函数式组件比较特殊,也非常的灵活,它可以根据传入该组件的内容动态的渲染成任意想要的节点,在一些比较复杂的高级组件里用到,比如Vue-router里的<router-view>组件就是一个函数式组件。
因为函数式组件只是函数,所以渲染开销也低很多,当需要做这些时,函数式组件非常有用:
程序化地在多个组件中选择一个来代为渲染。
在将children、props、data传递给子组件之前操作它们。
函数式组件的定义和普通组件类似,也是一个对象,不过而且为了区分普通的组件,定义函数式组件需要指定一个属性,名为functional,值为true,另外需要自定义一个render函数,该render函数可以带两个参数,分别如下:
createElement 等于全局的createElement函数,用于创建VNode
context 一个对象,组件需要的一切都是通过context参数传递
context对象可以包含如下属性:
parent ;父组件的引用
props ;提供所有prop的对象,经过验证了
children ;VNode 子节点的数组
slots ;一个函数,返回了包含所有插槽的对象
scopedSlots ;个暴露传入的作用域插槽的对象。也以函数形式暴露普通插槽。
data ;传递给组件的整个数据对象,作为 createElement 的第二个参数传入组件
listeners ;组件的自定义事件
injections ;如果使用了 inject 选项,则该对象包含了应当被注入的属性。
例如:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.5.16/dist/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <smart-list :items=items></smart-list> </div> <script> Vue.config.productionTip=false; Vue.config.devtools=false; Vue.component('smart-list', { functional: true, //指定这是一个函数式组件 render: function (createElement, context) { function appropriateListComponent (){ if (context.props.items.length==0){ //当父组件传来的items元素为空时渲染这个 return {template:"<div>Enpty item</div>"} } return 'ul' } return createElement(appropriateListComponent(),Array.apply(null,{length:context.props.items.length}).map(function(val,index){ return createElement('li',context.props.items[index].name) })) }, props: { items: {type: Array,required: true}, isOrdered: Boolean } }); var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data:{ items:[{name:'a',id:0},{name:'b',id:1},{name:'c',id:2}] } }) </script> </body> </html>
输出如下:

对应的DOM树如下:

如果items.item为空数组,则会渲染成:

这是在因为我们再render内做了判断,返回了该值
源码分析
组件在Vue实例化时会先执行createComponent()函数,在该函数内执行extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag)从组件的基础构造器上获取到props信息后就会判断options.functional是否为true,如果为true则执行createFunctionalComponent函数,如下:
function createComponent ( //第4181行 创建组件节点 Ctor, data, context, children, tag ) { /**/ var propsData = extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag); //对props做处理 // functional component if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) { //如果options.functional为true,即这是对函数组件 return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children) //则调用createFunctionalComponent()创建函数式组件 } /*略*/
例子执行到这里对应的propsData如下:
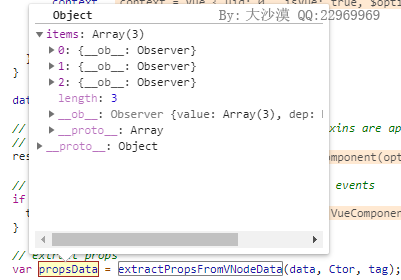
也就是获取到了组件上传入的props,然后执行createFunctionalComponent函数,并将结果返回,该函数如下:
function createFunctionalComponent ( //第4026行 函数式组件的实现 Ctor, //Ctro:组件的构造对象(Vue.extend()里的那个Sub函数) propsData, //propsData:父组件传递过来的数据(还未验证) data, //data:组件的数据 contextVm, //contextVm:Vue实例 children //children:引用该组件时定义的子节点 ) { var options = Ctor.options; var props = {}; var propOptions = options.props; if (isDef(propOptions)) { //如果propOptions非空(父组件向当前组件传入了信息) for (var key in propOptions) { //遍历propOptions props[key] = validateProp(key, propOptions, propsData || emptyObject); //调用validateProp()依次进行检验 } } else { if (isDef(data.attrs)) { mergeProps(props, data.attrs); } if (isDef(data.props)) { mergeProps(props, data.props); } } var renderContext = new FunctionalRenderContext( //创建一个函数的上下文 data, props, children, contextVm, Ctor ); var vnode = options.render.call(null, renderContext._c, renderContext); //执行render函数,参数1为createElement,参数2为renderContext,也就是我们在组件内定义的render函数 if (vnode instanceof VNode) { return cloneAndMarkFunctionalResult(vnode, data, renderContext.parent, options) } else if (Array.isArray(vnode)) { var vnodes = normalizeChildren(vnode) || []; var res = new Array(vnodes.length); for (var i = 0; i < vnodes.length; i++) { res[i] = cloneAndMarkFunctionalResult(vnodes[i], data, renderContext.parent, options); } return res } }
FunctionalRenderContext就是一个函数对应,new的时候会给当前对象设置一些data、props之类的属性,如下:
function FunctionalRenderContext ( //第3976行 创建rendrer函数的上下文 parent:调用当前组件的父组件实例 data, props, children, parent, Ctor ) { var options = Ctor.options; // ensure the createElement function in functional components // gets a unique context - this is necessary for correct named slot check var contextVm; if (hasOwn(parent, '_uid')) { //如果父Vue含有_uid属性(是个Vue实例) contextVm = Object.create(parent); //以parent为原型,创建一个实例,保存到contextVm里面 // $flow-disable-line contextVm._original = parent; } else { // the context vm passed in is a functional context as well. // in this case we want to make sure we are able to get a hold to the // real context instance. contextVm = parent; // $flow-disable-line parent = parent._original; } var isCompiled = isTrue(options._compiled); var needNormalization = !isCompiled; this.data = data; //data this.props = props; //props this.children = children; //children this.parent = parent; //parent,也就是引用当前函数组件的Vue实例 this.listeners = data.on || emptyObject; //自定义事件 this.injections = resolveInject(options.inject, parent); this.slots = function () { return resolveSlots(children, parent); }; // support for compiled functional template if (isCompiled) { // exposing $options for renderStatic() this.$options = options; // pre-resolve slots for renderSlot() this.$slots = this.slots(); this.$scopedSlots = data.scopedSlots || emptyObject; } if (options._scopeId) { this._c = function (a, b, c, d) { var vnode = createElement(contextVm, a, b, c, d, needNormalization); if (vnode && !Array.isArray(vnode)) { vnode.fnScopeId = options._scopeId; vnode.fnContext = parent; } return vnode }; } else { this._c = function (a, b, c, d) { return createElement(contextVm, a, b, c, d, needNormalization); }; //初始化一个_c函数,等于全局的createElement函数 } }
对于例子来说执行到这里FunctionalRenderContext返回的对象如下:

回到createFunctionalComponent最后会执行我们的render函数,也就是例子里我们自定义的smart-list组件的render函数,如下:
render: function (createElement, context) { function appropriateListComponent (){ if (context.props.items.length==0){ //当父组件传来的items元素为空时渲染这个 return {template:"<div>Enpty item</div>"} } return 'ul' } return createElement(appropriateListComponent(),Array.apply(null,{length:context.props.items.length}).map(function(val,index){ //调用createElement也就是Vue全局的createElement函数 return createElement('li',context.props.items[index].name) })) },
在我们自定义的render函数内,会先执行appropriateListComponent()函数,该函数会判断当前组件是否有传入items特性,如果有则返回ul,这样createElement的参数1就是ul了,也就是穿件一个tag为ul的虚拟VNode,如果没有传入items则返回一个内容为Emptry item的div
createElement的参数2是一个数组,每个元素又是一个createElement的返回值,Array.apply(null,{length:context.props.items.length})可以根据一个数组的个数再创建一个数组,新数组每个元素的值为undefined