一.为什么要使用PySide?
PySide由Qt的官方团队--Nokia Qt进行维护,集成了Qt和Python的优势。一个PySide程序员只需要使用简单的Python语言就能够发挥Qt的所有功能。PySide拥有LGPL2.1版授权许可,允许进行免费/开源软件和私有商业软件的开发。Matplotlib,PhotoGrabber,Wing IDE,Lucas Chess,Fminer等应用程序均使用PySide开发,这证明了PySide在软件行业的广泛普及和使用。另外,PySide Mobility工程还允许python访问Qt Mobile API,这对你进行移动开发是很有帮助的。现在让我们开始学习吧!
二.从创建窗口入手
一个简单的PySide程序示例:
1 #coding:utf-8 2 # 导入必须模块 3 import sys 4 from PySide.QtCore import Qt 5 from PySide.QtGui import QApplication, QLabel 6 7 # 主函数 8 if __name__ == '__main__': 9 # 创建main application 10 myApp = QApplication(sys.argv) 11 # 创建Label并设置它的属性 12 appLabel = QLabel() 13 appLabel.setText("Hello, World!!! Look at my first app using PySide") 14 appLabel.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter) 15 appLabel.setWindowTitle("My First Application") 16 appLabel.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 175) 17 # 显示这个Label 18 appLabel.show() 19 # 运行main application 20 myApp.exec_() 21 sys.exit()
运行后的效果如图:
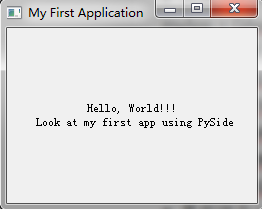
上面程序实际上就是在一个标题为“My First Application”的主窗体上添加一个label控件,在上面显示“Hello, World!!! Look at my first app using PySide”。通过上面的例子我们可以看到在主程序中,我们创建了一个QApplication类的实例。QApplication类管理图形用户界面应用程序的控制流和主要设置。它包含主事件循环,在其中来自窗口系统和其它资源的所有事件被处理和调度。它也处理应用程序的初始化和结束,并且提供对话管理。它也处理绝大多数系统范围和应用程序范围的设置。
对于任何一个使用Qt的图形用户界面应用程序,都正好存在一个QApplication对象,而不论这个应用程序在同一时间内是不是有一个或多个窗口。
2.1 创建应用图标
应用程序图标是在应用程序左上角以及任务栏显示的,强调应用程序设计目的的图片,一般是72 X 72大小,PNG格式。
1 #coding:utf-8 2 import sys 3 import time 4 from PySide.QtGui import QApplication, QWidget, QIcon 5 6 #QWidget是所有用户界面类的基类 7 class SampleWindow(QWidget): 8 #主窗口类 9 #构造函数 10 def __init__(self): 11 QWidget.__init__(self) 12 self.setWindowTitle("Sample Window") 13 #从屏幕上(300,300)位置开始(即为最左上角的点),显示一个200*150的界面(宽200,高150) 14 self.setGeometry(300, 300, 400, 350) 15 16 def setIcon(self): 17 #设置icon 18 appIcon = QIcon("pyside_logo.png") 19 self.setWindowIcon(appIcon) 20 21 if __name__ == "__main__": 22 try: 23 myApp = QApplication(sys.argv) 24 myWindow = SampleWindow() 25 myWindow.setIcon() 26 myWindow.show() 27 myApp.exec_() 28 sys.exit(0) 29 except NameError: 30 print("NameError:", sys.exc_info()[1]) 31 except SystemExit: 32 print("Closing Window...") 33 except Exception: 34 print(sys.exc_info()[1])
在上面的代码中我们在类中定义了一个函数来设置图标,然后在main函数中调用。从下面的运行结果可知,图标已经设置成功。
PySide.QtGui.QIcon类提供了一组函数可以对icon设置不同的大小和模式。QIcon包括以下几种构造函数:
QIcon()
QIcon(engine)
QIcon(other)
QIcon(pixmap)
QIcon(filename)
第一种构造函数构造了一个空图标。第二种形式需要PySide.QtGui.QIconEngineas作为参数。这个类为QIcon渲染器提供了一个抽象基类。每个图标都有一个对应的引擎,负责与请求的大小,绘制图标模式,状态。第三形式简单的从其它QIcon对象复制过来,这是最快的一种方法。第四种形式是从PySide.QtGui.QPixmap类构造图标。这个类是一个离屏图像表示,可以用作涂料设备。一个使用PySide.QtGui pixmapcan容易显示在屏幕上。类、PySide.QtGui QLabelor两个按钮中的一个。QPushButtonor PySide.QtGui.QToolButton。QLabelhas象素映射属性而QPushButton / QToolButtonhas图标属性。最后一种是通过给定的文件名构造一个图标。如果文件名包含相对路径,那它一定是相对于运行时的工作路径。
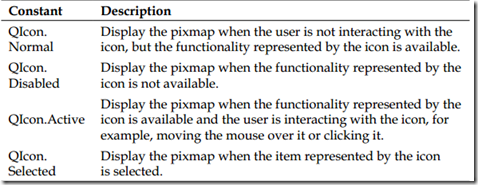
QIcon类中的pixmap函数提供了各种模式来展现icon图标。pixmap函数:PySide.QtGui.QIcon.pixmap(width, height[, mode=Normal[, state=Off]]),前两个参数表示了icon的大小,mode参数有下列四个取值可选择。
state参数表示哪个pixmap将被使用。
下面的函数是通过设置pixmap函数的mode参数来展现icon的各种模式的例子。我们将它添加到SampleWindow类中。
1 def setIconModes(self): 2 myIcon1 = QIcon('pyside_logo.png') 3 myLabel1 = QLabel('sample', self) 4 #图标可用,并且与用户有交互 5 pixmap1 = myIcon1.pixmap(50, 50, QIcon.Active, QIcon.On) 6 myLabel1.setPixmap(pixmap1) 7 myIcon2 = QIcon('pyside_logo.png') 8 myLabel2 = QLabel('sample', self) 9 #图标不可用 10 pixmap2 = myIcon2.pixmap(50, 50, QIcon.Disabled, QIcon.Off) 11 myLabel2.setPixmap(pixmap2) 12 myLabel2.move(50, 0) 13 myIcon3 = QIcon('pyside_logo.png') 14 myLabel3 = QLabel('sample', self) 15 #图标被选中 16 pixmap3 = myIcon3.pixmap(50, 50, QIcon.Selected, QIcon.On) 17 myLabel3.setPixmap(pixmap3) 18 myLabel3.move(100, 0)
然后在main函数中添加调用代码:
myWindow.setIconModes()
运行得到:
2.2 显示提示信息
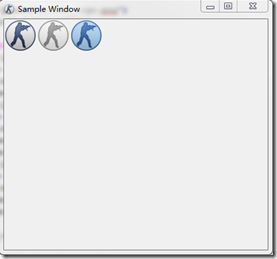
使用PySide.QtGui.QToolTip类来显示提示信息。QToolTip类可用设置提示信息的字体、颜色和富文本展示等等。如字体设置:
QToolTip.setFont(QFont("Decorative", 8, QFont.Bold))
将提示信息添加到控件:
myLabel1.setToolTip('Active Icon')
我们对之前的代码作以下修改:
1 def __init__(self): 2 QWidget.__init__(self) 3 self.setWindowTitle("Icon Sample") 4 self.setGeometry(300, 300, 200, 150) 5 QToolTip.setFont(QFont("Decorative", 8, QFont.Bold)) 6 self.setToolTip('Our Main Window') 7 ... 8 def setIconModes(self): 9 ... 10 myLabel1.setPixmap(pixmap1) 11 myLabel1.setToolTip('Active Icon') 12 ... 13 myLabel2.move(50, 0) 14 myLabel2.setToolTip('Disabled Icon') 15 ... 16 myLabel3.move(100, 0) 17 myLabel3.setToolTip('Selected Icon')
然后运行,将鼠标放到图标上就可以看到提示信息了。
2.3 增加按钮
使用最多的按钮是下压按钮或命令按钮,典型的下压按钮包括OK, Apply, Cancel, Close, Yes, No和Help几种。下压按钮在点击鼠标,按快捷键、空格键等事件时就会发出一个信号,与击键事件相关联的控件在接收到信号时就会执行,这在Qt中通常被称为槽。
除了下压按钮外,还包括QToolButton, QRadioButton, QCommandLinkButton和QCheckBox等其它按钮。
QPushButton有三种实例化方式,它包含3个不同特征的构造函数:
QPushButton(parent=None) QPushButton(text, [parent=None]) QPushButton(icon, text, [parent=None])
parent参数可以是任何控件,text参数可以是任何的字符串,icon是一个有效的QIcon对象。
在下面的例子中我们增加了一个按钮,用来实现关闭应用的功能:
def setButton(self): """增加退出按钮""" myButton = QPushButton("Quit",self) myButton.move(50, 100) myButton.clicked.connect(myApp.quit)
在上例中,用户可能会因为失误点击了按钮而造成程序退出。所以我们在用户点击退出按钮后必须要有用户的确认才能退出程序,QMessageBox便能实现这个功能。我们创建以下函数:
1 def quitApp(self): 2 """从用户获取确认消息""" 3 userInfo = QMessageBox.question(self, "Confirmation","This will quit the application. Do you want to Continue?", QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No) 4 if userInfo == QMessageBox.Yes: 5 myApp.quit() 6 if userInfo == QMessageBox.No: 7 pass
修改connect函数参数:
myButton.clicked.connect(myApp.quitApp)
在main函数中调用show函数之前添加以下语句:
myWindow.setButton()
运行后如图所示:
2.4 窗口居中
在PySide中没有现成的方法实现窗口居中显示,需要自己实现。首先需要获取窗口的大小和位置,然后再获取屏幕的中心位置,最后把窗口移到屏幕中间。
1 def center(self): 2 3 """将应用居中""" 4 5 qRect = self.frameGeometry() 6 7 centerPoint = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center() 8 9 qRect.moveCenter(centerPoint) 10 11 self.move(qRect.topLeft())
frameGeometry()函数返回一个PySide.QtCore.QRect对象,包含了窗口的高度、宽度、顶点和左边位置。QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()返回屏幕的中心位置,接下来的两行代码实现将窗口移到屏幕中心的功能,然后在myWindow.show()之前调用这个函数。
2.5 关于对话框
关于对话框是用来显示应用程序的开发者、版权和版本信息的。QMessageBox类提供了一个内置函数来实现这个功能。
PySide.QtGui.QMessageBox.about(parent, title, text)
下面我们在以前的代码中添加一个关于对话框:
1 def setAboutButton(self): 2 """设置about按钮""" 3 self.aboutButton = QPushButton("About", self) 4 self.aboutButton.move(150, 100) 5 self.aboutButton.clicked.connect(self.showAbout) 6 7 def showAbout(self): 8 """显示About窗口""" 9 QMessageBox.about(self.aboutButton, "About PySide","First PySide Program by gh0st.")
下图为运行结果:

QMessage类还提供了另外一个函数,PySide.QtGui.QMessageBox.aboutQt(parent[, title=""]),该函数用于显示开发者使用的Qt版本信息。
2.6 定时器
在Qt中使用定时器需要用到PySide.QtCore.QTimer和PySide.QtCore.QDateTime类,开启和关闭计时器的函数为QTimer.start(1000)和QTimer.stop(),计时的单位为ms。PySide.QtCore.QDateTime类提供了日历日期和时钟时间函数,是PySide.QtCore.QDate和PySide.QtCore.QTime类的组合。以下为一个数字时钟示例代码:
1 #coding:utf-8 2 3 import sys 4 from PySide.QtCore import QDateTime, QTimer, SIGNAL 5 from PySide.QtGui import QApplication, QWidget, QLCDNumber 6 7 class MyTimer(QWidget): 8 """计时器的主窗口类""" 9 def __init__(self): 10 QWidget.__init__(self) 11 self.setWindowTitle("My Digital Clock") 12 timer = QTimer(self) 13 self.connect(timer, SIGNAL("timeout()"), self.updtTime) 14 self.myTimeDisplay = QLCDNumber(self) 15 self.myTimeDisplay.setSegmentStyle(QLCDNumber.Filled) 16 self.myTimeDisplay.setDigitCount(8) 17 self.myTimeDisplay.resize(500, 150) 18 timer.start(1000) 19 20 def updtTime(self): 21 """更新当前时间""" 22 currentTime = QDateTime.currentDateTime().toString('hh:mm:ss') 23 self.myTimeDisplay.display(currentTime) 24 25 if __name__ == "__main__": 26 try: 27 myApp = QApplication(sys.argv) 28 myWindow = MyTimer() 29 myWindow.show() 30 myApp.exec_() 31 sys.exit(0) 32 except NameError: 33 print("Name Error", sys.exe_info()[1]) 34 except SystemExit: 35 print("Closing Window...") 36 except Exception: 37 print(sys.exe_info()[1])
2.7 Windows样式
未完待续,觉得好,点个赞!