牛客小白月赛30题解(部分)
A.黑白边
考点:并查集、最小生成树
根据题可以看出,就是一道最小生成树的裸模板题
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5+10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m;
int p[N];
struct Edge
{
int a, b, w;
bool operator < (const Edge &t) const
{
return w < t.w;
}
}edges[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int kruskal()
{
sort(edges, edges + m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
int res = 0, cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a = edges[i].a, b = edges[i].b, c = edges[i].w;
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if(a != b)
{
res += c;
cnt++;
p[a] = b;
}
}
if(cnt < n-1) return INF;
else return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) scanf("%d%d%d", &edges[i].a, &edges[i].b, &edges[i].w);
int t = kruskal();
if(t == INF) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}
B.最好的宝石
待补。。。。。。
C.滑板上楼梯
C.滑板上楼梯
考点:贪心、数学
根据题意:要使次数最少,就要尽可能多走3步;3+1为一组,除一下,然后特判最后剩余步数是否为3即可
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long n;
cin >> n;
cout << n / 4 * 2 + ((n % 4) == 3 ? 1 : n % 4) << endl;
return 0;
}
D.GCD
考点:筛法求质数
分析题目可得:如果我们把1~n所有的质数和1全部放入子集,则任意两个数的 gcd(x, y)均等于1
故要使题意成立,需满足两个条件:
1、1~n必须有合数
2、满足1的条件下,k的最小值为 质数+2(包含1和1个合数)
解法:求出1~n所有的质数cnt,如果不等于n-1,则k = cnt+2;否则不存在输出-1
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int cnt, primes[N];
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)
{
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if(!st[i]) primes[cnt++] = i;
for(int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j++)
{
st[primes[j] * i] = true;
if(i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
get_primes(n);
if(cnt + 1 == n) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << cnt + 2 << endl;
return 0;
}
E.牛牛的加法
考点:高精度加法(大数加法)、模拟
高精度加法模板题
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> A, B;
vector<int> add(vector<int> A, vector<int> B)
{
vector<int> C;
for(int i = 0; i < A.size() || i < B.size(); i++)
{
int t = 0;
if(i < A.size()) t += A[i];
if(i < B.size()) t += B[i];
C.push_back(t % 10);
}
return C;
}
int main()
{
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
for(int i = a.size() - 1; ~i; i--) A.push_back(a[i] - '0');
for(int i = b.size() - 1; ~i; i--) B.push_back(b[i] - '0');
vector<int> C = add(A, B);
while(C.size() > 1 && C.back() == 0) C.pop_back();
for(int i = C.size() - 1; ~i; i--) cout << C[i];
return 0;
}
F.石子合并
考点:贪心
贪心,每次选最大的和其相邻的某一个,记录总和,最后加上max*(n-2)即可
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
ll ans, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ll a;
scanf("%lld", &a);
ans += a;
m = max(m, a);
}
cout << ans + m * (n - 2) << endl;
return 0;
}
G.滑板比赛
待补。。。。。。
H.第k小
H.第k小
考点:小根堆(优先队列)
直接用STL的优先队列priority_queue<int> q;来维护k个数即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m, k;
priority_queue<int> q;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
q.push(a);
}
while(m--)
{
int i;
cin >> i;
//输入一个数,直接放入优先队列
if(i == 1)
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
q.push(x);
}
else
{
//如果优先队列的大小小于k个,则输出-1
//如果大于k个,就把优先队列开头的数弹出,直到大小为k,输出队头即可
if(q.size() < k) printf("-1
");
else
{
while(q.size() > k) q.pop();
printf("%d
", q.top());
}
}
}
return 0;
}
I.区间异或
待补。。。。。。
J.小游戏
考点:动态规划
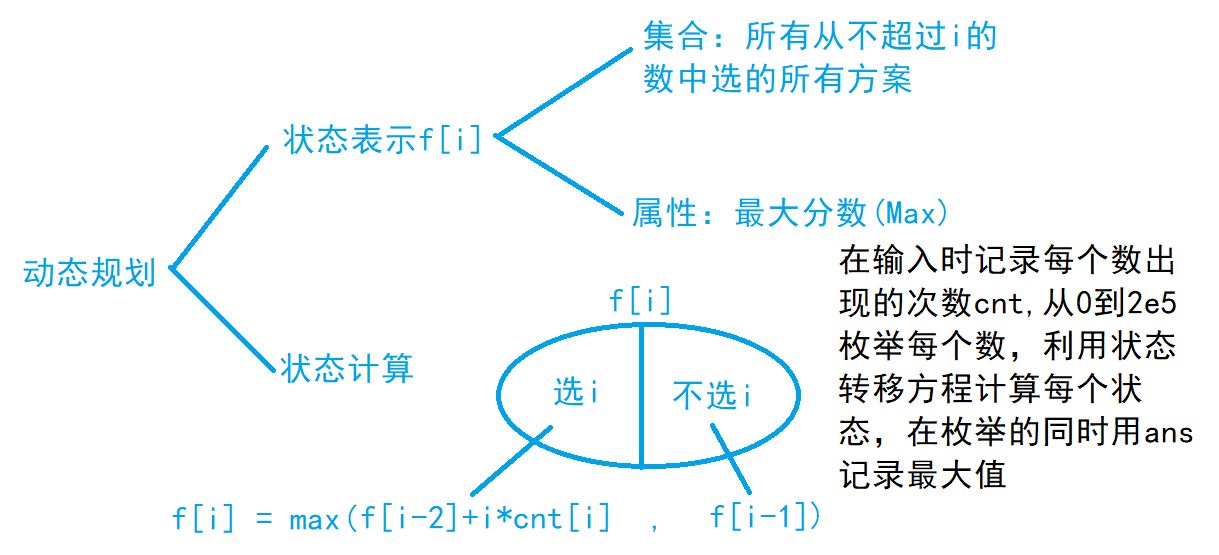
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5+10;
int n, cnt[N];
long long f[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
cnt[a]++;
}
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= 2e5; i++)
{
f[i] = max(f[max(0,i - 1)], f[max(0, i - 2)] + i * cnt[i]);
ans = max(ans, f[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}