一、pandas模块
pandas是BSD许可的开源库,为Python编程语言提供了高性能,易于使用的数据结构和数据分析工具。
pandas模块:操作excel/json/sql/ini/csv(配置文件)
使用pandas处理Excel文件需要根据报错内容安装两个插件,pd从Excel中读取的是DataFrame数据类型。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(10)
index = pd.date_range('2019-01-01',periods=6,freq='M')#产生以月为间隔的的时间(periods时间,freq频率相当于间隔的时间单位)
print(index)
columns = ['c1','c2','c3','c4']
print(columns)
val = np.random.randn(6,4)
print(val)
df = pd.DataFrame(index=index,columns=columns,data=val)#索引,列,值
print(df)
#保存文件
df.to_excel('date_c1.xls')
#读取文件
df = pd.read_excel('date_c.xls',index_col=[0])#index_col[0]第零列
print(df)
#接下来我们可以打印出来行和列的索引,然后根据索引打印出对应的行和列的数据然后对它们进行处理
print(df.index)#打印出行索引
print(df.columns)#打印出列索引
print(df.values)#打印出所有的值
#loc[]按照index取值
print(df.loc['2019-01-31'])#取出2019-01-31对应的数据(注意loc是中括号)
print(df.loc['2019-01-31':'2019-05-31'])#取出这两个时间段之间的所有数据
print(df)
二、matplotlib模块
Matplotlib是一个Python 2D绘图库,它以多种硬拷贝格式和跨平台的交互式环境生成出版物质量的图形。Matplotlib可用于Python脚本,Python和IPython Shell,Jupyter笔记本,Web应用程序服务器和四个图形用户界面工具包。
Matplotlib尝试使容易的事情变得容易,使困难的事情变得可能。您只需几行代码就可以生成图表,直方图,功率谱,条形图,误差图,散点图等。
为了简单绘图,该pyplot模块提供了类似于MATLAB的界面,尤其是与IPython结合使用时。对于高级用户,您可以通过面向对象的界面或MATLAB用户熟悉的一组功能来完全控制线型,字体属性,轴属性等。
matplotlib模块:用于画各种统计图
1.条形图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#约定俗成这样写
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
#修改字体
font = FontProperties(fname='C:WindowsFontssimsun.ttc')
plt.style.use('ggplot')#设置背景
clas = ['3班','4班','5班','6班']
stuents = [50,45,55,60]
clas_index = range(len(clas))
plt.bar(clas_index,stuents,color = 'darkblue')#使用bar()函数生成条形图
plt.xlabel('学生',fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('学生人数',fontproperties=font,fontsize=20,fontweight=25)#更改y轴的字体大小
plt.xticks(clas_index,clas,fontproperties=font)#获取或设置x轴的当前刻度位置和标签。
plt.show()#显示绘制的图形
2. 直方图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 约定俗成
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties # 修改字体
font = FontProperties(fname='C:WindowsFontssimsun.ttc')
plt.style.use('ggplot')
x1 = np.random.randn(10000)
x2 = np.random.randn(10000)
fig = plt.figure() # 生成一张画布
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1) # 将画布分成两块,取第一块
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax1.hist(x1, bins=50,color='darkblue')
ax2.hist(x2, bins=50,color='y')
fig.suptitle('两个正态分布',fontproperties=font,fontsize=20)
ax1.set_title('x1的正态分布',fontproperties=font) # 加子标题
ax2.set_title('x2的正态分布',fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
3.折线图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname='C:WindowsFontssimsun.ttc')
plt.style.use('ggplot')
np.random.seed(10)
x1 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x2 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x3 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x4 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
plt.plot(x1,c='r',linestyle='-',marker='o',label='红圆线')
plt.plot(x2,color='y',linestyle='--',marker='*',label='黄虚线')
plt.plot(x3,color = 'b',linestyle='-.',marker='s',label='蓝方线')
plt.plot(x4,color='black',linestyle=':',marker='s',label='黑方线')
plt.legend(loc='best',prop=font)#显示label(标签)
plt.show()
4.散点图+直线图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname='C:WindowsFontssimsun.ttc')
plt.style.use('ggplot')
fig = plt.figure()#创建一块新的画布
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)#将画布分成两块,取第一块
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
x = np.arange(20)#x的范围
y = x**2
x2 = np.arange(20)
y2 = x2
ax1.scatter(x,y,c='r',label='红')
ax1.scatter(x2,y2,c='b',label='蓝')
ax2.plot(x,y)#将y与x作图作为线和/或标记
ax2.plot(x2,y2)
fig.suptitle('两张图',FontProperties=font,fontsize=15)
ax1.set_title('散点图',fontproperties=font)
ax2.set_title('折线图',fontproperties=font)
ax1.legend(prop=font)#Legend(显示图中的标签)
plt.show()
三、numpy

NumPy是使用Python进行科学计算的基本软件包。它包含以下内容:
- 强大的N维数组对象
- 复杂的(广播)功能
- 集成C / C ++和Fortran代码的工具
- 有用的线性代数,傅立叶变换和随机数功能
除了其明显的科学用途外,NumPy还可以用作通用数据的高效多维容器。可以定义任意数据类型。这使NumPy可以无缝,快速地与各种数据库集成。
NumPy已获得BSD许可证的许可,从而可以无限制地进行重用。
numpy:用于数据分析的模块,可进行矩阵的运算,
对两个数组进行相乘的运算
lt1 = [1,2,3]
lt2 = [4,5,6]
lt = []
for i in range(len(lt1)):
lt.append(lt1[i]*lt2[i])
print(lt)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1,2,3])
arr2 = np.array([4,5,6])
print(arr1*arr2)
[4, 10, 18]
[ 4 10 18]数组和列表是不一样的
一维数组
arr3 = np.array([1,2,3])
#二维数组
arr4 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
#三维数组
arr5 = np.array([[[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]],
[[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]]])
print(arr3)#[1 2 3]
print(arr4)
# [[1 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
print(arr5)
[[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]]
这里只讨论二维数组
numpy的属性
T转置,就是矩阵的转置
arr = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
print(arr,'
',arr.T)
# [[1 4]
# [2 5]
# [3 6]
dtype 数组元素的数据类型,numpy数组是属于Python解释器的;int32/float64是属于numpy的
print(arr.dtype)#int32
size数组元素的个数
print(arr.size)#6
ndim 数组的维数
print(arr.ndim)#2
shape数组维度的大小(以元组的形式)
print(arr.shape[0])#2
print(arr.shape[1])#3就是指数组的行数和列数
astype数据类型转换
arr = arr.astype(np.float64)
print(arr)
[[1. 2. 3.]
[4. 5. 6.]]#浮点数据类型小数点后为零所以省略不写
切片numpy数组
lt = [1,23,4]
print(lt[1:])
arr = np.array([[11,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
print(arr[:,0])#数组的切片和列表的切片相似,但是这个是[行,列]也是通过索引取值,这个更类似与坐标,如果要取整行或者整列需要用冒号代替数字,如[:,0]就是取得第零列
#逻辑取值
print(arr[arr>4])#[11 5 6]去除所有大于4的数值构成一维数组
赋值
lt = [1,2,3]
lt[:] = [0,0,0]
print(lt)
arr = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
arr[0,0] = 0
print(arr)
# [[0 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
arr[:,0] = [2,5]
print(arr)
# [[2 2 3]
# [5 5 6]]
#数组的赋值可以通过坐标的方式一个一个的对其元素赋值,也可以整行整列对其元素进行互换
数组的合并:可以左右合并也可以上下合并,前提是对应的行和列要相等
arr1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
arr2 = np.array([[7,8,9],
['a','s','g']])
print(np.hstack((arr1,arr2)))#只能放元组行合并
print(np.vstack((arr1,arr2)))#列合并
print(np.concatenate((arr1,arr2),axis=1))#默认为列合并,0为列合并,1为行合并
# [['1' '2' '3' '7' '8' '9']
# ['4' '5' '6' 'a' 's' 'g']]
# [['1' '2' '3']
# ['4' '5' '6']
# ['7' '8' '9']
# ['a' 's' 'g']]
# [['1' '2' '3' '7' '8' '9']
# ['4' '5' '6' 'a' 's' 'g']]
通过函数创建numpy数组
print(np.ones((2,3)))#创建一个两行三列的元素都为一的矩阵数据类型是float类型
# [[1. 1. 1.]
# [1. 1. 1.]]
print(np.zeros((2,3)))#创建一个元素都为零的矩阵
# [[0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0.]]
print(np.eye(3))#创建一个单位阵这里括号里面不需要元组
# [[1. 0. 0.]
# [0. 1. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1.]]
print(np.linspace(1,100,10))#将0-100平均分成10份
#[ 1. 12. 23. 34. 45. 56. 67. 78. 89. 100.]
print(np.arange(2,10))#构造一个2-9的一维数组
#[2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
print(np.arange(1,20,2))#构造一个2-19的数组,步长为2
#[ 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19]
arr1 = np.zeros((1,12))
print(arr1.reshape((3,4)))#将原来的数组重构形状,reshape((行,列))
# [[0. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0. 0.]]
numpy数组运算
这里的数组运算其实就是矩阵的数学运算遵循所有矩阵的运算规则
arr1 = np.ones((3,4))*4#数乘
print(arr1)
# [[4. 4. 4. 4.]
# [4. 4. 4. 4.]
# [4. 4. 4. 4.]]
#numpy数组还可以进行正余弦等三角函数运算
print(np.sin(arr1))#对所有的元素都会进行运算
#数组的矩阵运算--》点乘
arr1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
arr2 = np.array([[1,2],
[4,5],
[8,7]])
print(np.dot(arr1,arr2))
# [[33 33]
# [72 75]]
#求逆运算
arr3 = np.dot(arr1,arr2)
print(np.linalg.inv(arr3))
# [[ 0.75757576 -0.33333333]
# [-0.72727273 0.33333333]]
#numpy的数学和统计方法
print(np.sum(arr3[0,:]))#对第一行元素求和
# np.random.seed(1)#让随机数暂停
# print(np.random.random((3,4)))#生成一个三行四列的随机数
print(np.random.rand(3,4))#产生均匀分布的随机数
s = np.random.RandomState(1)#让随机数暂停,和seed(1)得到的结果相同
print(s.random((3,4)))
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[4,5,6,7],[7,8,9,10],[11,23,45,67]])
np.random.shuffle(arr)#整行整行的乱序(将每一行都当做一个整体然后在乱序)
print(arr)
# [[7 8 9]
# [4 5 6]
# [1 2 3]]
print(np.random.choice([1,2,3],1))#随机选择一个数
print(np.random.randint(1,100,(3,4)))#对1-100内的整数进行随机,生成一个三行四列的矩阵
实例分析
按照要求对电影数据绘图
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
解决中文乱码配置
#### mac 系统需要配置下面所有的
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname='/Users/shangzekai/Downloads/font/simhei.ttf')
font1=FontProperties(fname='/Users/shangzekai/Downloads/font/simhei.ttf')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']#windows系统只需要这两行配置
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
movies = pd.read_csv('./douban_movie.csv')
movies.head()
| 名字 | 投票人数 | 类型 | 产地 | 上映时间 | 时长 | 年代 | 评分 | 首映地点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 肖申克的救赎 | 692795.0 | 剧情/犯罪 | 美国 | 1994-09-10 00:00:00 | 142.0 | 1994 | 9.6 | 多伦多电影节 |
| 1 | 控方证人 | 42995.0 | 剧情/悬疑/犯罪 | 美国 | 1957-12-17 00:00:00 | 116.0 | 1957 | 9.5 | 美国 |
| 2 | 美丽人生 | 327855.0 | 剧情/喜剧/爱情 | 意大利 | 1997-12-20 00:00:00 | 116.0 | 1997 | 9.5 | 意大利 |
| 3 | 阿甘正传 | 580897.0 | 剧情/爱情 | 美国 | 1994-06-23 00:00:00 | 142.0 | 1994 | 9.4 | 洛杉矶首映 |
| 4 | 霸王别姬 | 478523.0 | 剧情/爱情/同性 | 中国大陆 | 1993-01-01 00:00:00 | 171.0 | 1993 | 9.4 | 香港 |
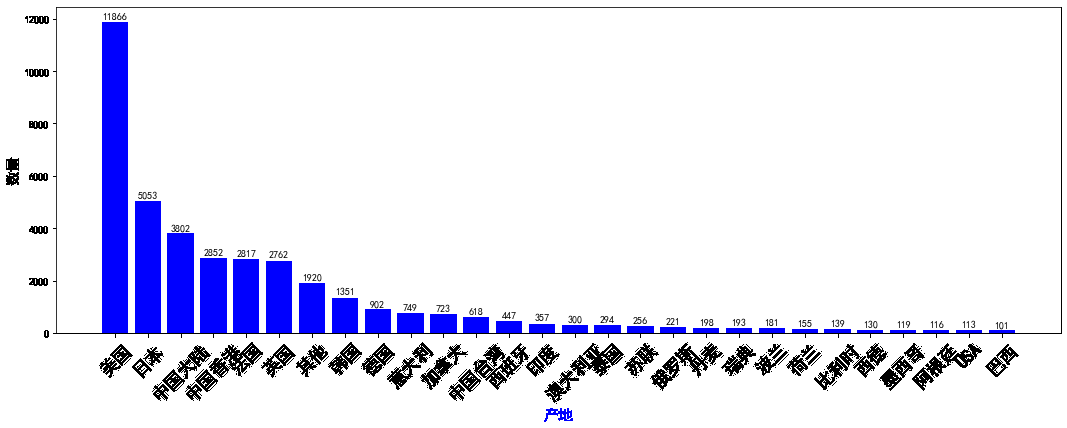
res = movies.groupby('产地').size().sort_values(ascending=False)
#条形图的绘制
x = res.index
y = res.values
plt.figure(figsize=(18,6))#画布大小
plt.xlabel('产地',size=15,color='blue')
plt.ylabel('数量',size=15)
plt.xticks(size=18,rotation=45)#对坐标轴上的刻度进行设置,rotation设置字体的角度
for a,b in zip(x,y):
plt.text(a,b+100,b,horizontalalignment='center')#将值写在坐标轴上点(a,b+100),horizontalalignment也可简写成ha,将数字居中
plt.bar(x,y,color="blue")#color可以设置树状图的颜色
# plt.savefig('/a.png')#保存图片,必须写在show前面
plt.show()
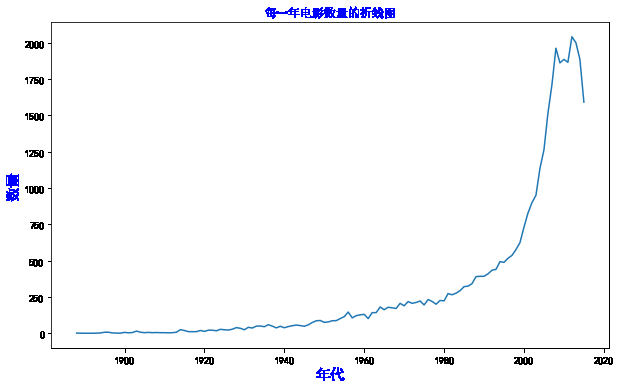
统计每一年电影的数量的折线图
res = movies.groupby('年代').size().sort_index()[:-3]
#折线图的绘制
x = res.index
y = res.values
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.title('每一年电影数量的折线图',color='blue')
plt.xlabel('年代',color='blue',size=15)
plt.ylabel('数量',color='blue',size=15)
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
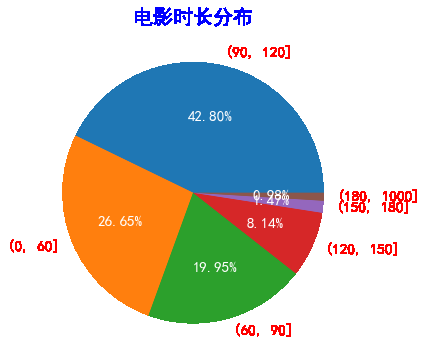
根据电影的时长分布绘制饼状图
movie_time = movies['时长']
movie_time
0 142.0
1 116.0
2 116.0
3 142.0
4 171.0
...
38730 58.0
38731 98.0
38732 91.0
38733 78.0
38734 97.0
Name: 时长, Length: 38735, dtype: float64
movie_time.sort_values(ascending=False)
19690 11500.0
38727 9200.0
36522 958.0
26910 934.0
30525 929.0
...
15241 1.0
22021 1.0
5582 1.0
26875 1.0
14153 1.0
Name: 时长, Length: 38735, dtype: float64
res_time = pd.cut(movie_time,(0,60,90,120,150,180,1000)).value_counts()
res_time
(90, 120] 16578
(0, 60] 10324
(60, 90] 7727
(120, 150] 3154
(150, 180] 571
(180, 1000] 379
Name: 时长, dtype: int64
#饼状图的绘制
x = res_time.index
y = res_time.values
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.title('电影时长分布',color='blue',size=20)
patchs, l_text, p_text = plt.pie(y,labels=x, autopct='%.2f%%')
#patchs是补丁,autopct是百分比的精确度
for l in l_text:#l_text是一个label的列表
l.set_size(15)
l.set_color('red')
for p in p_text:#p_text:就是百分比值
p.set_size(15)
p.set_color('white')
plt.show()