AbstractExecutorService 抽象ExecutorService
/** * 提供了ExecutorService方法的默认实现:submit、invokeAny、invokeAll * newTaskFor方法提供了将Runnable转换为RunnableFuture(默认为FutureTask实现,子类可以重写,返回其他RunnableFuture实现)*/ public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService { /** * 返回一个RunnableFuture类根据给定的Runnable和默认值*/ protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) { return new FutureTask<T>(runnable, value); } /** * 返回RunnableFuture根据给定的Callable*/ protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable) { return new FutureTask<T>(callable); } /** * 参见父类型接口文档 * RejectedExecutionException*/ public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);//Runnable包装为RunnableFuture execute(ftask);//提交任务 return ftask;//返回Future } /** * 参见父类型接口文档 * RejectedExecutionException*/ public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task, result);//Runnable包装为RunnableTuture execute(ftask);//提交任务 return ftask;//返回Future } /** * 参见父类型接口文档 * RejectedExecutionException*/ public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);//Future包装为RunnableFuture execute(ftask);//提交任务 return ftask;//返回future } /** * 主要的实现:doInvokeAny */ private <T> T doInvokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { if (tasks == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int ntasks = tasks.size(); if (ntasks == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<>(ntasks); ExecutorCompletionService<T> ecs = new ExecutorCompletionService<T>(this);//使用ExecutorCompletionService执行任务 // 为了提高效率特别是并行受限的executor,在提交更多任务前检查以前提交的任务是否已经完成 try { // 记录异常以便如果我们没有拿到结果,可以抛出我们最后得到的异常 ExecutionException ee = null; final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; Iterator<? extends Callable<T>> it = tasks.iterator(); // 一定执行第一个,其余的增量 futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next())); --ntasks; int active = 1; for (;;) { Future<T> f = ecs.poll();//检索已经完成的任务 if (f == null) {//没有任务完成,继续提交任务 if (ntasks > 0) { --ntasks; futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next())); ++active; } else if (active == 0)//没有计算中的任务,结束循环 break; else if (timed) {//允许超时 f = ecs.poll(nanos, NANOSECONDS);//等待计算结果 if (f == null) throw new TimeoutException(); nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();//防止虚假唤醒 } else f = ecs.take();//没有超时限定,等待结果返回 } if (f != null) {//已有计算结果 --active; //计算中任务-- try { return f.get();//返回结果 } catch (ExecutionException eex) { ee = eex; } catch (RuntimeException rex) { ee = new ExecutionException(rex);//包装异常,继续等待其他在途任务结果 } } } if (ee == null) ee = new ExecutionException(); throw ee;//抛出异常 } finally { cancelAll(futures);//取消在途任务 } } public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { try { return doInvokeAny(tasks, false, 0);//调用doInvokeAny,不限制超时 } catch (TimeoutException cannotHappen) { assert false; return null; } } public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { return doInvokeAny(tasks, true, unit.toNanos(timeout));//调用doInvokeAny 设置超时 } public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException { if (tasks == null) throw new NullPointerException(); ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<>(tasks.size()); try { for (Callable<T> t : tasks) {//遍历tasks RunnableFuture<T> f = newTaskFor(t);//包装Callable为RunnableFuture futures.add(f); execute(f);//执行RunnableFuture } for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++) {//遍历futures Future<T> f = futures.get(i); if (!f.isDone()) {//判断任务是否执行完成 try { f.get(); }//未完成则等待任务完成 catch (CancellationException | ExecutionException ignore) {} } } return futures; } catch (Throwable t) { cancelAll(futures);//异常则取消所有在途任务 throw t; } } public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { if (tasks == null) throw new NullPointerException(); final long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanos;//计算deadline ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<>(tasks.size()); int j = 0; timedOut: try { for (Callable<T> t : tasks) futures.add(newTaskFor(t)); final int size = futures.size(); // 交错检查执行时间,防止executor没有太多的并行 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (((i == 0) ? nanos : deadline - System.nanoTime()) <= 0L)//计算deadline是否超时 break timedOut; execute((Runnable)futures.get(i));//提价任务 } for (; j < size; j++) {//遍历futures Future<T> f = futures.get(j); if (!f.isDone()) {//任务未完成,等待任务完成 try { f.get(deadline - System.nanoTime(), NANOSECONDS); }//设置等待时间 catch (CancellationException | ExecutionException ignore) {} catch (TimeoutException timedOut) { break timedOut;//超时中断 } } } return futures; } catch (Throwable t) { cancelAll(futures);//取消任务 throw t; } // 在所任务完成前超时,则取消剩余任务 cancelAll(futures, j); return futures; } private static <T> void cancelAll(ArrayList<Future<T>> futures) { cancelAll(futures, 0); } /** 取消所有指定所有的任务 */ private static <T> void cancelAll(ArrayList<Future<T>> futures, int j) { for (int size = futures.size(); j < size; j++) futures.get(j).cancel(true); } }
任务模型分析:
定义任务:Runnable --》 Callable 转换:Executors.callable()
1.Runnable、run()一个无返回值的任务
2.Callable<T>、 T call()代表了有返回值的任务类型
计算结果:AbstractExecutorService.newTaskFor() 定义了 runnable、callable--》RunnableFuture
1.Future:代表了异步计算结果以及其获取方式的定义
2.RunnableFuture:可以执行的Future
3.FutureTask:实现了Runnable 、Callable --》 RunableFuture的转换
提交任务:定义任务的提交方式
1.Executor.execute(Runnable command) 运行执行的命令,无返回值
2.ExecutorService.submit(Callable task)、invokeAny()、invokeAll 提交执行的任务,返回Future对象
运行调度:
Thread:代表了线程的运行、状态、调度对象
可通过 Executors.callable(Runnable task,T result)方法将Runnable --> Callable
/** * 返回Callable对象,callable被调用是运行指定的任务返回指定的结果 * 对于需要Callable对象方法并且缺少结果的行动 * can be useful when applying methods requiring a*/ public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result); }
/**
* Callable对象,运行指定的任务,返回指定的结果
*/
private static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
private final Runnable task;
private final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {//模拟call方法
task.run();//运行指定任务
return result;//返回指定结果
}
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[Wrapped task = " + task + "]";
}
}
线程池运行状态变化:
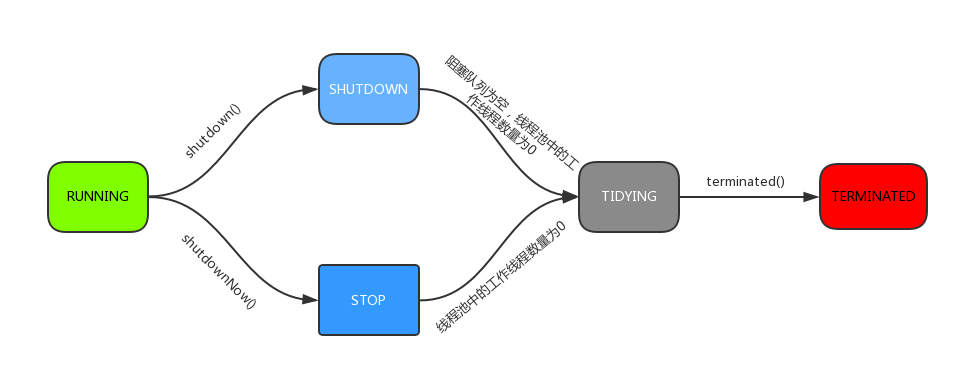
线程池任务提交过程中任务运行机制委托:
submit(Runnable,T result)/submit(Callable):通过AbstractExecutorService.newTaskFor方法 将 runnable/callable 委托为RunableFuture接口的实现类FutureTask类,
--(new FutureTask(Runnable)继续调用Executors.callbale(Runnable r,T result) 方法,将Runnable委托给RunnableAdapter())
submit 委托 execute(Runnable)执行提交的任务
execute(Runnable r) 委托 ThreadPoolExecutor.Worker内部类执行具体的任务运行 worker.run() 委托 ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(Worker w) 真正执行线程运行