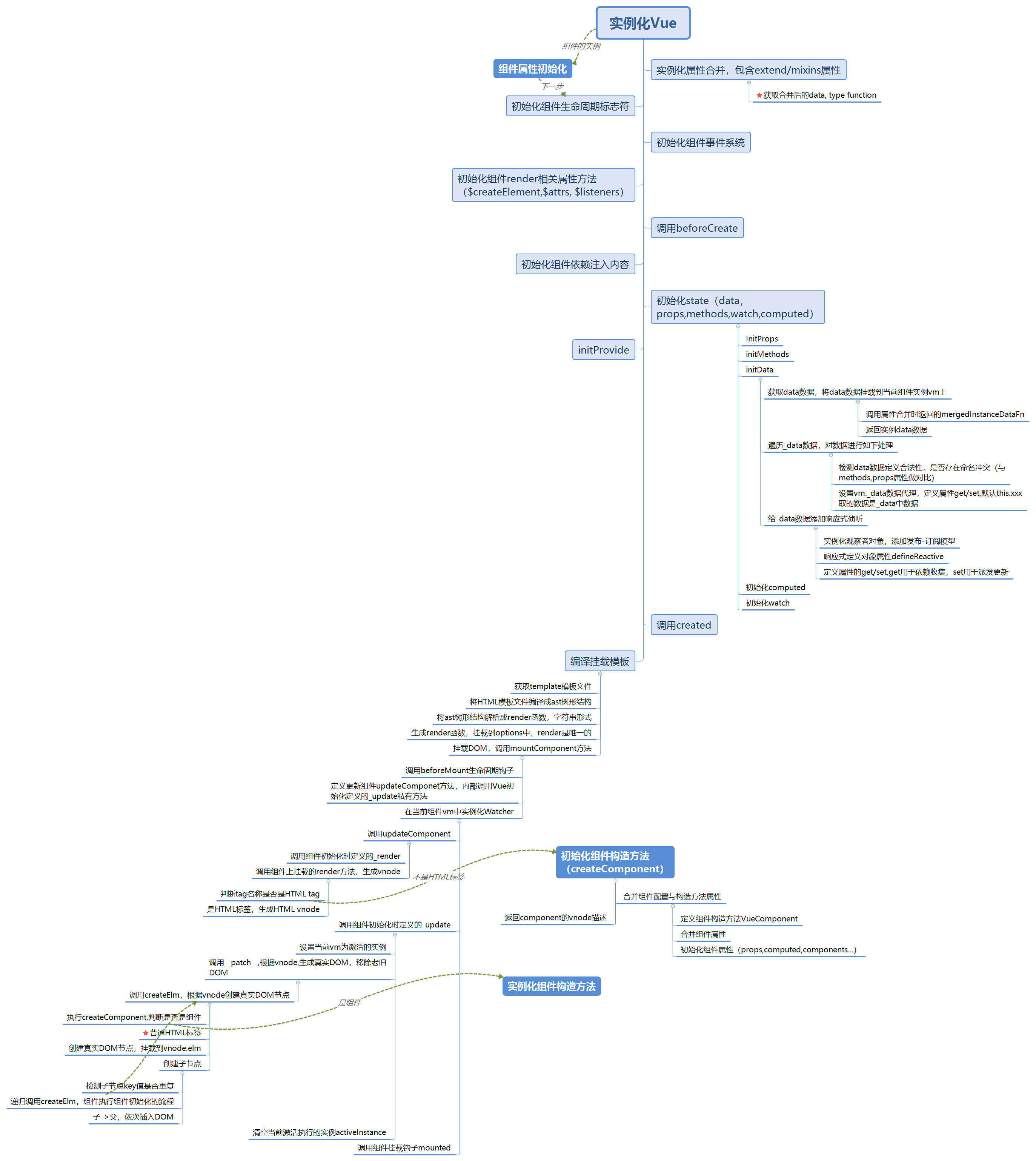
如上图所示,主流程与实例化Vue类似,只是在实例化Vue的过程中,额外走了一个创建组件的分支,其中createComponent方法实现如下:
export function createComponent ( Ctor: Class<Component> | Function | Object | void, data: ?VNodeData, context: Component, children: ?Array<VNode>, tag?: string ): VNode | Array<VNode> | void { if (isUndef(Ctor)) { return } // 获取Vue基础构造函数,在initGlobal中,将vue基础构造方法赋值给_base属性 const baseCtor = context.$options._base // plain options object: turn it into a constructor if (isObject(Ctor)) { // 将组件的配置,合并到构造方法中,extend是定义在Vue构造方法中的 Ctor = baseCtor.extend(Ctor) } // if at this stage it's not a constructor or an async component factory, // reject. if (typeof Ctor !== 'function') { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn(`Invalid Component definition: ${String(Ctor)}`, context) } return } // async component let asyncFactory if (isUndef(Ctor.cid)) { asyncFactory = Ctor Ctor = resolveAsyncComponent(asyncFactory, baseCtor) if (Ctor === undefined) { // return a placeholder node for async component, which is rendered // as a comment node but preserves all the raw information for the node. // the information will be used for async server-rendering and hydration. return createAsyncPlaceholder( asyncFactory, data, context, children, tag ) } } data = data || {} // resolve constructor options in case global mixins are applied after // component constructor creation resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor) // transform component v-model data into props & events if (isDef(data.model)) { transformModel(Ctor.options, data) } // extract props const propsData = extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag) // functional component if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) { return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children) } // extract listeners, since these needs to be treated as // child component listeners instead of DOM listeners const listeners = data.on // replace with listeners with .native modifier // so it gets processed during parent component patch. data.on = data.nativeOn if (isTrue(Ctor.options.abstract)) { // abstract components do not keep anything // other than props & listeners & slot // work around flow const slot = data.slot data = {} if (slot) { data.slot = slot } } // install component management hooks onto the placeholder node // 初始化组件的钩子函数 installComponentHooks(data) // return a placeholder vnode // 体现了组件名称在这里面的作用 const name = Ctor.options.name || tag // 创建vnode const vnode = new VNode( `vue-component-${Ctor.cid}${name ? `-${name}` : ''}`, data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context, { Ctor, propsData, listeners, tag, children }, asyncFactory ) // Weex specific: invoke recycle-list optimized @render function for // extracting cell-slot template. // https://github.com/Hanks10100/weex-native-directive/tree/master/component /* istanbul ignore if */ if (__WEEX__ && isRecyclableComponent(vnode)) { return renderRecyclableComponentTemplate(vnode) } return vnode }
从上述代码中可以看出,createComponent主要作用就是返回一个vnode,中间的流程主要作用有两点,一是组装组件的构造方法,用于实例化组件,另外一点就是调用installComponentHooks,初始化组件的生命周期入口。组件的声明周期钩子虽然与vue根实例一致,但是调用的位置还是有一定的差别,具体有以下几点:
1. Vue构造方法是在srccoreinstanceindex.js中,而组件的构造方法是基于Vue根构造方法,在上述createComponet中调用Vue.extend方法进行组装而成,本质上都是调用Vue实例上的_init方法,但是组件的构造方法VueComponent声明了一些属于自己的自定义属性,具体实现代码如下:
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function { extendOptions = extendOptions || {} const Super = this // 父级实例cid const SuperId = Super.cid const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {}) if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) { return cachedCtors[SuperId] } const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) { validateComponentName(name) } // 定义vue初始化方法,和实例化Vue走同一个路线 const Sub = function VueComponent (options) { this._init(options) } // super -> this -> Vue 继承Vue构造方法中的属性 Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype) // 指定子组件的构造方法为Sub -> VueComponent Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub Sub.cid = cid++ // 合并组件属性 Sub.options = mergeOptions( Super.options, extendOptions ) // 定义父级作用域 Sub['super'] = Super // For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on // the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This // avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created. if (Sub.options.props) { initProps(Sub) } if (Sub.options.computed) { initComputed(Sub) } // allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage // 子组件的实例,保持对vue构造方法的引用 Sub.extend = Super.extend Sub.mixin = Super.mixin Sub.use = Super.use // create asset registers, so extended classes // can have their private assets too. ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) { Sub[type] = Super[type] }) // enable recursive self-lookup if (name) { Sub.options.components[name] = Sub } // keep a reference to the super options at extension time. // later at instantiation we can check if Super's options have // been updated. Sub.superOptions = Super.options Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options) // cache constructor cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub return Sub } }
2. Vue根实例的模板解析与DOM挂载入口不一致,在_init方法中,提供了对根实例的模板解析与DOM挂载,而组件没有。在创建组件时,调用了installComponentHooks,componet hooks主要包含init、prepatch、insert、destory,init在实例化组件时调用,insert是插入DOM时调用,destory是在销毁组件时调用,而prepatch是在更新组件时调用,具体如下:
const componentVNodeHooks = { // 组件初始化方法 init (vnode: VNodeWithData, hydrating: boolean): ?boolean { if ( vnode.componentInstance && !vnode.componentInstance._isDestroyed && vnode.data.keepAlive ) { // kept-alive components, treat as a patch const mountedNode: any = vnode // work around flow componentVNodeHooks.prepatch(mountedNode, mountedNode) } else { // 实例化组件 const child = vnode.componentInstance = createComponentInstanceForVnode( vnode, activeInstance ) //挂载组件 child.$mount(hydrating ? vnode.elm : undefined, hydrating) } }, prepatch (oldVnode: MountedComponentVNode, vnode: MountedComponentVNode) { const options = vnode.componentOptions const child = vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance updateChildComponent( child, options.propsData, // updated props options.listeners, // updated listeners vnode, // new parent vnode options.children // new children ) }, insert (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) { const { context, componentInstance } = vnode if (!componentInstance._isMounted) { componentInstance._isMounted = true callHook(componentInstance, 'mounted') } if (vnode.data.keepAlive) { if (context._isMounted) { // vue-router#1212 // During updates, a kept-alive component's child components may // change, so directly walking the tree here may call activated hooks // on incorrect children. Instead we push them into a queue which will // be processed after the whole patch process ended. queueActivatedComponent(componentInstance) } else { activateChildComponent(componentInstance, true /* direct */) } } }, destroy (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) { const { componentInstance } = vnode if (!componentInstance._isDestroyed) { if (!vnode.data.keepAlive) { componentInstance.$destroy() } else { deactivateChildComponent(componentInstance, true /* direct */) } } } }
如上述代码所示,实例化组件调用的是createComponentInstanceForVnode,createComponentInstanceForVnode代码如下,调用在Vue.extend中组装的组件构造方法VueComponent,初始化调用的还是Vue原型上的_init方法,大致流程与Vue初始化类似,只是解析模板有所区别,组件解析模板调用的是child.$mount。
// 创建组件的作用域,执行组件的_init方法,同vue实例化过程 export function createComponentInstanceForVnode ( vnode: any, // we know it's MountedComponentVNode but flow doesn't parent: any, // activeInstance in lifecycle state ): Component { const options: InternalComponentOptions = { _isComponent: true, _parentVnode: vnode, parent } // check inline-template render functions const inlineTemplate = vnode.data.inlineTemplate if (isDef(inlineTemplate)) { options.render = inlineTemplate.render options.staticRenderFns = inlineTemplate.staticRenderFns } // 实例化组件的构造方法 return new vnode.componentOptions.Ctor(options) }
在installComponentHooks中,在vnode的data属性中初始化了hooks,后面在_patch__中,会调用patch.js中声明的createComponent -> init -> 实例化组件。组件实例化完成后,会将真实DOM元素,插入到上一级元素。patch.js中的createComponent方法如下:
// 创建组件,如果节点类型是组件,则直接走创建组件的方法 function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) { let i = vnode.data // 判断是否存在组件的生命周期,存在,即需要走创建组件的流程 if (isDef(i)) { const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) { // 执行component的init方法,获取组件的实例 i(vnode, false /* hydrating */) } // after calling the init hook, if the vnode is a child component // it should've created a child instance and mounted it. the child // component also has set the placeholder vnode's elm. // in that case we can just return the element and be done. // 组件的vnode对象中存在当前组件的作用域 if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) { initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) // 将子组件插入到父节点中 insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm) if (isTrue(isReactivated)) { reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) } return true } } }
在实例化完成后,会将生成的真实DOM元素插入到上级元素中,vue在获取真实DOM时,是从低往上,一级级添加,最终将渲染的元素添加到DOM body中,__patch__主流程如下:
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) { if (isUndef(vnode)) { if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode) return } let isInitialPatch = false const insertedVnodeQueue = [] if (isUndef(oldVnode)) { // empty mount (likely as component), create new root element isInitialPatch = true createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) } else { const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType) if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) { // patch existing root node patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly) } else { if (isRealElement) { // mounting to a real element // check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform // a successful hydration. // nodeType 1 元素 3 文字 if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) { oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR) hydrating = true } if (isTrue(hydrating)) { if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) { invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true) return oldVnode } else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn( 'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' + 'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' + 'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' + '<p>, or missing <tbody>. Bailing hydration and performing ' + 'full client-side render.' ) } } // either not server-rendered, or hydration failed. // create an empty node and replace it oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode) } // replacing existing element // 获取老旧节点 const oldElm = oldVnode.elm // 获取老旧节点的父节点 const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm) // create new node // 将虚拟DOM转换成真实DOM // 传入父级节点,一级级添加 createElm( vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, // extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a // leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition + // keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590) oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm) ) // update parent placeholder node element, recursively if (isDef(vnode.parent)) { let ancestor = vnode.parent const patchable = isPatchable(vnode) while (ancestor) { for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) { cbs.destroy[i](ancestor) } ancestor.elm = vnode.elm if (patchable) { for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) { cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor) } // #6513 // invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks. // e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook. const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert if (insert.merged) { // start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) { insert.fns[i]() } } } else { registerRef(ancestor) } ancestor = ancestor.parent } } // destroy old node // 移除老旧节点 if (isDef(parentElm)) { removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0) } else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) { invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode) } } } invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch) return vnode.elm }
模板的解析,是先把模板解析成HTML,然后再讲老旧节点移除。