一、二次代价函数
1. 形式:

其中,C为代价函数,X表示样本,Y表示实际值,a表示输出值,n为样本总数
2. 利用梯度下降法调整权值参数大小,推导过程如下图所示:

根据结果可得,权重w和偏置b的梯度跟激活函数的梯度成正比(即激活函数的梯度越大,w和b的大小调整的越快,训练速度也越快)
3. 激活函数是sigmoid函数时,二次代价函数调整参数过程分析
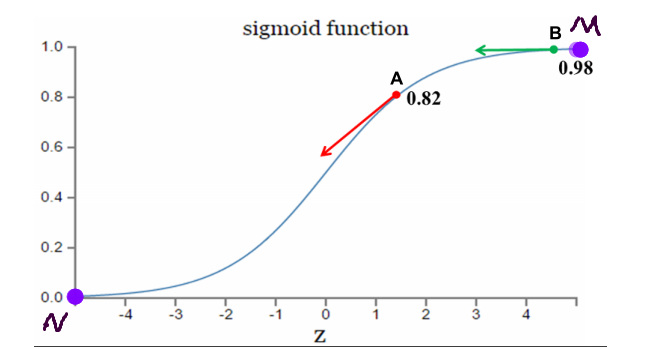
理想调整参数状态:距离目标点远时,梯度大,参数调整较快;距离目标点近时,梯度小,参数调整较慢。
如果我的目标点是调整到M点,从A点==>B点的调整过程,A点距离目标点远,梯度大,调整参数较快;B点距离目标较近,梯度小,调整参数慢。符合参数调整策略
如果我的目标点是调整到N点,从B点==>A点的调整过程,A点距离目标点近,梯度大,调整参数较快;B点距离目标较远,梯度小,调整参数慢。不符合参数调整策略
二、交叉熵代价函数
1.形式:

其中,C为代价函数,X表示样本,Y表示实际值,a表示输出值,n为样本总数
2. 利用梯度下降法调整权值参数大小,推导过程如下图所示:

根据结果可得,权重w和偏置b的梯度跟激活函数的梯度无关。而和输出值与实际值的误差成正比(即误差越大,w和b的大小调整的越快,训练速度也越快)
3.激活函数是sigmoid函数时,二次代价函数调整参数过程分析
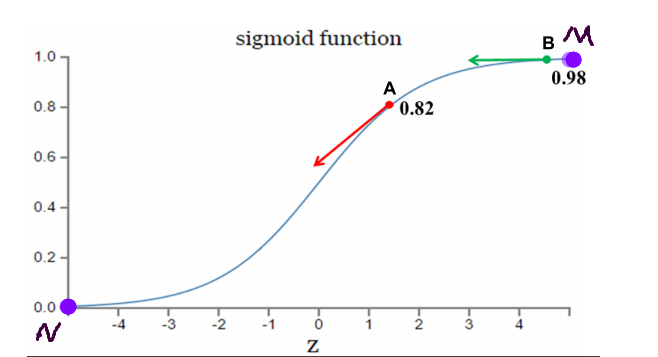
理想调整参数状态:距离目标点远时,梯度大,参数调整较快;距离目标点近时,梯度小,参数调整较慢。
如果我的目标点是调整到M点,从A点==>B点的调整过程,A点距离目标点远,误差大,调整参数较快;B点距离目标较近,误差小,调整参数较慢。符合参数调整策略
如果我的目标点是调整到N点,从B点==>A点的调整过程,A点距离目标点近,误差小,调整参数较慢;B点距离目标较远,误差大,调整参数较快。符合参数调整策略
总结:
- 如果输出神经元是线性的,选择二次代价函数较为合适
- 如果输出神经元是S型函数(sigmoid函数),选择交叉熵代价函数较为合适
- 如果输出神经元是softmax回归的代价函数,选择对数释然代价函数较为合适
二、利用代价函数优化MNIST数据集识别程序
1.在Tensorflow中代价函数的选择:
如果输出神经元是线性的,选择二次代价函数较为合适 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square())
如果输出神经元是S型函数(sigmoid函数),选择交叉熵代价函数较为合适 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits())
如果输出神经元是softmax回归的代价函数,选择对数释然代价函数较为合适 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits())
2.通过代价函数选择对MNIST数据集分类程序优化
#使用交叉熵代价函数

1 import os 2 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 5 #载入数据集 6 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) 7 #每个批次的大小(即每次训练的图片数量) 8 batch_size = 50 9 #计算一共有多少个批次 10 n_bitch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size 11 #定义两个placeholder 12 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) 13 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) 14 #创建一个只有输入层(784个神经元)和输出层(10个神经元)的简单神经网络 15 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) 16 Biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) 17 Wx_plus_B = tf.matmul(x, Weights) + Biases 18 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_B) 19 #交叉熵代价函数 20 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction)) 21 #使用梯度下降法 22 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.15).minimize(loss) 23 #初始化变量 24 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 25 #结果存放在一个布尔型列表中 26 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1)) #argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置,标签值和预测值相同,返回为True 27 #求准确率 28 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) #cast函数将correct_prediction的布尔型转换为浮点型,然后计算平均值即为准确率 29 30 with tf.Session() as sess: 31 sess.run(init) 32 #将测试集循环训练20次 33 for epoch in range(21): 34 #将测试集中所有数据循环一次 35 for batch in range(n_bitch): 36 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) #取测试集中batch_size数量的图片及对应的标签值 37 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys}) #将上一行代码取到的数据进行训练 38 acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels}) #准确率的计算 39 print('Iter : ' + str(epoch) + ',Testing Accuracy = ' + str(acc))
#执行结果

1 Iter : 0,Testing Accuracy = 0.8323 2 Iter : 1,Testing Accuracy = 0.8947 3 Iter : 2,Testing Accuracy = 0.9032 4 Iter : 3,Testing Accuracy = 0.9068 5 Iter : 4,Testing Accuracy = 0.909 6 Iter : 5,Testing Accuracy = 0.9105 7 Iter : 6,Testing Accuracy = 0.9126 8 Iter : 7,Testing Accuracy = 0.9131 9 Iter : 8,Testing Accuracy = 0.9151 10 Iter : 9,Testing Accuracy = 0.9168 11 Iter : 10,Testing Accuracy = 0.9178 12 Iter : 11,Testing Accuracy = 0.9173 13 Iter : 12,Testing Accuracy = 0.9181 14 Iter : 13,Testing Accuracy = 0.9194 15 Iter : 14,Testing Accuracy = 0.9201 16 Iter : 15,Testing Accuracy = 0.9197 17 Iter : 16,Testing Accuracy = 0.9213 18 Iter : 17,Testing Accuracy = 0.9212 19 Iter : 18,Testing Accuracy = 0.9205 20 Iter : 19,Testing Accuracy = 0.9215
#使用二次代价函数

1 import os 2 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 5 #载入数据集 6 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) 7 #每个批次的大小(即每次训练的图片数量) 8 batch_size = 100 9 #计算一共有多少个批次 10 n_bitch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size 11 #定义两个placeholder 12 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) 13 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) 14 #创建一个只有输入层(784个神经元)和输出层(10个神经元)的简单神经网络 15 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) 16 Biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) 17 Wx_plus_B = tf.matmul(x, Weights) + Biases 18 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_B) 19 #二次代价函数 20 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - prediction)) 21 #使用梯度下降法 22 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss) 23 #初始化变量 24 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 25 #结果存放在一个布尔型列表中 26 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1)) #argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置,标签值和预测值相同,返回为True 27 #求准确率 28 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) #cast函数将correct_prediction的布尔型转换为浮点型,然后计算平均值即为准确率 29 30 with tf.Session() as sess: 31 sess.run(init) 32 #将测试集循环训练20次 33 for epoch in range(21): 34 #将测试集中所有数据循环一次 35 for batch in range(n_bitch): 36 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) #取测试集中batch_size数量的图片及对应的标签值 37 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys}) #将上一行代码取到的数据进行训练 38 acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels}) #准确率的计算 39 print('Iter : ' + str(epoch) + ',Testing Accuracy = ' + str(acc))
#执行结果

1 Iter : 0,Testing Accuracy = 0.8325 2 Iter : 1,Testing Accuracy = 0.8711 3 Iter : 2,Testing Accuracy = 0.8831 4 Iter : 3,Testing Accuracy = 0.8876 5 Iter : 4,Testing Accuracy = 0.8942 6 Iter : 5,Testing Accuracy = 0.898 7 Iter : 6,Testing Accuracy = 0.9002 8 Iter : 7,Testing Accuracy = 0.9014 9 Iter : 8,Testing Accuracy = 0.9036 10 Iter : 9,Testing Accuracy = 0.9052 11 Iter : 10,Testing Accuracy = 0.9065 12 Iter : 11,Testing Accuracy = 0.9073 13 Iter : 12,Testing Accuracy = 0.9084 14 Iter : 13,Testing Accuracy = 0.909 15 Iter : 14,Testing Accuracy = 0.9095 16 Iter : 15,Testing Accuracy = 0.9115 17 Iter : 16,Testing Accuracy = 0.912 18 Iter : 17,Testing Accuracy = 0.9126 19 Iter : 18,Testing Accuracy = 0.913 20 Iter : 19,Testing Accuracy = 0.9136 21 Iter : 20,Testing Accuracy = 0.914
结论:(二者只有代价函数不同)
- 正确率达到90%所用迭代次数:使用交叉熵代价函数为第三次;使用二次代价函数为第六次(在MNIST数据集分类中,使用交叉熵代价函数收敛速度较快)
- 最终正确率:使用交叉熵代价函数为92.15%,使用二次代价函数为91.4%(在MNIST数据集分类中,使用交叉熵代价函数识别准确率较高)
三、拟合问题
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/willduan1/article/details/53070777
1.根据拟合结果分类:
- 欠拟合:模型没有很好地捕捉到数据特征,不能够很好地拟合数据
- 正确拟合
- 过拟合:模型把数据学习的太彻底,以至于把噪声数据的特征也学习到了,这样就会导致在后期测试的时候不能够很好地识别数据,即不能正确的分类,模型泛化能力太差
2.解决欠拟合和过拟合
解决欠拟合常用方法:
- 添加其他特征项,有时候我们模型出现欠拟合的时候是因为特征项不够导致的,可以添加其他特征项来很好地解决。
- 添加多项式特征,这个在机器学习算法里面用的很普遍,例如将线性模型通过添加二次项或者三次项使模型泛化能力更强。
- 减少正则化参数,正则化的目的是用来防止过拟合的,但是现在模型出现了欠拟合,则需要减少正则化参数。
解决过拟合常用方法:
- 增加数据集
- 正则化方法
- Dropout(通俗一点讲就是dropout方法在训练的时候让神经元以一定的概率不工作)
四、初始化优化MNIST数据集分类问题
#改变初始化方法
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([784, 10]))
Biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]) + 0.1)
五、优化器优化MNIST数据集分类问题
大多数机器学习任务就是最小化损失,在损失定义的情况下,后面的工作就交给优化器。
因为深度学习常见的是对于梯度的优化,也就是说,优化器最后其实就是各种对于梯度下降算法的优化。
1.梯度下降法分类及其介绍
- 标准梯度下降法:先计算所有样本汇总误差,然后根据总误差来更新权值
- 随机梯度下降法:随机抽取一个样本来计算误差,然后更新权值
- 批量梯度下降法:是一种折中方案,从总样本中选取一个批次(batch),然后计算这个batch的总误差,根据总误差来更新权值
2.常见优化器介绍
参考文章:
https://www.leiphone.com/news/201706/e0PuNeEzaXWsMPZX.html
3.优化器优化MNIST数据集分类问题
#选择Adam优化器

1 import os 2 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 5 #载入数据集 6 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) 7 #每个批次的大小(即每次训练的图片数量) 8 batch_size = 50 9 #计算一共有多少个批次 10 n_bitch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size 11 #定义两个placeholder 12 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) 13 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) 14 #创建一个只有输入层(784个神经元)和输出层(10个神经元)的简单神经网络 15 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) 16 Biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) 17 Wx_plus_B = tf.matmul(x, Weights) + Biases 18 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_B) 19 #交叉熵代价函数 20 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction)) 21 #使用Adam优化器 22 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-2).minimize(loss) 23 #初始化变量 24 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 25 #结果存放在一个布尔型列表中 26 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1)) #argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置,标签值和预测值相同,返回为True 27 #求准确率 28 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) #cast函数将correct_prediction的布尔型转换为浮点型,然后计算平均值即为准确率 29 30 with tf.Session() as sess: 31 sess.run(init) 32 #将测试集循环训练20次 33 for epoch in range(21): 34 #将测试集中所有数据循环一次 35 for batch in range(n_bitch): 36 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) #取测试集中batch_size数量的图片及对应的标签值 37 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys}) #将上一行代码取到的数据进行训练 38 acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels}) #准确率的计算 39 print('Iter : ' + str(epoch) + ',Testing Accuracy = ' + str(acc))
#执行结果

Iter : 1,Testing Accuracy = 0.9224 Iter : 2,Testing Accuracy = 0.9293 Iter : 3,Testing Accuracy = 0.9195 Iter : 4,Testing Accuracy = 0.9282 Iter : 5,Testing Accuracy = 0.926 Iter : 6,Testing Accuracy = 0.9291 Iter : 7,Testing Accuracy = 0.9288 Iter : 8,Testing Accuracy = 0.9274 Iter : 9,Testing Accuracy = 0.9277 Iter : 10,Testing Accuracy = 0.9249 Iter : 11,Testing Accuracy = 0.9313 Iter : 12,Testing Accuracy = 0.9301 Iter : 13,Testing Accuracy = 0.9315 Iter : 14,Testing Accuracy = 0.9295 Iter : 15,Testing Accuracy = 0.9299 Iter : 16,Testing Accuracy = 0.9303 Iter : 17,Testing Accuracy = 0.93 Iter : 18,Testing Accuracy = 0.9304 Iter : 19,Testing Accuracy = 0.9269 Iter : 20,Testing Accuracy = 0.9273
注意:不同优化器参数的设置是关键。在机器学习中,参数的调整应该是技术加经验,而不是盲目调整。这边是我以后需要学习和积累的地方
六、根据今天所学内容,对MNIST数据集分类进行优化,准确率达到95%以上
#优化程序

1 import os 2 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 5 #载入数据集 6 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) 7 #每个批次的大小(即每次训练的图片数量) 8 batch_size = 50 9 #计算一共有多少个批次 10 n_bitch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size 11 #定义两个placeholder 12 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) 13 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) 14 #创建一个只有输入层(784个神经元)和输出层(10个神经元)的简单神经网络 15 Weights1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([784, 200])) 16 Biases1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([200]) + 0.1) 17 Wx_plus_B_L1 = tf.matmul(x, Weights1) + Biases1 18 L1 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_B_L1) 19 20 Weights2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([200, 50])) 21 Biases2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([50]) + 0.1) 22 Wx_plus_B_L2 = tf.matmul(L1, Weights2) + Biases2 23 L2 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_B_L2) 24 25 Weights3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([50, 10])) 26 Biases3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]) + 0.1) 27 Wx_plus_B_L3 = tf.matmul(L2, Weights3) + Biases3 28 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_B_L3) 29 30 #交叉熵代价函数 31 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction)) 32 #使用梯度下降法 33 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2e-3).minimize(loss) 34 #初始化变量 35 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 36 #结果存放在一个布尔型列表中 37 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1)) 38 #求准确率 39 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) 40 41 with tf.Session() as sess: 42 sess.run(init) 43 #将测试集循环训练50次 44 for epoch in range(51): 45 #将测试集中所有数据循环一次 46 for batch in range(n_bitch): 47 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) #取测试集中batch_size数量的图片及对应的标签值 48 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys}) #将上一行代码取到的数据进行训练 49 test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels}) #准确率的计算 50 print('Iter : ' + str(epoch) + ',Testing Accuracy = ' + str(test_acc))
#执行结果

1 Iter : 0,Testing Accuracy = 0.6914 2 Iter : 1,Testing Accuracy = 0.7236 3 Iter : 2,Testing Accuracy = 0.8269 4 Iter : 3,Testing Accuracy = 0.8885 5 Iter : 4,Testing Accuracy = 0.9073 6 Iter : 5,Testing Accuracy = 0.9147 7 Iter : 6,Testing Accuracy = 0.9125 8 Iter : 7,Testing Accuracy = 0.922 9 Iter : 8,Testing Accuracy = 0.9287 10 Iter : 9,Testing Accuracy = 0.9248 11 Iter : 10,Testing Accuracy = 0.9263 12 Iter : 11,Testing Accuracy = 0.9328 13 Iter : 12,Testing Accuracy = 0.9316 14 Iter : 13,Testing Accuracy = 0.9387 15 Iter : 14,Testing Accuracy = 0.9374 16 Iter : 15,Testing Accuracy = 0.9433 17 Iter : 16,Testing Accuracy = 0.9419 18 Iter : 17,Testing Accuracy = 0.9379 19 Iter : 18,Testing Accuracy = 0.9379 20 Iter : 19,Testing Accuracy = 0.9462 21 Iter : 20,Testing Accuracy = 0.9437 22 Iter : 21,Testing Accuracy = 0.9466 23 Iter : 22,Testing Accuracy = 0.9479 24 Iter : 23,Testing Accuracy = 0.9498 25 Iter : 24,Testing Accuracy = 0.9481 26 Iter : 25,Testing Accuracy = 0.9489 27 Iter : 26,Testing Accuracy = 0.9496 28 Iter : 27,Testing Accuracy = 0.95 29 Iter : 28,Testing Accuracy = 0.9508 30 Iter : 29,Testing Accuracy = 0.9533 31 Iter : 30,Testing Accuracy = 0.9509 32 Iter : 31,Testing Accuracy = 0.9516 33 Iter : 32,Testing Accuracy = 0.9541 34 Iter : 33,Testing Accuracy = 0.9513 35 Iter : 34,Testing Accuracy = 0.951 36 Iter : 35,Testing Accuracy = 0.9556 37 Iter : 36,Testing Accuracy = 0.9527 38 Iter : 37,Testing Accuracy = 0.9521 39 Iter : 38,Testing Accuracy = 0.9546 40 Iter : 39,Testing Accuracy = 0.9544 41 Iter : 40,Testing Accuracy = 0.9555 42 Iter : 41,Testing Accuracy = 0.9546 43 Iter : 42,Testing Accuracy = 0.9553 44 Iter : 43,Testing Accuracy = 0.9534 45 Iter : 44,Testing Accuracy = 0.9576 46 Iter : 45,Testing Accuracy = 0.9535 47 Iter : 46,Testing Accuracy = 0.9569 48 Iter : 47,Testing Accuracy = 0.9556 49 Iter : 48,Testing Accuracy = 0.9568 50 Iter : 49,Testing Accuracy = 0.956 51 Iter : 50,Testing Accuracy = 0.9557
#写在后面
呀呀呀呀
本来想着先把python学差不多再开始机器学习和这些框架的学习
老师触不及防的任务
给了论文 让我搭一个模型出来
我只能硬着头皮上了
不想用公式编译器了
手写版计算过程 请忽略那丑丑的字儿
加油哦!小伙郭
