一课后作业 字串加密
1.设计思想
1)设置主方法,引入包;2)定义字符串,输入字符串;3)设置一个字符变量,设置循环,令字符变量等于字符串中下标为i的字符,根据ASCII码设置,输出。
2.流程图
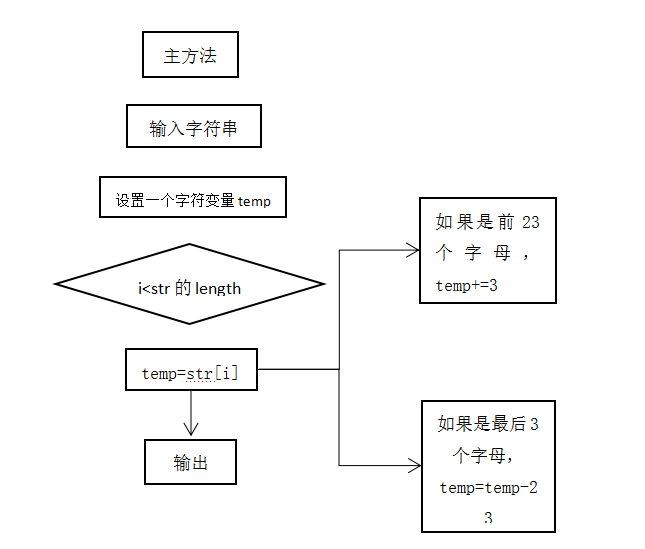
3.源程序
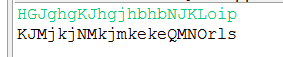
1 //2016/10/25 高雪彤 2 //字串加密 3 4 import java.io.*; 5 public class Exercise { 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 7 8 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));//输入 9 String str = reader.readLine(); 10 11 char CharArray; 12 for(int i =0;i<str.length();i++)//逐个输出字符 13 { 14 CharArray=(char)(str.charAt(i)); 15 if((CharArray>=65&&CharArray<=87)||(CharArray>=97&&CharArray<=119)) 16 { 17 CharArray += 3; 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 CharArray = (char) (CharArray-23); 22 } 23 System.out.print(CharArray); 24 } 25 } 26 }
4.结果截图
二动手动脑 字符串判等问题
1)问题:请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?
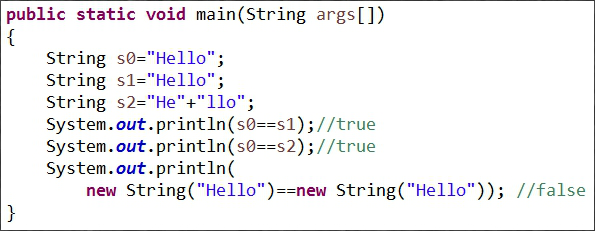
2)分析:
在Java中,内容相同的字串常量(“Hello”)只保存一份以节约内存,所以s0,s1,s2实际上引用的是同一个对象。
编译器在编译s2一句时,会去掉“+”号,直接把两个字串连接起来得一个字串(“Hello”)。这种优化工作由Java编译器自动完成。
当直接使用new关键字创建字符串对象时,虽然值一致(都是“Hello”),但仍然是两个独立的对象。
3)问题:为什么会有上述的输出结果?从中你又能总结出什么?

4)结果:
给字串变量赋值意味着:两个变量(s1,s2)现在引用同一个字符串对象“a”!
String对象的内容是只读的,使用“+”修改s1变量的值,实际上是得到了一个新的字符串对象,其内容为“ab”,它与原先s1所引用的对象”a”无关,所以,s1==s2返回false;
代码中的“ab”字符串是一个常量,它所引用的字符串与s1所引用的“ab”对象无关。 但是若"s1="ab"",再判断“s1=="ab"",结果为true。
String.equals()方法可以比较两个字符串的内容。
三动手动脑 String.equals()
1)问题:请查看String.equals()方法的实现代码,注意学习其实现方法。
2)代码:
1 public class StringEquals { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 String s1=new String("Hello"); 5 String s2=new String("Hello"); 6 7 System.out.println(s1==s2); 8 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); 9 10 String s3="Hello"; 11 String s4="Hello"; 12 13 System.out.println(s3==s4); 14 System.out.println(s3.equals(s4)); 15 } 16 }
3)结果截图:
4)分析:
equals()或equalsIgnoreCase()方法比较两字串内容是否相同,使用==比较两字串变量是否引用同一字串对象;
compareTo:使用字典法进行比较,返回0表两字串相等,小于返回负值,大于返回正值;
regionMatches:比较两字串中的某一部分是否相等。
四动手动脑 字符串常用功能
1)源代码:
1 //StringMisc.java 2 // This program demonstrates the length, charAt and getChars 3 // methods of the String class. 4 // 5 // Note: Method getChars requires a starting point 6 // and ending point in the String. The starting point is the 7 // actual subscript from which copying starts. The ending point 8 // is one past the subscript at which the copying ends. 9 import javax.swing.*; 10 11 public class StringMisc { 12 public static void main( String args[] ) 13 { 14 String s1, output; 15 char charArray[]; 16 17 s1 = new String( "hello there" ); 18 charArray = new char[ 5 ]; 19 20 // output the string 21 output = "s1: " + s1; 22 23 // test the length method 24 output += " Length of s1: " + s1.length(); 25 26 // loop through the characters in s1 and display reversed 27 output += " The string reversed is: "; 28 29 for ( int i = s1.length() - 1; i >= 0; i-- ) 30 output += s1.charAt( i ) + " "; 31 32 // copy characters from string into char array 33 //四个参数的含义 34 //1.被拷贝字符在字串中的起始位置 35 //2.被拷贝的最后一个字符在字串中的下标再加1 36 //3.目标字符数组 37 //4.拷贝的字符放在字符数组中的起始下标 38 s1.getChars( 0, 5, charArray, 0 ); 39 output += " The character array is: "; 40 41 for ( int i = 0; i < charArray.length;i++ ) 42 output += charArray[ i ]; 43 44 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, output, 45 "Demonstrating String Class Constructors", 46 JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE ); 47 48 System.exit( 0 ); 49 } 50 }
2)结果截图:
3)Length():获取字串长度
1 java中的length属性是针对数组说的,比如说你声明了一个数组,想知道这个数组的长度则用到了length这个属性.
2 java中的length()方法是针对字符串String说的,如果想看这个字符串的长度则用到length()这个方法.
3.java中的size()方法是针对泛型集合说的,如果想看这个泛型有多少个元素,就调用此方法来查看!
4)charAt():获取指定位置的字符
str.charAt() :方法返回指定索引处的char值。索引范围是从0到length() - 1。对于数组索引,序列的第一个char值是在索引为0,索引1,依此类推。
5)getChars():获取从指定位置起的子串复制到字符数组中。
str.getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
要复制的第一个字符在索引srcBegin处,被复制的最后一个字符是在的索引srcEnd1即要复制的字符总数是srcEnd srcBegin处。
字符被复制到子数组的夏令时开始在指数dstBegin和结束于索引:dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
6)replace():子串替换
str.replace(char oldChar,char newChar)返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用newChar替换此字符串中出现的所有oldChar而生成的。
7)toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase():大小写转换
str.toUpperCase/()str.toLowerCase(),将所有的字符在这个字符串为大写。
8)trim():去除头尾空格:
str.trim(),该方法返回一个该字符串的副本,但将该字符串的开头和结尾的白色空格去掉;如果这个字符串头尾没有空白,将返回一个字符串的副本。
9)toCharArray():将字符串对象转换为字符数组
str.toCharArray() 返回一个新分配的字符数组,它的长度是此字符串的长度,而且内容被初始化为包含此字符串表示的字符序列。