Generic Programming and Graph
链接:http://ecee.colorado.edu/~siek/boostcon2010bgl.pdf
原文中还介绍了一点boost graph library相关的内容。由于对于boost graph library的介绍比较少。这里仅覆盖Generic Programming和Generic Graph Demo。
Introduction to Generic Programming
Why using generic programming
如果用基于面向对象的方式设计算法和数据结构,那么类似如下:
struct vector {
void merge(const vector& a, const vector& b) { ... }
void reverse() { .. }
void sort() { ... }
};
struct list {
void merge(const list& a, const list& b) { ... }
void reverse() { .. }
void sort() { ... }
}
使用上面这种方式进行实现的话,如果有M种算法,N种数据结构,那么就需要写O(MxN)的代码量。
如果采用泛型编程呢?
template<class InputIter1, class InputIter2, class OutputIter>
OutputIter merge(InputIter1 first1, InputIter last1, InputIter2 first2, InputIter2 last2, OutputIter result);
template<class BidirectionalIter>
void reverse(BidirectionalIter first, BidirectionalIter last);
template<class RandomAccessIter>
void sort(RandomAccessIter first, RandomAccessIter last);
struct vector {
struct iterator;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
};
struct list {
struct iterator;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
};
这样只要实现O(M+N)的代码量。
Type Requirements and Concepts
那么上面实现的模板函数可以匹配哪些类型呢?
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
sort(v.begin(), v.end()); // ok
list<int> l;
sort(l.begin(), l.end()); // error!
}
具体错误示例如下:
stl algo.h: In function ’void std::sort( _RandomAccessIterator,
_RandomAccessIterator)
[with _RandomAccessIterator = std::_List_iterator<int>]’:
sortterror.cpp:6: instantiated from here
stl algo.h:2570: error: no match for ’operator--’ in ’last - first’
为了说明模板会有特定的需求,这里引出了“Concepts”的概念:Concepts就是各种需求的集合。再引入一个概念,叫做“Models”,用来表示基于Concepts的具体实现。这样,对于算法:
template<class Iter>
void sort(Iter first, Iter last);
类型的需求为:
- Iter需要是Random Access Iterator;
- Iter类型的值,支持Less Than Comparable
这里就提出了两个概念:随机访问迭代器,支持自增,自减,支持任意步长的前后移动,和less比较。
而在通常情况下一个概念会包括以下类型的需求:
- 合法表达式;
- 相关联的类型,这些类型的需求;
- 精简;??
- 对操作提供有效保证;
- 操作相关的语义需求(前置,后置条件,不变性等);
关联类型举例
inputIterator概念,含有value_type, difference_type两个关联类型;支持的有效操作为*i,++i。
对应一个model如下:
template<class T> struct list_iterator {
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
T& operator*() const { return current->data; }
list_iterator& operator++() { current = current->next; return *this; }
}
在算法实现中对关联类型的访问:
template<typename InputIterator1, typename InputIterator2>
void iter_swap(InputIterator1 a, InputIterator2 b)
{
typedef typename InputIterator1::value_type T;
T tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
但是这样简单的实现会有一个问题,如果类型是内置类型,如指针,那么就没法使用这个算法了,为了解决这个问题,就引入了traits class。
// Default version for class type
template <class Iter> struct iterator_traits {
typedef typename Iter::value_type value_type;
typedef typename Iter::difference_type difference_type;
}
// Partial specialization for pointer types
template <class T> struct iterator_traits<T*> {
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
}
template<typename InputIterator1, typename InputIterator2>
void iter_swap(InputIterator1 a, InputIterator2 b)
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<InputIterator1>::value_type T;
T tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp;
}
小结
- 使用泛型编程,在设计算法和数据结构的时候,可以将代码量从O(MxN)减少到O(M+N);
- 创建概念,用来描述和组织模板对于类型的需求;
- 创建traits 类,用来访问概念中涉及到的关联的类型(associated types);
- 满足概念具体需求的类型,被称为model;
- 最小化模板上的需求以最大限度地提高重用的可能性;
Graphs
下面会以图算法的实现为例,将泛型编程应用起来。
问题描述以及伪代码实现
问题:如何找到迷宫的出路?
解决方案:深度优先查找,对走过的路都做上标记。
伪代码:
DFS(G, u)
if u is the exit
return success
mark[u] <- BLACK
for ecah v in Adjacent(u)
if mark[v] == WHITE
if DFS(G, v) == success
return success
return failure
如何实现generic深度优先查找算法
需求
- 需要能够对点的值进行访问;
- 需要能够访问给定顶点的邻接点;
- 需要能够对点的颜色进行设置(黑色或白色);(对于颜色可以进一步修正,没有访问过的用白色,访问过但不知道走得通走不通,用灰色,访问过走不通的用黑色,这样有个好处,当遍历的时候如果遇到灰色,那么就说明走了一圈,回到原处了)
- 需要一种方法在搜索期间执行自定义操作,例如检查是否成功和终止;
针对这些需求可以引申出不同的概念。
概念: 邻接图(Adjacency Graph)
由需求:需要能够访问给定顶点的邻接点引出。
定义接口用来定义访问图中邻接顶点。
相关联的类型有(通过graph_traits访问):
- vertex_descriptor
- adjacency_iterator:必须是多通输入迭代器?,他的value_type必须是vertex_descriptor
有效表达式有:
- adjacent_vertices(v, g) : pair<adjacency_iterator>, 其中v是graph,g是vertex_descriptor
概念:属性map(Property Map)
由需求:需要能够对点的颜色进行设置(黑色或白色)引出。
有两个子概念:
- Readable Property Map。
- 相关的类型有(通过property_traits访问):
- key_type
- value_type
- reference
- 相关的表达式有:
- get(pmap, k) : reference
- 相关的类型有(通过property_traits访问):
- Writable Property Map.
- 相关类型和Readable Property Map一致;
- 相关表达式:
- put(pmap, k, v) : void
概念:DFS Visitor
由需求:需要一种方法在搜索期间执行自定义操作,例如检查是否成功和终止;引出。
相关的表达式为:
- vis.initialize_vertex(v,g) : 开始search前初始化;即,在初始化需要执行的操作;
- vis.discover_vertex(v,g) : 第一次选中一个顶点;即,找到第一个点的时候需要执行的操作
- vis.examine_edge(e,g) : 在发现源顶点之后,但在目标之前;即,从第源点到目标点行进的过程中需要执行的操作;
- vis.tree_edge(e, g): 当edge添加到DFS-tree;即,当要继续search的时候需要执行的操作;
- vis.back_edge(e,g): 当目标顶点是DFS树中源顶点的祖先时;即,当发现下一个顶点是之前经过的顶点你的时候,需要执行的操作;
- vis.forward_or_cross_edge(e, g): 当源和目标不是彼此的后代;对于遇到之前走不通的顶点的时候需要执行的操作;
上面的各种表达式,可以理解成不同的时期,需要执行的特定的操作。各个时期的示意图如下:
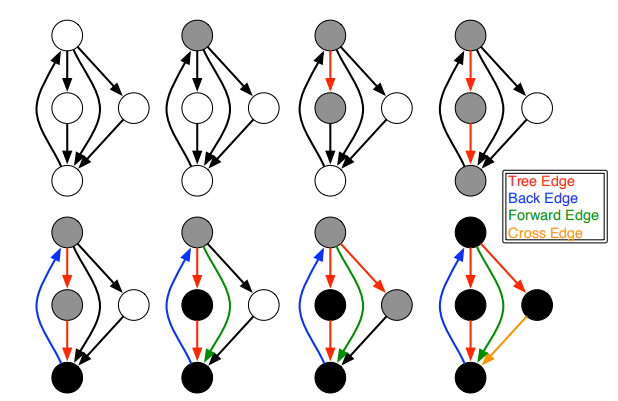
概念:关联图
定义用来访问图中一个顶点的出边。
相关的类型有(通过graph_traits访问):
- vertex_descriptor:
- edge_descriptor
- out_edge_iterator:value_type必须是edge_descriptor
相关的操作有:
- out_edges(v,g) : pair<out_edge_iterator>
- source(e,g): vertex_descriptor
- target(e,g): vertex_descriptor
模板函数实现
// Graph 是满足Incidence Graph概念的model
// Map 是Readable和Writable Property Map的model,
// 其key_type是Graph的vertex_descriptor, value_type是bool
// Visitor是概念DFS Visitor的model。Visitor的vertex和edge的类型和Graph一致
template<class Graph, class Map, class Visitor>
void depth_first_visit(const Graph& G,
typename graph_traits<Graph>::vertex_descriptor u,
Map color,
Visitor vis)
{
typedef typename graph_traits<Graph>::vertex_descriptor vertex;
typedef typename graph_traits<Graph>::edge_descriptor edge;
put(color, u, gray); vis.discover_vertex(u,G);
for (edge e : out_edges(u, G)) {
vertex v = target(e, G); vis.examine_edge(e, G);
if (get(color, v) == white) {
vis.tree_edge(e, G);
depth_first_visit(G, v, color, vis);
} else if (get(color, v) == gray) vis.back_edge(e, G);
else vis.forward_or_cross_edge(e, G);
}
put(color, u, black);
}