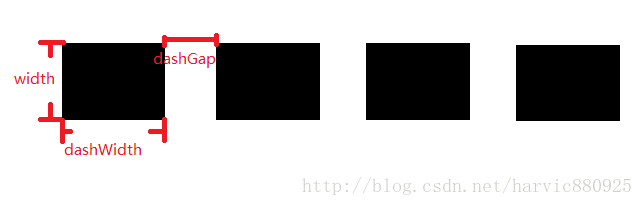首先我们先来了解状态效果
android:state_pressed=["true" | "false"] 按下状态
android:state_focused=["true" | "false"] 聚焦状态
android:state_selected=["true" | "false"] 选中状态
android:state_active=["true" | "false"] 激活状态
android:state_checkable=["true" | "false"] 可校验状态
android:state_checked=["true" | "false"] 检查状态
android:state_enabled=["true" | "false"] 启用状态
android:state_window_focused=["true" | "false"] 状态栏聚焦状态
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:state_checked="true" android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/enabled_on_pressed" /> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:state_checked="false" android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/enabled_off_pressed" /> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:state_checked="true" android:drawable="@drawable/enabled_on" /> <item android:state_enabled="true" android:state_checked="false" android:drawable="@drawable/enabled_off" /> <item android:state_enabled="false" android:state_checked="true" android:drawable="@drawable/disabled_on" /> <item android:state_enabled="false" android:state_checked="false" android:drawable="@drawable/disabled_off" /> </selector>
Item顺序是有讲究的,条件限定越细致,则应该放到前面。比如这儿如果把1,2行和3,4行的item交换,那么pressed的就永远无法触发了,因为有item已经满足条件返回了。可以理解为代码中的if语句。
基本属性(corners、gradient、padding、size、solid、stroke)
上面给大家简单的讲了下shape标签组的简单使用方法,下面就具体讲讲shape标签里所具有的几个子标签及所具有的属性。
1、Corners
<corners //定义圆角 android:radius="dimension" //全部的圆角半径 android:topLeftRadius="dimension" //左上角的圆角半径 android:topRightRadius="dimension" //右上角的圆角半径 android:bottomLeftRadius="dimension" //左下角的圆角半径 android:bottomRightRadius="dimension" /> //右下角的圆角半径
Corners标签是用来字义圆角的,其中radius与其它四个并不能共同使用。
android:radius:定义四个角的的圆角半径。
其它四个是逐个字义每个角的圆角半径。
2、solid
solid用以指定内部填充色
只有一个属性:
<solid android:color="color" /> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <solid android:color="#ffff00"/> </shape>
效果
3、gradient
gradient用以定义渐变色,可以定义两色渐变和三色渐变,及渐变样式,它的属性有下面几个:
<gradient android:type=["linear" | "radial" | "sweep"] //共有3中渐变类型,线性渐变(默认)/放射渐变/扫描式渐变 android:angle="integer" //渐变角度,必须为45的倍数,0为从左到右,90为从上到下 android:centerX="float" //渐变中心X的相当位置,范围为0~1 android:centerY="float" //渐变中心Y的相当位置,范围为0~1 android:startColor="color" //渐变开始点的颜色 android:centerColor="color" //渐变中间点的颜色,在开始与结束点之间 android:endColor="color" //渐变结束点的颜色 android:gradientRadius="float" //渐变的半径,只有当渐变类型为radial时才能使用 android:useLevel=["true" | "false"] /> //使用LevelListDrawable时就要设置为true。设为false时才有渐变效果
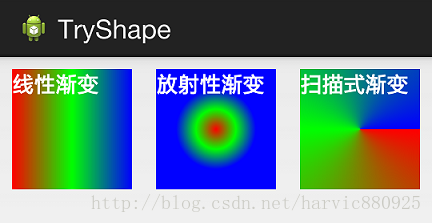
首先有三种渐变类型,分别是:linear(线性渐变)、radial(放射性渐变)、sweep(扫描式渐变
先看看这几个属性的使用方法:
android:type=["linear" | "radial" | "sweep"]
android:startColor="color" //渐变开始点的颜色
android:centerColor="color" //渐变中间点的颜色,在开始与结束点之间
android:endColor="color" //渐变结束点的颜色
android:gradientRadius="float" //渐变的半径,只有当渐变类型为radial时才能使用
下面我们使用三色渐变来看看这三种渐变方式都是怎么显示的:(如果不使用centerColor属性就是双色渐变,这个属性是可选的)
需要注意的一点是,在构造放射性渐变时,要加上android:gradientRadius属性(渐变半径),即必须指定渐变半径的大小才会起作用,下面列出这三个渐变方式的shape代码,供大家参考:
线性渐变:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="linear" android:startColor="#ff0000" android:centerColor="#00ff00" android:endColor="#0000ff"/> </shape>
放射性渐变:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="radial" android:startColor="#ff0000" android:centerColor="#00ff00" android:endColor="#0000ff" android:gradientRadius="100"/> </shape>
扫描式渐变:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="sweep" android:startColor="#ff0000" android:centerColor="#00ff00" android:endColor="#0000ff"/> </shape>
可见放射性渐变,只是比其它两个多了个android:gradientRadius属性
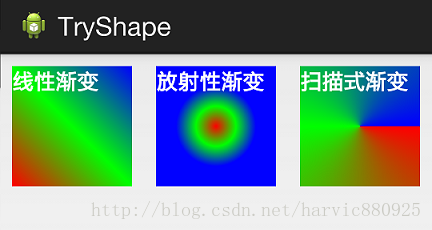
android:angle属性(仅对线性渐变有效)
android:angle="integer" //渐变角度,必须为45的倍数,0为从左到右,90为从上到下 我们在上面的三种渐变上都加上angle属性,看看效果如何:
能过跟上一个图对比可以发现,angle属性确实只对线性渐变有效,其它两种渐变方式都没有任何动静,下面是此时的线性渐变shape代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="linear" android:startColor="#ff0000" android:centerColor="#00ff00" android:endColor="#0000ff" android:angle="45"/> </shape>
android:centerX与android:centerY:
centerX、centerY两个属性用于设置渐变的中心点位置,仅当渐变类型为放射渐变时有效,类型为分数或小数,不接受Dimension。默认值是0.5,有效值是0.0~1.0,超出该范围后会看不出渐变效果。centerX、centerY的取值其实是宽和高的百分比;不难理解,下面看代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="sweep" android:startColor="#ff0000" android:centerColor="#00ff00" android:endColor="#0000ff" android:centerX="0.2" android:centerY="0.8"/> </shape>
取宽度的20%和高度的80%的位置,作为新的渐变原点,效果是这样的:
android:useLevel
useLevel属性通常不使用。该属性用于指定是否将该shape当成一个LevelListDrawable来使用,默认值为false。
4、stroke
这是描边属性,可以定义描边的宽度,颜色,虚实线等
<stroke android:width="dimension" //描边的宽度 android:color="color" //描边的颜色 // 以下两个属性设置虚线 android:dashWidth="dimension" //虚线的宽度,值为0时是实线 android:dashGap="dimension" /> //虚线的间隔
上面各个属性的意义如下:
我们使用绿色虚线描边,虚线高度是20dp,虚线宽度为10dp虚线间距为1dp:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <stroke android:width="20dp" android:color="#00ff00" android:dashWidth="10dp" android:dashGap="1dp" /> </shape>
从效果图中,我们也能清晰的看出这三个参数(width、dashwidth、dashGap)之间的区别,另外请注意!如果你发现一直没有虚线效果,可能是你没关闭硬件加速导致的:
你可以在Activity里选择关闭硬件加速:
<activity ... /> <activity android:hardwareAccelerated="false" />
也可以指定某个View关闭硬件加速:
代码里:
myView.setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
xml里:
android:layerType="software"
5、size和padding
这两个基本上不怎么用,因为他们所具有的功能,控件本身也能实现。
size:是用来定义图形的大小的。
<size android:width="dimension" android:height="dimension" />
padding:用来定义内部边距
<padding android:left="dimension" android:top="dimension" android:right="dimension" android:bottom="dimension" />
三、Shape的属性(rectangle、oval、line、ring)
上面我们讲了Shape的子标签的的作用,但Shape本身还没讲,Shape自已是可以定义当前Shape的形状的,比如上面的矩形,还有椭圆形,线形和环形;这些都是通过Shape标签的 shape属性来定义的,Shape标签总共有下面几个属性,我们一个个讲:
android:shape=["rectangle" | "oval" | "line" | "ring"]
shape的形状,默认为矩形,可以设置为矩形(rectangle)、椭圆形(oval)、线性形状(line)、环形(ring)
下面的属性只有在android:shape="ring时可用:
android:innerRadius 尺寸,内环的半径。
android:innerRadiusRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示内环的半径,
android:thickness 尺寸,环的厚度
android:thicknessRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示环的厚度,例如,如果android:thicknessRatio="2",
android:useLevel boolean值,如果当做是LevelListDrawable使用时值为true,否则为false. 可见,只有第一个shape是可用的,其它五个都是shape等于ring时所特有的。
注意,无论这里shape取什么形状,他的子标签都是可用的,但有时并不会有效果,比如在shape为椭圆时,那corners标签就不会有效果,很显然的道理。下面一个个看看各个形状都是怎么样的;
1、rectangle (矩形)
不指定shape属性时,默认就是矩形的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="rectangle"> <solid android:color="#ff00ff"/> </shape>
对应图形:
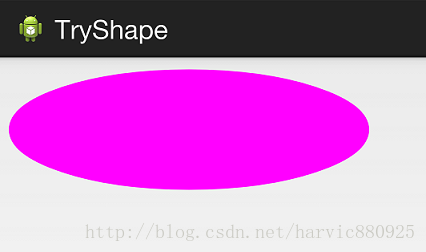
2、oval(椭圆)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="oval"> <solid android:color="#ff00ff"/> </shape>
对应图形:(控件大小的矩形所对应的椭圆)
3、line(线形)
虚线
拿shape 做虚线,shape 设置为line , stroke 是描边属性,
其中 dashGap dashWidth 两个属性彼此一起存在才生效。
请注意!如果你发现一直没有虚线效果,可能是你没关闭硬件加速导致的,指定某个View关闭硬件加速:
xml里:
android:layerType="software"
dashGap :两段之间的空隙宽度、
dashWidth :一段线的宽度
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="line" > <stroke android:dashGap="3dp" android:dashWidth="8dp" android:width="1dp" android:color="#009999" /> </shape>
效果如下:
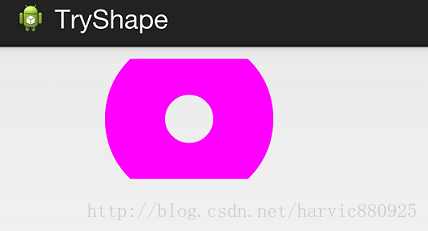
4、ring(环形)
还记得他所特有的几个属性么:
android:innerRadius 尺寸,内环的半径。
android:thickness 尺寸,环的厚度
android:innerRadiusRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示内环的半径,
例如,如果android:innerRadiusRatio,表示内环半径等于环的宽度除以5,这个值是可以被覆盖的,默认为9.
android:thicknessRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示环的厚度,例如,如果android:thicknessRatio="2",
那么环的厚度就等于环的宽度除以2。这个值是可以被android:thickness覆盖的,默认值是3.
android:useLevel boolean值,如果当做是LevelListDrawable使用时值为true,否则为false.这么几个属性无外乎就是定义环形的内环尺寸和环的宽度。
举个例子:
控件定义:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:textColor="#ffffff" android:textSize="18sp" android:textStyle="bold" android:background="@drawable/try_shape_2"/> </LinearLayout>
shape定义:(这里一定要要加上useLevel属性并定义为false,不然没有效果)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="ring" android:innerRadius="20dp" android:thickness="50dp" android:useLevel="false"> <solid android:color="#ff00ff"/> </shape>
效果图:
---------------------------例子代码-----------------------------------
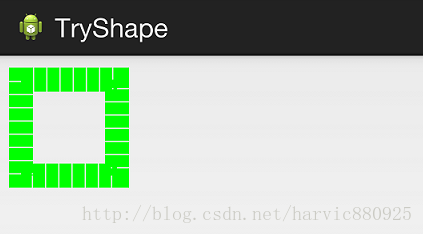
1.圆角空心正方形
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="rectangle"> <stroke android:width="2dp" android:color="@color/colorPrimary"/> <corners android:radius="20dp"/> <padding android:left="10dp" android:bottom="10dp" android:right="10dp" android:top="10dp"/> </shape>
效果如下:
2.有按下效果的正方形
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_pressed="false"> <shape android:shape="rectangle"> <solid android:color="@color/colorBlue"></solid> <corners android:radius="5dp"/> <padding android:bottom="10dp" android:left="10dp" android:right="10dp" android:top="10dp"/> </shape> </item> <item android:state_pressed="true"> <shape android:shape="rectangle"> <solid android:color="@color/colorDownBlue"></solid> <corners android:radius="5dp"/> <padding android:bottom="10dp" android:left="10dp" android:right="10dp" android:top="10dp"/> </shape> </item> </selector>
效果如下:
3.按下效果的圆形
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_pressed="true"> <shape android:shape="oval" > <size android:width="@dimen/size_40" android:height="@dimen/size_40"/> <solid android:color="@color/ivory"/> </shape> </item> <item android:state_pressed="false"> <shape android:shape="oval"> <size android:height="@dimen/size_40" android:width="@dimen/size_40"/> <solid android:color="@color/yellow"/> </shape> </item> </selector>
4.shape做渐变实线
gradient 表示渐变
angle 渐变角度,45的倍数。
startColor endColor centerColor 起 止 中 的颜色
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <gradient android:type="linear" android:angle="0" android:endColor="#F028A2" android:startColor="#2A99F3" /> </shape>
5.另一个实现环形的办法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="oval"> <size android:height="5dp" android:width="5dp"/> <stroke android:width="0.5dp" android:color="@color/theme_color"/> </shape>
6.实现一个底部带线条的正方形背景
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item > <shape> <solid android:color="@color/color_blue" /> </shape> </item> <!-- 注意! item是相反的,蓝色线条应该在上面,黑色背景反而在下面 --> <item android:bottom="30dp"> <shape > <solid android:color="@color/color_black"/> </shape> </item> </layer-list>
效果图: