题目描述
思路
初步过滤
如果两个字符串的字符种类和数量不太一样,那么肯定不互为扰乱字符串
暴力递归方式
f(str1,str2, L1, L2, k)
表示: str1 从L1开始往后推k个长度字符,和str2从L2往后推k个长度字符,是否互为扰乱字符串
那么主函数调用:
f(str1, str2, 0, 0, str1.length)
暴力方法中,我们枚举第一刀切str1的位置,切完第一刀后,分成的两个字符串可以旋转也可以不旋转,枚举出所有情况后,如果str2和str1互为扰动字符串,那么str2必在其中。
假设两个字符串str1和str2分别是:
str1: ABCDEFGH
str2: IJKLMNOP
假设第一刀的位置在str1的F和G之间位置
str1 就被分割成了 ABCDEF GH
这种情况下, 如下图
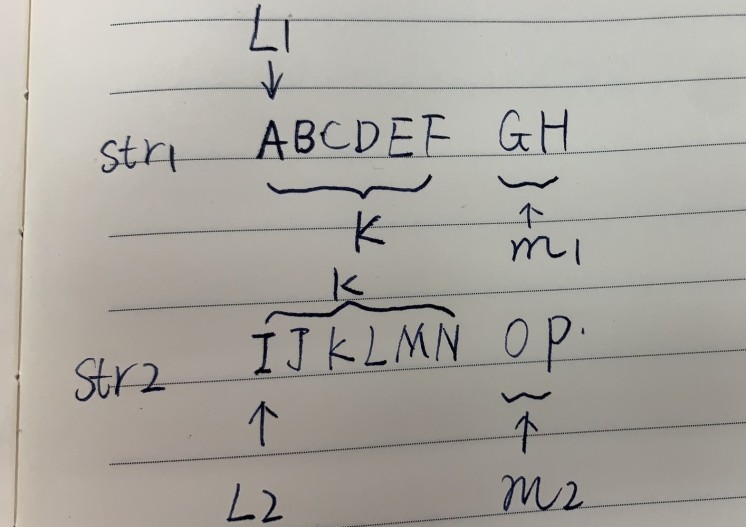
则判断两个条件:
L1往后k长度和L2往后k长度是否为扰动字符串
m1部分和m2部分是否互为扰动字符串
即:
boolean case1 = f(str1, str2, L1, L2, cutPoint) && f(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2 + cutPoint, k - cutPoint);
其中cutPoint就是str1第一刀切的位置,即:F和G之间
还有一种情况,如下图
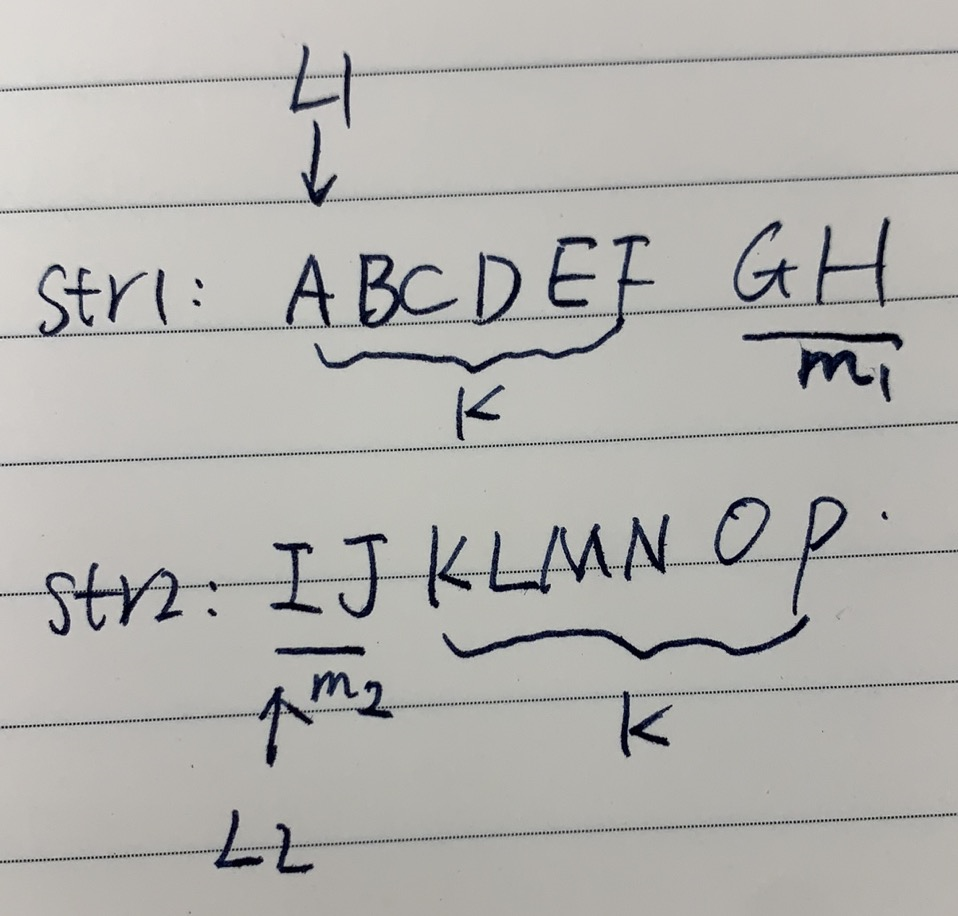
这种情况下:
boolean case2 = f(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2, k - cutPoint) && f(str1, str2, L1, L2 + k - cutPoint, cutPoint);
以上两个情况,只要一个满足,就说这两个是互为扰动串
所以,暴力方法的完整代码:
public static boolean isScramble(String s1, String s2) {
if (s1 == null && s2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (s1 == null) {
return false;
}
if (s2 == null) {
return false;
}
char[] str1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = s2.toCharArray();
if (!isValid(str1, str2)) {
return false;
}
return f(str1, str2, 0, 0, str2.length);
}
// str1中,L1往后(包括L1)一共k个字符串 以及 str2中,L2往后(包括L2)一共k个字符串 是否互为扰动串
private static boolean f(char[] str1, char[] str2, int L1, int L2, int k) {
if (k == 1) {
// base case, 针对这样的情况,只需要判断str1[L1], str2[L2]
return str1[L1] == str2[L2];
}
// 枚举第一刀的位置
for (int cutPoint = 1; cutPoint < k; cutPoint++) {
boolean case1 = f(str1, str2, L1, L2, cutPoint) && f(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2 + cutPoint, k - cutPoint);
boolean case2 = f(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2, k - cutPoint) && f(str1, str2, L1, L2 + k - cutPoint, cutPoint);
if (case1 || case2) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static boolean isValid(char[] str1, char[] str2) {
if (str1.length != str2.length) {
return false;
}
int[] map = new int[26];
for (char c : str1) {
map[c - 'a']++;
}
for (char c : str2) {
map[c - 'a']--;
if (map[c - 'a'] < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
注: isValid() 方法就是判断两个字符串的长度和字符种类个数是否一致,因为比较简单,不做赘述
这个方法在Leetcode上会超时,接下来,我们需要把这个方法改成动态规划。
记忆化搜索
由上面的暴力递归过程可知,暴力方法有三个可变参数:
L1:取值范围是0....N-1 (其中N是字符串的长度)
L2:取值范围是0....N-1
k: 取值范围是0....N
我们可以设置一个三维数组来存暴力过程中的结果
int[][][] dp = new int[N][N][N+1]
dp[i][j][k] 的取值有三种情况:
0: 表示没有计算过
1: 表示str1中i开始推后k个字符和str2中j开始推后k个字符 是互为扰动串
-1:表示str1中i开始推后k个字符和str2中j开始推后k个字符 不是互为扰动串
把这个三维数组加入暴力递归方法中,作为缓存数据,暴力递归方法可以改成:
private static boolean f2(char[] str1, char[] str2, int L1, int L2, int k, int[][][] dp) {
if (dp[L1][L2][k] != 0) {
return dp[L1][L2][k] == 1;
}
if (k == 1) {
// base case, 针对这样的情况,只需要判断str1[L1], str2[L2]
dp[L1][L2][k] = (str1[L1] == str2[L2] ? 1 : -1);
return dp[L1][L2][k] == 1;
}
// 枚举第一刀的位置
boolean ans = false;
for (int cutPoint = 1; cutPoint < k; cutPoint++) {
boolean case1 = f2(str1, str2, L1, L2, cutPoint, dp) && f2(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2 + cutPoint, k - cutPoint, dp);
boolean case2 = f2(str1, str2, L1 + cutPoint, L2, k - cutPoint, dp) && f2(str1, str2, L1, L2 + k - cutPoint, cutPoint, dp);
if (case1 || case2) {
ans = true;
break;
}
}
dp[L1][L2][k] = ans ? 1 : -1;
return ans;
}
其中第一句逻辑:
if (dp[L1][L2][k] != 0) {
return dp[L1][L2][k] == 1;
}
表示 dp[L1][L2][k] 如果不等于0,说明计算的结果已经算过了,则直接可以拿结果即可。
动态规划
public static boolean isScramble(String s1, String s2) {
if (s1 == null && s2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (s1 == null) {
return false;
}
if (s2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (s1.equals(s2)) {
return true;
}
char[] str1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = s2.toCharArray();
if (!isValid(str1, str2)) {
return false;
}
int N = str1.length;
boolean[][][] dp = new boolean[N][N][N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
dp[i][j][1] = (str1[i] == str2[j]);
}
}
for (int k = 2; k < N + 1; k++) {
for (int L1 = 0; L1 <= N - k; L1++) {
for (int L2 = 0; L2 <= N - k; L2++) {
for (int cutPoint = 1; cutPoint < k; cutPoint++) {
boolean case1 = dp[L1][L2][cutPoint] && dp[L1 + cutPoint][L2 + cutPoint][k - cutPoint];
boolean case2 = dp[L1 + cutPoint][L2][k - cutPoint] && dp[L1][L2 + k - cutPoint][cutPoint];
if (case1 || case2) {
dp[L1][L2][k] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][N];
}