线性时间排序算法
线性时间排序算法列表
给定含 n 个元素的输入序列,任何比较排序在最坏情况下都需要 Ω(n log n) 次比较来进行排序。合并排序和堆排序在最坏情况下达到上界 O(n log n),它们都是渐进最优的排序算法,快速排序在平均情况下达到上界 O(n log n)。
本文介绍的三种以线性时间运行的算法:计数排序、基数排序和桶排序,都用非比较的一些操作来确定排序顺序。因此,下界 Ω(n log n) 对它们是不适用的。
计数排序(Counting Sort)
计数排序(Counting Sort)假设 n 个输入元素中的每一个都是介于 0 到 k 之间的整数,此处 k 为某个整数。
计数排序的基本思想就是对每一个输入元素 x,确定出小于 x 的元素个数。有了这一信息,就可以把 x 直接放到它在最终输出数组中的位置上。
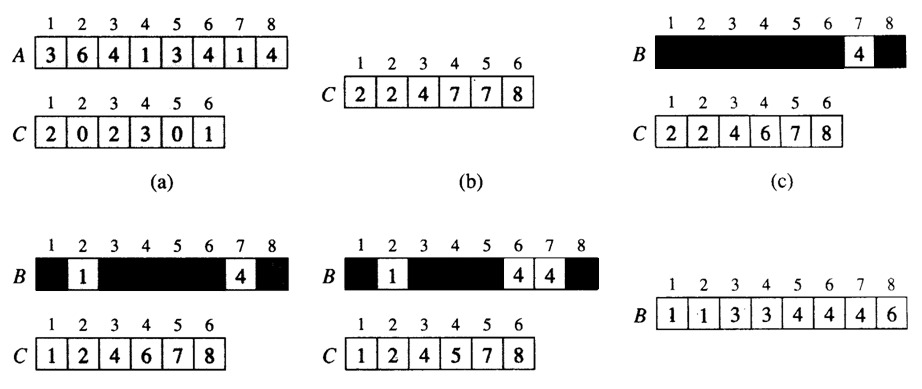
例如:有 10 个年龄不同的人,统计出有 8 个人的年龄比 A 小,那 A 的年龄就排在第 9 位,用这个方法可以得到其他每个人的位置,也就排好了序。当然,年龄有重复时需要特殊处理(保证稳定性),这就是为什么最后要反向填充目标数组,以及将每个数字的统计减去 1 的原因。
算法描述
算法的步骤如下:
- 找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素;
- 统计数组中每个值为 i 的元素出现的次数,存入数组 C 的第 i 项;
- 对所有的计数累加(从 C 中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加);
- 反向填充目标数组,将每个元素 i 放在新数组的第 C(i) 项,每放一个元素就将 C(i) 减去 1;
算法复杂度
- 最差时间复杂度 O(n + k)
- 平均时间复杂度 O(n + k)
- 最差空间复杂度 O(n + k)
计数排序不是比较排序,排序的速度快于任何比较排序算法。
计数排序的一个重要性质就是它是稳定的:具有相同值的元素在输出数组中的相对次序与它们在输入数组中的次序相同。
之所以说计数排序的稳定性非常重要,还有一个原因是因为计数排序经常用作基数排序算法的一个子过程,其稳定性对于基数排序的正确性来说非常关键。
代码示例
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int[] unsorted =
6 {
7 5, 9, 3, 9, 10, 9, 2, 4, 13, 10
8 };
9
10 OptimizedCountingSort(unsorted);
11
12 foreach (var key in unsorted)
13 {
14 Console.Write("{0} ", key);
15 }
16
17 Console.Read();
18 }
19
20 static int[] CountingSort(int[] unsorted)
21 {
22 // find min and max value
23 int min = unsorted[0], max = unsorted[0];
24 for (int i = 1; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
25 {
26 if (unsorted[i] < min) min = unsorted[i];
27 else if (unsorted[i] > max) max = unsorted[i];
28 }
29
30 // creates k buckets
31 int k = max - min + 1;
32 int[] C = new int[k];
33
34 // calculate the histogram of key frequencies
35 for (int i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
36 {
37 C[unsorted[i] - min]++;
38 }
39
40 // recalculate
41 C[0]--;
42 for (int i = 1; i < C.Length; i++)
43 {
44 C[i] = C[i] + C[i - 1];
45 }
46
47 // sort the array
48 int[] B = new int[unsorted.Length];
49 for (int i = unsorted.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
50 {
51 // keep stable
52 B[C[unsorted[i] - min]--] = unsorted[i];
53 }
54
55 return B;
56 }
57
58 static void OptimizedCountingSort(int[] unsorted)
59 {
60 // find min and max value
61 int min = unsorted[0], max = unsorted[0];
62 for (int i = 1; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
63 {
64 if (unsorted[i] < min) min = unsorted[i];
65 else if (unsorted[i] > max) max = unsorted[i];
66 }
67
68 // creates k buckets
69 int k = max - min + 1;
70 int[] C = new int[k];
71
72 // calculate the histogram of key frequencies
73 for (int i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
74 {
75 C[unsorted[i] - min]++;
76 }
77
78 // copy to output array,
79 // preserving order of inputs with equal keys
80 int increment = 0;
81 for (int i = min; i <= max; i++)
82 {
83 for (int j = 0; j < C[i - min]; j++)
84 {
85 // in place, may not stable if you care
86 unsorted[increment++] = i;
87 }
88 }
89 }
90 }
基数排序(Radix Sort)
基数排序(Radix Sort)是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数值按相同的有效位进行分组,然后在有效位区间内进行排序。
算法描述
每个元素值首先被放入一个该值的最右位所对应的桶中,桶内会保持被放入元素值最初的顺序。这使得桶的数量和值的数量能够根据其最右位建立一对一的关系。然后,通过相同的方式重复处理下一位,直到所有的位都已被处理。
- 获得值的最右侧的最小的位。
- 根据该位的值将数组内的元素值进行分组,但仍然保持元素的顺序。(以此来保持算法稳定性)
- 重复上述分组过程,直到所有的位都已被处理。
上述第 2 步中通常可以使用桶排序(Bucket Sort)或计数排序(Counting Sort)算法,因为它们在元素较少时拥有更好的效率。
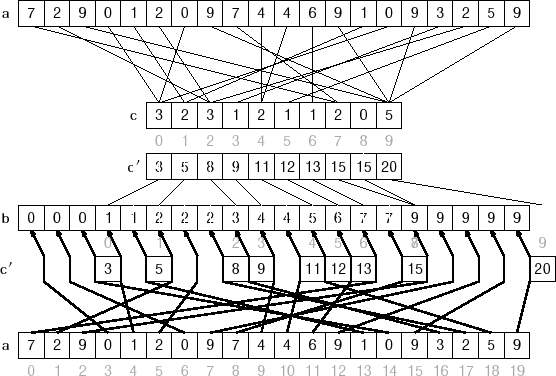
基数排序中可以选择采用最低有效位基数排序(LSD Radix Sort:Least Significant Digit Radix Sort)或最高有效位基数排序(MSD Radix Sort:Most Significant Digit Radix Sort)。LSD 的排序方式由值的最低位也就是最右边开始,而 MSD 则相反,由值的最高位也就是最左边开始。

例如,如下这个无序的数列需要排序:
170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 2, 24, 66
使用 LSD 方式从最低位开始(个位)排序的结果是:
170, 90, 802, 2, 24, 45, 75, 66
再继续从下一位(十位)继续排序的结果是:
802, 2, 24, 45, 66, 170, 75, 90
再继续从下一位(百位)继续排序的结果是:
2, 24, 45, 66, 75, 90, 170, 802
算法复杂度
- 最差时间复杂度 O(k*n)
- 最差空间复杂度 O(k*n)
代码示例
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int[] unsorted =
6 {
7 15, 19, 13, 19, 10, 33, 12, 14, 13, 10,
8 };
9
10 RadixSort(unsorted);
11
12 foreach (var key in unsorted)
13 {
14 Console.Write("{0} ", key);
15 }
16
17 Console.Read();
18 }
19
20 static void RadixSort(int[] unsorted)
21 {
22 // our helper array
23 int[] t = new int[unsorted.Length];
24
25 // number of bits our group will be long
26 // try to set this also to 2, 8 or 16 to see if it is quicker or not
27 int r = 4;
28
29 // number of bits of a C# int
30 int b = 32;
31
32 // counting and prefix arrays
33 // (note dimensions 2^r which is the number of
34 // all possible values of a r-bit number)
35 int[] count = new int[1 << r];
36 int[] pref = new int[1 << r];
37
38 // number of groups
39 int groups = (int)Math.Ceiling((double)b / (double)r);
40
41 // the mask to identify groups
42 int mask = (1 << r) - 1;
43
44 // the algorithm:
45 for (int c = 0, shift = 0; c < groups; c++, shift += r)
46 {
47 // reset count array
48 for (int j = 0; j < count.Length; j++)
49 count[j] = 0;
50
51 // counting elements of the c-th group
52 for (int i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
53 count[(unsorted[i] >> shift) & mask]++;
54
55 // calculating prefixes
56 pref[0] = 0;
57 for (int i = 1; i < count.Length; i++)
58 pref[i] = pref[i - 1] + count[i - 1];
59
60 // from a[] to t[] elements ordered by c-th group
61 for (int i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
62 t[pref[(unsorted[i] >> shift) & mask]++] = unsorted[i];
63
64 // a[]=t[] and start again until the last group
65 t.CopyTo(unsorted, 0);
66 }
67 // a is sorted
68 }
69 }
桶排序(Bucket Sort)
桶排序(Bucket Sort)的工作原理是将数组分解到有限数量的桶里,每个桶再分别进行排序。桶内排序有可能使用其他排序算法或是以递归的方式继续使用桶排序。
算法描述
桶排序的步骤:
- 在数组中查找数值的最大值和最小值;
- 初始化一个数组当作空桶,长度为 (MaxValue - MinValue + 1)。
- 遍历被排序数组,并把数值逐个放入对应的桶中。
- 对每个不是空的桶进行排序。
- 从不是空的桶里把数值再放回原来的数组中。


算法复杂度
- 最差时间复杂度 O(n2)
- 平均时间复杂度 O(n+k)
- 最差空间复杂度 O(n*k)
当要被排序的数组中的数值是均匀分布时,桶排序的运行时间为线性时间 Θ(n)。桶排序不是比较排序,它不受 Ω(n log n) 下界的影响。
代码示例
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int[] unsorted =
6 {
7 15, 19, 13, 19, 10, 33, 12, 14, 13, 10,
8 };
9
10 BucketSort(unsorted);
11
12 foreach (var key in unsorted)
13 {
14 Console.Write("{0} ", key);
15 }
16
17 Console.Read();
18 }
19
20 static void BucketSort(int[] unsorted)
21 {
22 // find the maximum and minimum values in the array
23 int max = unsorted[0]; //start with first element
24 int min = unsorted[0];
25
26 // start from index 1
27 for (int i = 1; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
28 {
29 if (unsorted[i] < min) min = unsorted[i];
30 else if (unsorted[i] > max) max = unsorted[i];
31 }
32
33 // create a temporary "buckets" to store the values in order
34 // each value will be stored in its corresponding index
35 // scooting everything over to the left as much as possible
36 // e.g. 34 => index at 34 - minValue
37 List<int>[] buckets = new List<int>[max - min + 1];
38
39 // initialize the buckets
40 for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++)
41 {
42 buckets[i] = new List<int>();
43 }
44
45 // move items to bucket
46 for (int i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
47 {
48 buckets[unsorted[i] - min].Add(unsorted[i]);
49 }
50
51 // move items in the bucket back to the original array in order
52 int k = 0; //index for original array
53 for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++)
54 {
55 if (buckets[i].Count > 0)
56 {
57 for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].Count; j++)
58 {
59 unsorted[k] = buckets[i][j];
60 k++;
61 }
62 }
63 }
64 }
65 }
参考资料
- Sorting Algorithms
- Counting Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort
- C# Counting Sort Algorithm Implementation
- Radix Sorting Implementation with C#
- Algorithm Implementation/Sorting/Radix sort
- Category:Algorithm Implementation
- Counting Sort and Radix Sort
- Data Structures and Algorithms with Object-Oriented Design Patterns in C++
本篇文章《线性时间排序算法》由 Dennis Gao 发表自博客园,任何未经作者同意的爬虫或人为转载均为耍流氓。
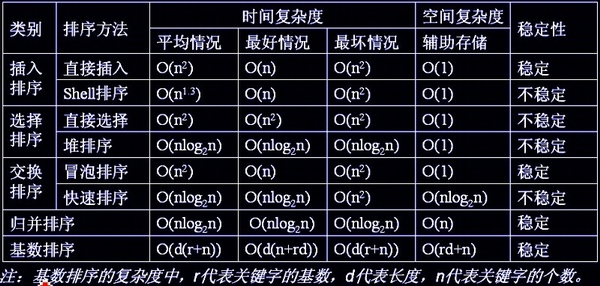
总结
各种排序的稳定性,时间复杂度和空间复杂度总结:
我们比较时间复杂度函数的情况:

时间复杂度函数O(n)的增长情况
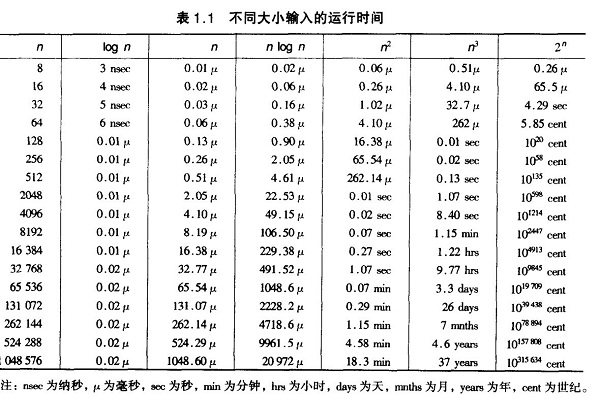
所以对n较大的排序记录。一般的选择都是时间复杂度为O(nlog2n)的排序方法。
时间复杂度来说:
(1)平方阶(O(n2))排序
各类简单排序:直接插入、直接选择和冒泡排序;
(2)线性对数阶(O(nlog2n))排序
快速排序、堆排序和归并排序;
(3)O(n1+§))排序,§是介于0和1之间的常数。
希尔排序
(4)线性阶(O(n))排序
基数排序,此外还有桶、箱排序。
说明:
当原表有序或基本有序时,直接插入排序和冒泡排序将大大减少比较次数和移动记录的次数,时间复杂度可降至O(n);
而快速排序则相反,当原表基本有序时,将蜕化为冒泡排序,时间复杂度提高为O(n2);
原表是否有序,对简单选择排序、堆排序、归并排序和基数排序的时间复杂度影响不大。
稳定性:
排序算法的稳定性:若待排序的序列中,存在多个具有相同关键字的记录,经过排序, 这些记录的相对次序保持不变,则称该算法是稳定的;若经排序后,记录的相对 次序发生了改变,则称该算法是不稳定的。
稳定性的好处:排序算法如果是稳定的,那么从一个键上排序,然后再从另一个键上排序,第一个键排序的结果可以为第二个键排序所用。基数排序就是这样,先按低位排序,逐次按高位排序,低位相同的元素其顺序再高位也相同时是不会改变的。另外,如果排序算法稳定,可以避免多余的比较;
稳定的排序算法:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序和基数排序
不是稳定的排序算法:选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序
选择排序算法准则:
每种排序算法都各有优缺点。因此,在实用时需根据不同情况适当选用,甚至可以将多种方法结合起来使用。
选择排序算法的依据
影响排序的因素有很多,平均时间复杂度低的算法并不一定就是最优的。相反,有时平均时间复杂度高的算法可能更适合某些特殊情况。同时,选择算法时还得考虑它的可读性,以利于软件的维护。一般而言,需要考虑的因素有以下四点:
1.待排序的记录数目n的大小;
2.记录本身数据量的大小,也就是记录中除关键字外的其他信息量的大小;
3.关键字的结构及其分布情况;
4.对排序稳定性的要求。
设待排序元素的个数为n.
1)当n较大,则应采用时间复杂度为O(nlog2n)的排序方法:快速排序、堆排序或归并排序序。
快速排序:是目前基于比较的内部排序中被认为是最好的方法,当待排序的关键字是随机分布时,快速排序的平均时间最短;
堆排序 : 如果内存空间允许且要求稳定性的,
归并排序:它有一定数量的数据移动,所以我们可能过与插入排序组合,先获得一定长度的序列,然后再合并,在效率上将有所提高。
2) 当n较大,内存空间允许,且要求稳定性 =》归并排序
3)当n较小,可采用直接插入或直接选择排序。
直接插入排序:当元素分布有序,直接插入排序将大大减少比较次数和移动记录的次数。
直接选择排序 :元素分布有序,如果不要求稳定性,选择直接选择排序
5)一般不使用或不直接使用传统的冒泡排序。
6)基数排序
它是一种稳定的排序算法,但有一定的局限性:
1、关键字可分解。
2、记录的关键字位数较少,如果密集更好
3、如果是数字时,最好是无符号的,否则将增加相应的映射复杂度,可先将其正负分开排序。
