整个工程使用的是Windows版pyCharm和tensorflow。
源码地址:https://github.com/Irvinglove/tensorflow_poems/tree/master
唐诗生成
一、读取诗的数据集(poems.py)
import collections import os import sys import numpy as np import codecs start_token = 'G' end_token = 'E' def process_poems(file_name): # 诗集 poems = [] with codecs.open(file_name, "r", encoding='utf-8', ) as f: for line in f.readlines(): try: title, content = line.strip().split(':') content = content.replace(' ', '') if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content or start_token in content or end_token in content: continue if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79: continue content = start_token + content + end_token poems.append(content) except ValueError as e: pass # 按诗的字数排序 poems = sorted(poems, key=lambda line: len(line)) # 统计每个字出现次数 all_words = [] for poem in poems: all_words += [word for word in poem] # 这里根据包含了每个字对应的频率 counter = collections.Counter(all_words) count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) # 取前多少个常用字 words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',) # 每个字映射为一个数字ID word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words)))) # poems_vector = [list(map(lambda word: word_int_map.get(word, len(words)), poem)) for poem in poems] poems_vector = [list(map(word_int_map.get, poem)) for poem in poems] return poems_vector, word_int_map, words def generate_batch(batch_size, poems_vec, word_to_int): # 每次取64首诗进行训练 n_chunk = len(poems_vec) // batch_size x_batches = [] y_batches = [] for i in range(n_chunk): start_index = i * batch_size end_index = start_index + batch_size batches = poems_vec[start_index:end_index] # 找到这个batch的所有poem中最长的poem的长度 length = max(map(len, batches)) # 填充一个这么大小的空batch,空的地方放空格对应的index标号 x_data = np.full((batch_size, length), word_to_int[' '], np.int32) for row in range(batch_size): # 每一行就是一首诗,在原本的长度上把诗还原上去 x_data[row, :len(batches[row])] = batches[row] y_data = np.copy(x_data) # y的话就是x向左边也就是前面移动一个 y_data[:, :-1] = x_data[:, 1:] """ x_data y_data [6,2,4,6,9] [2,4,6,9,9] [1,4,2,8,5] [4,2,8,5,5] """ x_batches.append(x_data) y_batches.append(y_data) return x_batches, y_batches
这段代码主要是有两个函数构成:
1. process_poems:读取诗歌数据集(诗歌:标题、内容);
排除一些不必要的数据;
统计每个字出现的次数,获取常用字;
将每个字映射为一个数字ID(word_int_map),从而获得诗歌矢量(poems_vector)
2. generate_batch:每次取一个batch进行训练(这里取64),获得一个epoch内多少个batch;
在一个epoch内迭代,获取这个batch的所有poem中最长的poem长度;
填充它,空的地方放空格对应获得index标号
二、模型构建(model.py)
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np def rnn_model(model, input_data, output_data, vocab_size, rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64, learning_rate=0.01): end_points = {} # 构建RNN基本单元RNNcell if model == 'rnn': cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell elif model == 'gru': cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell else: cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True) # 构建堆叠rnn,这里选用两层的rnn cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True) # 如果是训练模式,output_data不为None,则初始状态shape为[batch_size * rnn_size] # 如果是生成模式,output_data为None,则初始状态shape为[1 * rnn_size] if output_data is not None: initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32) else: initial_state = cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32) # 构建隐层 with tf.device("/cpu:0"): embedding = tf.get_variable('embedding', initializer=tf.random_uniform( [vocab_size + 1, rnn_size], -1.0, 1.0)) inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_data) # [batch_size, ?, rnn_size] = [64, ?, 128] outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state) output = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, rnn_size]) weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([rnn_size, vocab_size + 1])) bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[vocab_size + 1])) logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output, weights), bias=bias) # [?, vocab_size+1] if output_data is not None: # output_data must be one-hot encode labels = tf.one_hot(tf.reshape(output_data, [-1]), depth=vocab_size + 1) # should be [?, vocab_size+1] loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits) # loss shape should be [?, vocab_size+1] total_loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(total_loss) end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state end_points['output'] = output end_points['train_op'] = train_op end_points['total_loss'] = total_loss end_points['loss'] = loss end_points['last_state'] = last_state else: prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits) end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state end_points['last_state'] = last_state end_points['prediction'] = prediction return end_points
主要构建RNN基本单元RNNcell;确立隐层、输出;初始化权重和偏置
三、模型训练(tang_poems.py)
import collections import os import sys import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from models.model import rnn_model from dataset.poems import process_poems, generate_batch import heapq # main函数的参数 tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 64, 'batch size.') tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float('learning_rate', 0.01, 'learning rate.') # set this to 'main.py' relative path tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('checkpoints_dir', os.path.abspath('./checkpoints/poems/'), 'checkpoints save path.') tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('file_path', os.path.abspath('./dataset/data/poems.txt'), 'file name of poems.') tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('begin_word', '白', 'file name of poems.') tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('model_prefix', 'poems', 'model save prefix.') tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('epochs', 20, 'train how many epochs.') FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS start_token = 'G' end_token = 'E' def run_training(): if not os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)): os.mkdir(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)) if not os.path.exists(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir): os.mkdir(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir) # 处理数据集 poems_vector, word_to_int, vocabularies = process_poems(FLAGS.file_path) # 生成batch batches_inputs, batches_outputs = generate_batch(FLAGS.batch_size, poems_vector, word_to_int) input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [FLAGS.batch_size, None]) output_targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [FLAGS.batch_size, None]) # 构建模型 end_points = rnn_model(model='lstm', input_data=input_data, output_data=output_targets, vocab_size=len( vocabularies), rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64, learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate) saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables()) init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer()) with tf.Session() as sess: # sess = tf_debug.LocalCLIDebugWrapperSession(sess=sess) # sess.add_tensor_filter("has_inf_or_nan", tf_debug.has_inf_or_nan) sess.run(init_op) start_epoch = 0 checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir) # 从上次中断的checkpoint开始训练 if checkpoint: saver.restore(sess, checkpoint) print("[INFO] restore from the checkpoint {0}".format(checkpoint)) start_epoch += int(checkpoint.split('-')[-1]) print('[INFO] start training...') try: for epoch in range(start_epoch, FLAGS.epochs): n = 0 n_chunk = len(poems_vector) // FLAGS.batch_size for batch in range(n_chunk): loss, _, _ = sess.run([ end_points['total_loss'], end_points['last_state'], end_points['train_op'] ], feed_dict={input_data: batches_inputs[n], output_targets: batches_outputs[n]}) n += 1 print('[INFO] Epoch: %d , batch: %d , training loss: %.6f' % (epoch, batch, loss)) if epoch % 6 == 0: saver.save(sess, os.path.join(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir, FLAGS.model_prefix), global_step=epoch) except KeyboardInterrupt: # 如果Ctrl+c中断,保存checkpoint, print('[INFO] Interrupt manually, try saving checkpoint for now...') saver.save(sess, os.path.join(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir, FLAGS.model_prefix), global_step=epoch) print('[INFO] Last epoch were saved, next time will start from epoch {}.'.format(epoch)) def to_word(predict, vocabs): t = np.cumsum(predict) s = np.sum(predict) # 改代码是作者写的,t的长度为vocab_size + 1, 随机生成一个数然后判断能插入第几个位置 # 个人感觉这使得训练变得毫无意义 # sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1) * s)) # 而实际上输出的预测向量predict,随着训练过程应该逐渐向one-hot编码靠拢,所以应该取argmax函数 sample = np.argmax(predict) if sample > len(vocabs): sample = len(vocabs) - 1 return vocabs[sample] def gen_poem(begin_word): batch_size = 1 print('[INFO] loading corpus from %s' % FLAGS.file_path) poems_vector, word_int_map, vocabularies = process_poems(FLAGS.file_path) input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None]) end_points = rnn_model(model='lstm', input_data=input_data, output_data=None, vocab_size=len( vocabularies), rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64, learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate) saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables()) init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer()) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir) saver.restore(sess, checkpoint) x = np.array([list(map(word_int_map.get, start_token))]) [predict, last_state] = sess.run([end_points['prediction'], end_points['last_state']], feed_dict={input_data: x}) # 如果指定开始的字 if begin_word: word = begin_word #print(type(begin_word.dtype)) # 如果不指定开始的字,就按根据start_token生成第一个字 else: word = to_word(predict, vocabularies) poem = '' while word != end_token: poem += word x = np.zeros((1, 1)) # 比如,指定第一个字为“白”,则x就为x[[36]],即batch_size为1,并且poems_length为1,生成下一个字 x[0, 0] = word_int_map[word] # 传入input_data,此时没有output_data即为生成模式,并且传入初始状态为训练结束的状态 # state_shape为[1,rnn_size] [predict, last_state] = sess.run([end_points['prediction'], end_points['last_state']], feed_dict={input_data: x, end_points['initial_state']: last_state}) # 根据预测结果生成对应的字 word = to_word(predict, vocabularies) return poem def pretty_print_poem(poem): poem_sentences = poem.split('。') for s in poem_sentences: if s != '' and len(s) > 10: print(s + '。') def main(is_train): if is_train: print('[INFO] train tang poem...') run_training() else: print('[INFO] write tang poem...') poem2 = gen_poem(FLAGS.begin_word.encode('utf-8').decode(encoding="utf-8")) pretty_print_poem(poem2) if __name__ == '__main__': tf.app.run()
1. 确定main函数的参数。
2. 开始训练。处理数据,生成batch,构建模型,创建会话
3. 如果没有开头字,随机生成一个字作为开头
4. 生成诗歌。处理数据,构建模型,创建会话(加载已经训练好的模型,生成唐诗)
源代码出现的问题如下:

其实很好改 ,只要将字节转换为字符串即可,修改如下,
poem2 = gen_poem(FLAGS.begin_word.encode('utf-8').decode(encoding="utf-8"))
四、主函数(main.py)
import argparse def parse_args(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Intelligence Poem and Lyric Writer.') help_ = 'you can set this value in terminal --write value can be poem or lyric.' parser.add_argument('-w', '--write', default='poem', choices=['poem', 'lyric'], help=help_) help_ = 'choose to train or generate.' parser.add_argument('--train', dest='train', action='store_true', help=help_) parser.add_argument('--no-train', dest='train', action='store_false', help=help_) parser.set_defaults(train=True) args_ = parser.parse_args() return args_ if __name__ == '__main__': args = parse_args() if args.write == 'poem': from inference import tang_poems if args.train: tang_poems.main(True) else: tang_poems.main(False) elif args.write == 'lyric': from inference import song_lyrics print(args.train) if args.train: song_lyrics.main(True) else: song_lyrics.main(False) else: print('[INFO] write option can only be poem or lyric right now.')
1. 训练唐诗生成模型。直接在pyCharm中Run main
2. 生成唐诗,将main函数中的train参数改成False
parser.set_defaults(train=False)
开头是"白"
白日无人识,清风不可攀。
何时得相见,不觉此时同。
不觉人间事,何时更有诗。
无因不可见,不觉此心违。
不得闲人去,无因得见诗。
当然也可以更换开头字
五、小结
关于歌词的生成将在下一篇中介绍:Tensorflow生成唐诗和歌词(下)
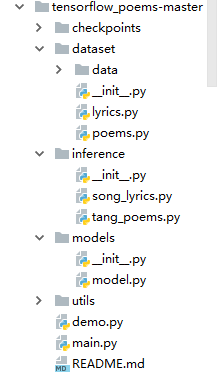
整个工程分为5个文件夹。checkpoints是生成唐诗时自动创建的。
dataset存放数据集和读取诗歌文件(poem.py)。
models存放模型构建(model.py)这是歌词与唐诗的共用代码。
inference存放模型训练,包括训练和生成
最后是主函数,主要是命令行的参数的构建