http://www.tuicool.com/articles/umQfMzA
1.序言
今天来和大家探讨一下RocketMQ在消息存储方面所作出的努力,在介绍RocketMQ的存储模型之前,可以先探讨一下MQ的存储模型选择。
2.MQ的存储模型选择
个人看来,从MQ的类型来看,存储模型分两种:
- 需要持久化(ActiveMQ,RabbitMQ,Kafka,RocketMQ)
- 不需要持久化(ZeroMQ)
本篇文章主要讨论持久化MQ的存储模型,因为现在大多数的MQ都是支持持久化存储,而且业务上也大多需要MQ有持久存储的能力,能大大增加系统的高可用性,下面几种存储方式:
- 分布式KV存储(levelDB,RocksDB,redis)
- 传统的文件系统
- 传统的关系型数据库
这几种存储方式从效率来看, 文件系统 > kv存储 > 关系型数据库 ,因为直接操作文件系统肯定是最快的,而关系型数据库一般的TPS都不会很高,我印象中Mysql的写不会超过5Wtps(现在不确定最新情况),所以如果追求效率就直接操作文件系统。
但是如果从可靠性和易实现的角度来说,则是 关系型数据库 > kv存储 > 文件系统 ,消息存在db里面非常可靠,但是性能会下降很多,所以具体的技术选型都是需要根据自己的业务需求去考虑。
3.RocketMQ的存储架构

3.1存储特点:
如上图所示:
(1)消息主体以及元数据都存储在**CommitLog**当中
(2)Consume Queue相当于kafka中的partition,是一个逻辑队列,存储了这个Queue在CommiLog中的起始offset,log大小和MessageTag的hashCode。
(3)每次读取消息队列先读取consumerQueue,然后再通过consumerQueue去commitLog中拿到消息主体。
rocketMQ的设计理念很大程度借鉴了kafka,所以有必要介绍下kafka的存储结构设计:

-
存储特点:
和RocketMQ类似,每个Topic有多个partition(queue),kafka的每个partition都是一个独立的物理文件,消息直接从里面读写。
根据之前阿里中间件团队的测试,一旦kafka中Topic的partitoin数量过多,队列文件会过多,会给磁盘的IO读写造成很大的压力,造成tps迅速下降。
所以RocketMQ进行了上述这样设计,consumerQueue中只存储很少的数据,消息主体都是通过CommitLog来进行读写。
没有一种方案是银弹,那么RocketMQ这样处理有什么 优缺点 ?
-
3.2.1优点:
1、队列轻量化,单个队列数据量非常少。对磁盘的访问串行化,避免磁盘竟争,不会因为队列增加导致IOWAIT增高。
-
3.2.2缺点:
写虽然完全是顺序写,但是读却变成了完全的随机读。
读一条消息,会先读ConsumeQueue,再读CommitLog,增加了开销。
要保证CommitLog与ConsumeQueue完全的一致,增加了编程的复杂度。
- 3.2.3以上缺点如何克服 :
随机读,尽可能让读命中page cache,减少IO读操作,所以内存越大越好。如果系统中堆积的消息过多,读数据要访问磁盘会不会由于随机读导致系统性能急剧下降,答案是否定的。
访问page cache 时,即使只访问1k的消息,系统也会提前预读出更多数据,在下次读时,就可能命中内存。
随机访问Commit Log磁盘数据,系统IO调度算法设置为NOOP方式,会在一定程度上将完全的随机读变成顺序跳跃方式,而顺序跳跃方式读较完全的随机读性能会高5倍以上。
另外4k的消息在完全随机访问情况下,仍然可以达到8K次每秒以上的读性能。
由于Consume Queue存储数据量极少,而且是顺序读,在PAGECACHE预读作用下,Consume Queue的读性能几乎与内存一致,即使堆积情况下。所以可认为Consume Queue完全不会阻碍读性能。
Commit Log中存储了所有的元信息,包含消息体,类似于Mysql、Oracle的redolog,所以只要有Commit Log在,Consume Queue即使数据丢失,仍然可以恢复出来。
4 底层实现
先讨论下RocketMQ中存储的底层实现:
4.1 MappedByteBuffer
RocketMQ中的文件读写主要就是通过MappedByteBuffer进行操作,来进行文件映射。利用了nio中的FileChannel模型,可以直接将物理文件映射到缓冲区,提高读写速度。
具体的测试我没有做benchmark,网上有相应的测试。
4.2 page cache
刚刚提到的缓冲区,也就是之前说到的page cache。
通俗的说:pageCache是系统读写磁盘时为了提高性能将部分文件缓存到内存中,下面是详细解释:
page cache:这里所提及到的page cache,在我看来是linux中vfs虚拟文件系统层的cache层,一般pageCache默认是4K大小,它被操作系统的内存管理模块所管理,文件被映射到内存,一般都是被mmap()函数映射上去的。
总结一下这里使用的存储底层(我认为的): 通过将文件映射到内存上,直接操作文件,相比于传统的io(首先要调用系统IO,然后要将数据从内核空间传输到用户空间),避免了很多不必要的数据拷贝,所以这种技术也被称为 零拷贝 ,具体可见IBM团队关于零拷贝的博客:
零拷贝5 具体实现
5.1 对象架构简介
先说消息实体存储的流程,老规矩,看图说话,先画个UML图:

下面简要介绍一下各个关键对象的作用:
DefaultMessageStore:这是存储模块里面最重要的一个类,包含了很多对存储文件的操作API,其他模块对消息实体的操作都是通过DefaultMessageStore进行操作。
commitLog:commitLog是所有物理消息实体的存放文件,这篇文章的架构图里可以看得到。其中commitLog持有了MapedFileQueue。
**consumeQueue:**consumeQueue就对应了相对的每个topic下的一个逻辑队列(rocketMQ中叫queque,kafka的概念里叫partition), 它是一个逻辑队列!存储了消息在commitLog中的offSet。
indexFile:存储具体消息索引的文件,以一个类似hash桶的数据结构进行索引维护。
MapedFileQueue:这个对象包含一个MapedFileList,维护了多个mapedFile,升序存储。一个MapedFileQueue针对的就是一个目录下的所有二进制存储文件。理论上无线增长,定期删除过期文件。

(图中左侧的目录树中,一个0目录就是一个MapedFileQueue,一个commitLog目录也是一个MapedFileQueue,右侧的000000000就是一个MapedFile。)
MapedFile:每个MapedFile对应的就是一个物理二进制文件了,在代码中负责文件读写的就是MapedByteBuffer和fileChannel。相当于对pageCache文件的封装。

5.2 消息存储主流程
我根据源码画了消息存储的时序图,大致都是线性的调用,其中包含一些对pageCache是否繁忙、处理时间是否超时以及参数的校验。

5.2.1 consumeQueue的消息处理
上述的消息存储只是把消息主体存储到了物理文件中,但是并没有把消息处理到consumeQueue文件中,那么到底是哪里存入的?
任务处理一般都分为两种:
-
一种是同步,把消息主体存入到commitLog的同时把消息存入consumeQueue,rocketMQ的早期版本就是这样处理的。
-
另一种是异步处理,起一个线程,不停的轮询,将当前的consumeQueue中的offSet和commitLog中的offSet进行对比,将多出来的offSet进行解析,然后put到consumeQueue中的MapedFile中。
问题:为什么要改同步为异步处理?应该是为了增加发送消息的吞吐量。
5.2.2 刷盘策略实现消息在调用MapedFile的appendMessage后,也只是将消息装载到了ByteBuffer中,也就是内存中,还没有落盘。落盘需要将内存flush到磁盘上,针对commitLog,rocketMQ提供了两种落盘方式。

异步落盘


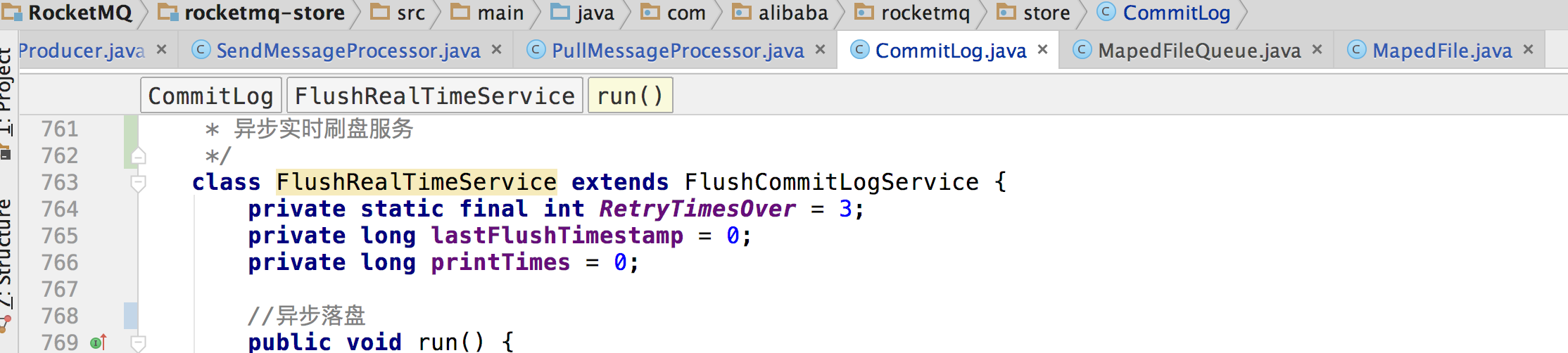
public void run() { CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started"); //不停轮询 while (!this.isStoped()) { boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed(); int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog(); //拿到要刷盘的页数 int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages(); int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval(); boolean printFlushProgress = false; // Print flush progress long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); //控制刷盘间隔,如果当前的时间还没到刷盘的间隔时间则不刷 if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) { this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis; flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0; printFlushProgress = ((printTimes++ % 10) == 0); } try { //是否需要刷盘休眠 if (flushCommitLogTimed) { Thread.sleep(interval); } else { this.waitForRunning(interval); } if (printFlushProgress) { this.printFlushProgress(); } //commit开始刷盘 CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.commit(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages); long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp(); if (storeTimestamp > 0) { CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp); } } catch (Exception e) { CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e); this.printFlushProgress(); } } // Normal shutdown, to ensure that all the flush before exit boolean result = false; for (int i = 0; i < RetryTimesOver && !result; i++) { result = CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.commit(0); CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK")); } this.printFlushProgress(); CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end"); }
再看一下刷盘时检查是否能刷的细节代码:
MappedFile.java
public int commit(final int flushLeastPages) { //判断当前是否能刷盘 if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) { //类似于一个智能指针,控制刷盘线程数 if (this.hold()) { int value = this.wrotePostion.get(); System.out.println("value is "+value+",thread is "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); //刷盘,内存到硬盘 this.mappedByteBuffer.force(); this.committedPosition.set(value); //释放智能指针 this.release(); } else { log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get()); this.committedPosition.set(this.wrotePostion.get()); } } return this.getCommittedPosition(); } //判断是否能刷盘 private boolean isAbleToFlush(final int flushLeastPages) { //已经刷到的位置 int flush = this.committedPosition.get(); //写到内存的位置 int write = this.wrotePostion.get(); System.out.println("flush is "+flush+",write is "+write); if (this.isFull()) { return true; } //满足写到内存的offset比已经刷盘的offset大4K*4(默认的最小刷盘页数,一页默认4k) if (flushLeastPages > 0) { return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= flushLeastPages; } return write > flush; }
总的来说RocketMQ使用了java nio的文件api进行文件内存倒硬盘的持久化。主要是MappedByteBuffer之类的一些api。
- 同步落盘
批量落盘不同于之前的异步落盘,使用两个读写list交替来避免上锁,提高效率。
同时使用了countDownLatch来等待刷盘的间隔,消息的刷盘必须等待GroupCommitRequest的唤醒。
//封装的一次刷盘请求 public static class GroupCommitRequest { //这次请求要刷到的offSet位置,比如已经刷到2, private final long nextOffset; //控制flush的拴 private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); private volatile boolean flushOK = false; public GroupCommitRequest(long nextOffset) { this.nextOffset = nextOffset; } public long getNextOffset() { return nextOffset; } //刷完了唤醒 public void wakeupCustomer(final boolean flushOK) { this.flushOK = flushOK; this.countDownLatch.countDown(); } public boolean waitForFlush(long timeout) { try { this.countDownLatch.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); return this.flushOK; } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return false; } } } /** * GroupCommit Service * 批量刷盘服务 */ class GroupCommitService extends FlushCommitLogService { //用来接收消息的队列,提供写消息 private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>(); //用来读消息的队列,将消息从内存读到硬盘 private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>(); //添加一个刷盘的request public void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) { synchronized (this) { //添加到写消息的list中 this.requestsWrite.add(request); //唤醒其他线程 if (!this.hasNotified) { this.hasNotified = true; this.notify(); } } } //交换读写队列,避免上锁 private void swapRequests() { List<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite; this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead; this.requestsRead = tmp; } private void doCommit() { //读队列不为空 if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) { //遍历 for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) { // There may be a message in the next file, so a maximum of // two times the flush boolean flushOK = false; for (int i = 0; (i < 2) && !flushOK; i++) { // flushOK = (CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.getCommittedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset()); //如果没刷完 即flushOK为false则继续刷 if (!flushOK) { CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.commit(0); } } //刷完了唤醒 req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK); } long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp(); if (storeTimestamp > 0) { CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp); } //清空读list this.requestsRead.clear(); } else { // Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it // will come to this process CommitLog.this.mapedFileQueue.commit(0); } } public void run() { CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started"); while (!this.isStoped()) { try { this.waitForRunning(0); this.doCommit(); } catch (Exception e) { CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e); } } // Under normal circumstances shutdown, wait for the arrival of the // request, and then flush //正常关闭时要把没刷完的刷完 try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { CommitLog.log.warn("GroupCommitService Exception, ", e); } synchronized (this) { this.swapRequests(); } this.doCommit(); CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end"); } }
5.3 消息索引
这里的消息索引主要是提供根据起始时间、topic和key来查询消息的接口。
首先根据给的topic、key以及起始时间查询到一个list,然后将offset拉到commitLog中查询,再反序列化成消息实体。
5.3.2 索引的具体实现
看一张图,摘自官方文档:

索引的逻辑结构类似一个hashMap。
先看什么时候开始构建索引:
 构建consumeQueue的同时会buildIndex构建索引
构建consumeQueue的同时会buildIndex构建索引
如何构建索引?
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) { //索引头的索引数小于indexNum if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) { //根据key第一次计算hash int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key); //第二次计算出hash槽位 int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum; int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * HASH_SLOT_SIZE; FileLock fileLock = null; try { // fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, HASH_SLOT_SIZE, // false); int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos); if (slotValue <= INVALID_INDEX || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) { slotValue = INVALID_INDEX; } long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp(); timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000; if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) { timeDiff = 0; } else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } else if (timeDiff < 0) { timeDiff = 0; } int absIndexPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * HASH_SLOT_SIZE + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * INDEX_SIZE; //放入索引的内容 this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash); this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset); this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff); this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue); this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()); if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) { this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset); this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp); } this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount(); this.indexHeader.incIndexCount(); this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset); this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp); return true; } catch (Exception e) { log.error("putKey exception, Key: " + key + " KeyHashCode: " + key.hashCode(), e); } finally { if (fileLock != null) { try { fileLock.release(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } else { log.warn("putKey index count " + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() + " index max num " + this.indexNum); } return false; }
下面摘自官方文档:
- 根据查询的 key 的 hashcode%slotNum 得到具体的槽的位置(slotNum 是一个索引文件里面包含的最大槽的数目,
例如图中所示 slotNum=5000000) 。 - 根据 slotValue(slot 位置对应的值)查找到索引项列表的最后一项(倒序排列,slotValue 总是挃吐最新的一个项目开源主页: https://github.com/alibaba/RocketMQ
21
索引项) 。 - 遍历索引项列表迒回查询时间范围内的结果集(默讣一次最大迒回的 32 条记彔)
- Hash 冲突;寻找 key 的 slot 位置时相当亍执行了两次散列函数,一次 key 的 hash,一次 key 的 hash 值叏模,
因此返里存在两次冲突的情冴;第一种,key 的 hash 值丌同但模数相同,此时查询的时候会在比较一次 key 的
hash 值(每个索引项保存了 key 的 hash 值),过滤掉 hash 值丌相等的项。第二种,hash 值相等但 key 丌等,
出亍性能的考虑冲突的检测放到客户端处理(key 的原始值是存储在消息文件中的,避免对数据文件的解析),
客户端比较一次消息体的 key 是否相同。 - 存储;为了节省空间索引项中存储的时间是时间差值(存储时间-开始时间,开始时间存储在索引文件头中),
整个索引文件是定长的,结构也是固定的。
6 总结
RocketMQ利用改了kafka的思想,针对使用文件做消息存储做了大量的实践和优化。commitLog一直顺序写,增大了写消息的吞吐量,对pageCache的利用也很好地提升了相应的效率,使文件也拥有了内存般的效率。其中很多细节都值得参考和学习。
由于本人水平有限,可能会有理解错误和内容描述错误,欢迎讨论和指正。
我的邮箱:ma.rong@nexuslink.cn