一、 命令(Command)模式
命令(Command)模式属于对象的行为模式【GOF95】。命令模式又称为行动(Action)模式或交易(Transaction)模式。命令模式把一个请求或者操作封装到一个对象中。命令模式允许系统使用不同的请求把客户端参数化,对请求排队或者记录请求日志,可以提供命令的撤销和恢复功能。
命令模式是对命令的封装。命令模式把发出命令的责任和执行命令的责任分割开,委派给不同的对象。
每一个命令都是一个操作:请求的一方发出请求要求执行一个操作;接收的一方收到请求,并执行操作。命令模式允许请求的一方和接收的一方独立开来,使得请求的一方不必知道接收请求的一方的接口,更不必知道请求是怎么被接收,以及操作是否被执行、何时被执行,以及是怎么被执行的。
二、 命令模式的结构
既然,命令模式是实现把发出命令的责任和执行命令的责任分割开,然而中间必须有某个对象来帮助发出命令者来传达命令,使得执行命令的接收者可以收到命令并执行命令。例如,开学了,院领导说计算机学院要进行军训,计算机学院的学生要跑1000米,院领导的话也就相当于一个命令,他不可能直接传达给到学生,他必须让教官来发出命令,并监督学生执行该命令。在这个场景中,发出命令的责任是属于学院领导,院领导充当与命令发出者的角色,执行命令的责任是属于学生,学生充当于命令接收者的角色,而教官就充当于命令的发出者或命令请求者的角色,然而命令模式的精髓就在于把每个命令抽象为对象。从而命令模式的结构如下图所示:
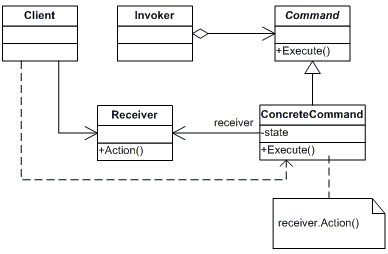
从命令模式的结构图可以看出,它涉及到五个角色,它们分别是:
- 客户(Client)角色:发出一个具体的命令(ConcreteCommand)并确定其接受者。
- 命令(Command)角色:声明了一个给所有具体命令类实现的抽象接口
- 具体命令(ConcreteCommand)角色:定义了一个接受者和行为的弱耦合,负责调用接受者的相应方法。
- 请求者(Invoker)角色:负责调用命令对象执行命令。
- 接受者(Receiver)角色:负责具体行为的执行。任何一个类都可以成为接收者,实施和执行请求的方法叫做行动方法。
三、 命令模式的示意性源代码
// Command pattern -- Structural example using System; // "Command" abstract class Command { // Fields protected Receiver Receiver; // Constructors protected Command(Receiver receiver) { this.Receiver = receiver; } // Methods abstract public void Execute(); } // "ConcreteCommand" class ConcreteCommand : Command { // Constructors public ConcreteCommand(Receiver receiver) : base(receiver) { } // Methods public override void Execute() { Receiver.Action(); } } // "Receiver" class Receiver { // Methods public void Action() { Console.WriteLine("Called Receiver.Action()"); } } // "Invoker" class Invoker { // Fields private Command _command; // Methods public void SetCommand(Command command) { this._command = command; } public void ExecuteCommand() { _command.Execute(); } } /// <summary> /// Client test /// </summary> public class Client { public static void Main(string[] args) { // Create receiver, command, and invoker var r = new Receiver(); Command c = new ConcreteCommand(r); var i = new Invoker(); // Set and execute command i.SetCommand(c); i.ExecuteCommand(); } }
四、 命令模式的实现
首先命令应当"重"一些还是"轻"一些。在不同的情况下,可以做不同的选择。如果把命令设计得"轻",那么它只是提供了一个请求者和接收者之间的耦合而己,命令代表请求者实现请求。
相反,如果把命令设计的"重",那么它就应当实现所有的细节,包括请求所代表的操作,而不再需要接收者了。当一个系统没有接收者时,就可以采用这种做法。
更常见的是处于最"轻"和最"重"的两个极端之间时情况。命令类动态地决定调用哪一个接收者类。
其次是否支持undo和redo。如果一个命令类提供一个方法,比如叫unExecute(),以恢复其操作的效果,那么命令类就可以支持undo和redo。具体命令类需要存储状态信息,包括:
- 接收者对象实际上实施请求所代表的操作;
- 对接收者对象所作的操作所需要的参数;
- 接收者类的最初的状态。接收者必须提供适当的方法,使命令类可以通过调用这个方法,以便接收者类恢复原有状态。
如果只需要提供一层的undo和redo,那么系统只需要存储最后被执行的那个命令对象。如果需要支持多层的undo和redo,那么系统就需要存储曾经被执行过的命令的清单,清单能允许的最大的长度便是系统所支持的undo和redo的层数。沿着清单逆着执行清单上的命令的反命令(unExecute())便是undo;沿着清单顺着执行清单上的命令便是redo。
五、 命令模式的实际应用案例
下面的代码使用命令模式演示了一个简单的计算器,并允许执行undo与redo。注意:"operator"在C#中是关键词,所以在前面添加一个"@"将其变为标识符。
// Command pattern -- Real World example using System; using System.Collections; // "Command" abstract class Command { // Methods abstract public void Execute(); abstract public void UnExecute(); } // "ConcreteCommand" class CalculatorCommand : Command { // Fields char _operator; int _operand; readonly Calculator _calculator; // Constructor public CalculatorCommand(Calculator calculator, char @operator, int operand) { this._calculator = calculator; this._operator = @operator; this._operand = operand; } // Properties public char Operator { set { _operator = value; } } public int Operand { set { _operand = value; } } // Methods override public void Execute() { _calculator.Operation(_operator, _operand); } override public void UnExecute() { _calculator.Operation(Undo(_operator), _operand); } // Private helper function private char Undo(char @operator) { char undo = ' '; switch (@operator) { case '+': undo = '-'; break; case '-': undo = '+'; break; case '*': undo = '/'; break; case '/': undo = '*'; break; } return undo; } } // "Receiver" class Calculator { // Fields private int _total = 0; // Methods public void Operation(char @operator, int operand) { switch (@operator) { case '+': _total += operand; break; case '-': _total -= operand; break; case '*': _total *= operand; break; case '/': _total /= operand; break; } Console.WriteLine("Total = {0} (following {1} {2})", _total, @operator, operand); } } // "Invoker" class User { // Fields private readonly Calculator _calculator = new Calculator(); private readonly ArrayList _commands = new ArrayList(); private int _current = 0; // Methods public void Redo(int levels) { Console.WriteLine("---- Redo {0} levels ", levels); // Perform redo operations for (int i = 0; i < levels; i++) if (_current < _commands.Count - 1) ((Command)_commands[_current++]).Execute(); } public void Undo(int levels) { Console.WriteLine("---- Undo {0} levels ", levels); // Perform undo operations for (int i = 0; i < levels; i++) if (_current > 0) ((Command)_commands[--_current]).UnExecute(); } public void Compute(char @operator, int operand) { // Create command operation and execute it Command command = new CalculatorCommand( _calculator, @operator, operand); command.Execute(); // Add command to undo list _commands.Add(command); _current++; } } /// <summary> /// CommandApp test /// </summary> public class Client { public static void Main(string[] args) { // Create user and let her compute var user = new User(); user.Compute('+', 100); user.Compute('-', 50); user.Compute('*', 10); user.Compute('/', 2); // Undo and then redo some commands user.Undo(4); user.Redo(3); } }
六、 命令模式的适用场景
在下面的情况下可以考虑使用命令模式:
- 系统需要支持命令的撤销(undo)。命令对象可以把状态存储起来,等到客户端需要撤销命令所产生的效果时,可以调用undo方法吧命令所产生的效果撤销掉。命令对象还可以提供redo方法,以供客户端在需要时,再重新实现命令效果。
- 系统需要在不同的时间指定请求、将请求排队。一个命令对象和原先的请求发出者可以有不同的生命周期。意思为:原来请求的发出者可能已经不存在了,而命令对象本身可能仍是活动的。这时命令的接受者可以在本地,也可以在网络的另一个地址。命令对象可以串行地传送到接受者上去。
- 如果一个系统要将系统中所有的数据消息更新到日志里,以便在系统崩溃时,可以根据日志里读回所有数据的更新命令,重新调用方法来一条一条地执行这些命令,从而恢复系统在崩溃前所做的数据更新。
- 系统需要使用命令模式作为“CallBack(回调)”在面向对象系统中的替代。Callback即是先将一个方法注册上,然后再以后调用该方法。
- 一个系统需要支持交易(Transaction)。一个交易结构封装了一组数据更新命令。使用命令模式来实现交易结构可以使系统增加新的交易类型。
七、 命令模式的优缺点
命令模式使得命令发出的一个和接收的一方实现低耦合,从而有以下的优点:
- 命令模式使得新的命令很容易被加入到系统里。
- 可以设计一个命令队列来实现对请求的Undo和Redo操作。
- 可以较容易地将命令写入日志。
- 可以把命令对象聚合在一起,合成为合成命令。合成命令式合成模式的应用。
命令模式的缺点:
- 使用命令模式可能会导致系统有过多的具体命令类。这会使得命令模式在这样的系统里变得不实际。