本次笔记记录两个问题:
1,条件变量在使用时会有信号丢失现象;(使用g_nums记录信号,防止信号丢失)
2,条件变量的wait内部锁操作会在惊群现象的时候访问不可用资源,存在潜在的风险;(wait后再次对可用资源进行判断,防止操作不可用资源情况的发生)
在例子代码中都对上面两个现象实现对应的解决方案。
先列出第一种情况的例子
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 7 pthread_cond_t cond; 8 9 10 void* thread1( void* arg) 11 { 12 while(1) 13 { 14 15 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 16 17 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); 18 19 std::cout<<"the thread1 info: "<<std::endl; 20 21 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 22 sleep(1); 23 } 24 25 return NULL; 26 } 27 28 void* thread2(void* arg) 29 { 30 31 while(true){ 32 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 33 34 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); 35 36 std::cout<<"the thread2 info: "<<std::endl; 37 38 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 39 40 sleep(1); 41 } 42 43 return NULL; 44 } 45 46 47 int main( int argc, char*argv[] ) 48 { 49 pthread_t t1,t2; 50 51 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 52 53 pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); 54 55 pthread_create(&t1, NULL, thread1, NULL); 56 pthread_create(&t2, NULL, thread2, NULL); 57 58 //sleep(3); 59 60 for(size_t i=0; i<10; ++i) 61 { 62 //when send a signal to a cond, if no thread is waiting for this cond, so the signal will lost. 63 64 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 65 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); 66 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 67 68 //sleep(1); 69 } 70 71 std::cout<<"Please input the Enter to quit. "; 72 getchar();//sleep(10); 73 74 return 0; 75 }
运行结果:
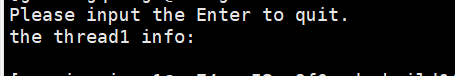
可见,发送了10次信号 ,条件变量却只触发了一次。该问题的解决方案会在后面给出的代码中写出,即使用g_nums来记录条件信号的个数。
下面来看看该笔记中的2)这种情况,惊群现象。。。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 7 pthread_cond_t cond; 8 9 int g_nums=0;//如果没有这个计数,条件信号会有部分丢失,即在wait之前发的信号都会丢失 10 11 void* thread1( void* arg) 12 { 13 while(1) 14 { 15 16 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 17 18 if(g_nums <=0 ) 19 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); 20 21 //sleep(2); 22 if(g_nums <=0 ){//防止惊群现象,wait后再次lock但另一个线程已经用光了资源,如果不检查就使用会出问题 23 std::cout<<"the thread1 conflict.. "; 24 continue; 25 } 26 27 --g_nums; 28 29 std::cout<<"the thread1 info: "<<std::endl; 30 31 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 32 sleep(1); 33 } 34 35 return NULL; 36 } 37 38 void* thread2(void* arg) 39 { 40 41 while(true){ 42 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 43 44 if(g_nums <=0) 45 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); 46 47 if(g_nums <= 0){//防止惊群现象,wait后再次lock但另一个线程已经用光了资源,如果不检查就使用会出问题 48 std::cout<<"thread2 conflict... "; 49 continue; 50 } 51 --g_nums; 52 53 std::cout<<"the thread2 info: "<<std::endl; 54 55 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 56 57 sleep(1); 58 } 59 60 return NULL; 61 } 62 63 64 int main( int argc, char*argv[] ) 65 { 66 pthread_t t1,t2; 67 68 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 69 70 pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); 71 72 pthread_create(&t1, NULL, thread1, NULL); 73 pthread_create(&t2, NULL, thread2, NULL); 74 75 //sleep(3); 76 77 for(size_t i=0; i<1; ++i) 78 { 79 //when send a signal to a cond, if no thread is waiting for this cond, so the signal will lost. 80 81 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 82 ++g_nums; 83 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); 84 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 85 86 //sleep(1); 87 } 88 89 std::cout<<"Please input the Enter to quit. "; 90 getchar();//sleep(10); 91 92 return 0; 93 }
运行结果如下:

这种惊群现象不是必现的,但是有这个风险;所以在编程的时候需要注意这个坑。
造成这种情况的原因:
条件变量在与互斥量配合使用中,wait对互斥进行了如下操作,
1)lock——>2)如果没有可用资源则unlock,同时等待条件唤醒——>3)收到条件通知后——>4)lock——处理任务,dosomething...——>5)unlock
从上面的过程可以发现,3)是一个风险点,就像上面的例子一样,thread1和thread2同时收到通知,但thread2处理的快,thread1比较慢,此时thread2处理完任务并unlock,然后thread1才到4)lock,接下来如果thread1继续处理任务就是不对的了,如果是处理一个指针就可能造成系统崩溃;
本文为原创文章,如果转载请写明出处https://www.cnblogs.com/guoliushui/p/9510359.html