设计模式介绍
-
设计模式是程序员在面对同类软件工程设计问题所总结出来的有用的经验,模式不是代码,而是某类问题的通用解决方案,设计模式(Design pattern)代表了最佳的实践。这些解决方案是众多软件开发人员经过相当长的 一段时间的试验和错误总结出来的
-
设计模式的本质提高软件的维护性,通用性和扩展性,并降低软件的复杂度
-
<<设计模式>> 是经典的书,作者是 Erich Gamma、Richard Helm、Ralph Johnson 和 John Vlissides Design(俗称“四人组 GOF”)
-
设计模式并不局限于某种语言,java,php,c++ 都有设计模式
设计模式类型
设计模式有两种分类方法,即根据模式的目的来分和根据模式的作用的范围来分。
根据模式是用来完成什么工作来分,设计模式分为三种类型:
-
创建型模式:单例模式、抽象工厂模式、原型模式、建造者模式、工厂模式
-
结构型模式:适配器模式、桥接模式、装饰模式、组合模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式
-
行为型模式:模版方法模式、命令模式、访问者模式、迭代器模式、观察者模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、 解释器模式(Interpreter 模式)、状态模式、策略模式、职责链模式(责任链模式)
根据模式是主要用于类上还是主要用于对象上来分,设计模式分为两种类型:
-
类模式:用于处理类与子类之间的关系,这些关系通过继承来建立,是静态的,在编译时刻便确定下来了。GoF中的工厂方法、(类)适配器、模板方法、解释器属于该模式。
-
对象模式:用于处理对象之间的关系,这些关系可以通过组合或聚合来实现,在运行时刻是可以变化的,更具动态性。GoF 中除了以上 4 种,其他的都是对象模式。
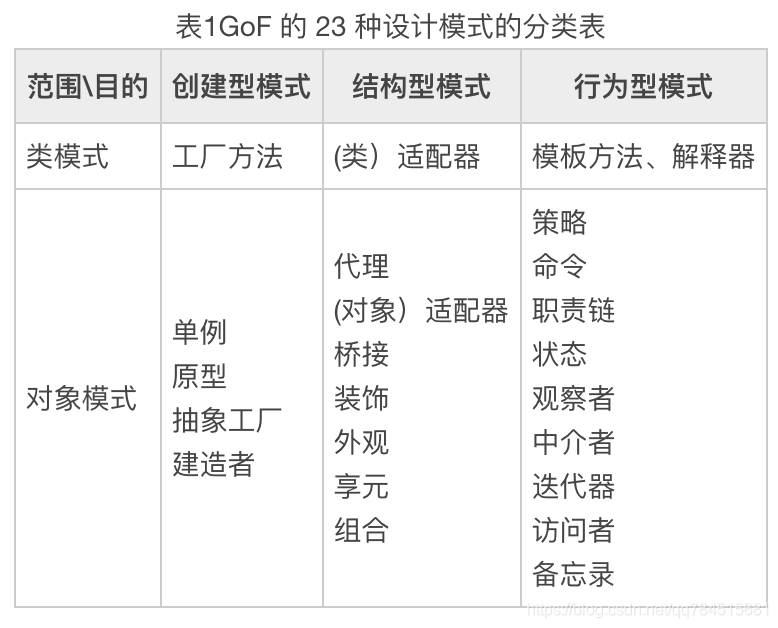
注意:不同的书籍上对分类和名称略有差别
单例(Singleton)模式
单例设计模式介绍
某个类只能生成一个实例,该类提供了一个全局访问点供外部获取该实例,其拓展是有限多例模式。
所谓类的单例设计模式,就是采取一定的方法保证在整个软件系统中,对某个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法(静态方法)。
比如 Hibernate 的 SessionFactory,它充当数据存储源的代理,并负责创建 Session 对象。SessionFactory 并不是轻量级的,一般情况下,一个项目通常只需要一个 SessionFactory 就够了,这是就会使用到单例模式。
单例设计模式八种方式
-
饿汉式(静态常量)
-
饿汉式(静态代码块)
-
懒汉式(线程不安全)
-
懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)
-
懒汉式(线程安全,同步代码块)
-
双重检查
-
静态内部类
-
枚举
饿汉式(静态常量)
饿汉式(静态常量)应用实例,步骤如下:
-
构造器私有化(防止 new)
-
类的内部创建对象
-
向外暴露一个静态的公共方法(getInstance)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type1; 2 3 public class SingletonTest01 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // 测试 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // 饿汉式(静态变量) 17 class Singleton { 18 19 // 1.构造器私有化,外部不能new 20 private Singleton() { 21 } 22 // 2.本类内部创建对象实例 23 private final static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); 24 // 3.提供一个公有的静态方法,返回实例对象 25 public static Singleton getInstance() { 26 return instance; 27 } 28 }
优缺点说明:
-
优点:这种写法比较简单,就是在类装载的时候就完成实例化。避免了线程同步问题
-
缺点:在类装载的时候就完成实例化,没有达到LazyLoading(懒加载)的效果。如果从始至终从未使用过这个实例,则会造成内存的浪费
-
这种方式基于classloder机制避免了多线程的同步问题,不过,instance在类装载时就实例化,在单例模式中大多数都是调用 getInstance 方法,但是导致类装载的原因有很多种,因此不能确定有其他的方式(或者其他的静态方法)导致类装载,这时候初始化 instance 就没有达到LazyLoading(懒加载)的效果
-
结论:这种单例模式可用,可能造成内存浪费
饿汉式(静态代码块)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type2; 2 3 public class SingletonTest02 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // 测试 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // 饿汉式(静态变量) 17 class Singleton { 18 19 // 1.构造器私有化, 外部不能 new 20 private Singleton() { 21 } 22 23 // 2.本类内部创建对象实例 24 private static Singleton instance; 25 26 static { 27 // 在静态代码块中,创建单例对象 28 instance = new Singleton(); 29 } 30 31 // 3.提供一个公有的静态方法,返回实例对象 32 public static Singleton getInstance() { 33 return instance; 34 } 35 }
优缺点说明:
-
这种方式和上面的方式其实类似,只不过将类实例化的过程放在了静态代码块中,也是在类装载的时候,就执行静态代码块中的代码,初始化类的实例。优缺点和上面是一样的
-
结论:这种单例模式可用,但是可能造成内存浪费
懒汉式(线程不安全)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type3; 2 3 public class SingletonTest03 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 System.out.println("懒汉式 1 , 线程不安全~"); 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Singleton { 17 18 private static Singleton instance; 19 20 private Singleton() { 21 } 22 23 // 提供一个静态的公有方法,当使用到该方法时,才去创建 instance 24 // 即懒汉式 25 public static Singleton getInstance() { 26 if(instance == null) { 27 instance = new Singleton(); 28 } 29 return instance; 30 } 31 }
优缺点说明:
-
优点:起到了LazyLoading(懒加载)的效果
-
缺点:只能在单线程下使用,如果在多线程下,一个线程进入了if(singleton==null)判断语句块,还未来得及往下执行,另一个线程也通过了这个判断语句,这时便会产生多个实例。所以在多线程环境下不可使用这种方式
-
结论:在实际开发中,不要使用这种方式
懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type4; 2 3 public class SingletonTest04 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 System.out.println("懒汉式 2 , 线程安全~"); 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法) 17 class Singleton { 18 19 private static Singleton instance; 20 21 private Singleton() { 22 } 23 24 // 提供一个静态的公有方法,加入同步处理的代码,解决线程安全问题 25 // 即懒汉式 26 public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() { 27 if(instance == null) { 28 instance = new Singleton(); 29 } 30 return instance; 31 } 32 }
优缺点说明:
-
优点:解决了线程安全问题
-
缺点:效率太低了,每个线程在想获得类的实例时候,执行getInstance()方法都要进行同步。而其实这个方法只执行一次实例化代码就够了,后面的想获得该类实例,直接 return 就行了。方法进行同步效率太低
-
结论:在实际开发中,不推荐使用这种方式
懒汉式(线程安全,同步代码块)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type5; 2 3 public class SingletonTest05 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 System.out.println("懒汉式 2 , 线程安全~"); 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Singleton { 17 18 private static Singleton singleton; 19 20 private Singleton() { 21 } 22 23 public static Singleton getInstance() { 24 if(singleton == null) { 25 synchronized(Singleton.class) { 26 singleton = new Singleton(); 27 } 28 } 29 return singleton; 30 } 31 }
结论:不推荐使用
双重检查(Double Check)
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type6; 2 3 public class SingletonTest06 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 System.out.println("双重检查"); 8 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 10 // true 11 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 12 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 13 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法) 18 class Singleton { 19 20 private static volatile Singleton instance; 21 22 private Singleton() { 23 } 24 25 // 提供一个静态的公有方法,加入双重检查代码,解决线程安全问题, 同时解决懒加载问题 26 // 同时保证了效率, 推荐使用 27 public static Singleton getInstance() { 28 if(instance == null) { 29 synchronized (Singleton.class) { 30 if(instance == null) { 31 instance = new Singleton(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 return instance; 36 } 37 }
优缺点说明:
-
优点:Double-Check 概念是多线程开发中常使用到的,如代码中所示,我们进行了两次 if (singleton == null)检查,这样就可以保证线程安全了
-
这样,实例化代码只用执行一次,后面再次访问时,判断if(singleton==null),直接return实例化对象,也避免的反复进行方法同步
-
线程安全;延迟加载;效率较高
-
结论:在实际开发中,推荐使用这种单例设计模式
静态内部类
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type7; 2 3 public class SingletonTest07 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 System.out.println("使用静态内部类完成单例模式"); 7 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 8 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 9 // true 10 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 11 System.out.println("instance.hashCode=" + instance.hashCode()); 12 System.out.println("instance2.hashCode=" + instance2.hashCode()); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // 静态内部类完成,推荐使用 17 class Singleton { 18 19 private static volatile Singleton instance; 20 21 // 构造器私有化 22 private Singleton() { 23 } 24 25 // 写一个静态内部类,该类中有一个静态属性 Singleton 26 private static class SingletonInstance { 27 private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton(); 28 } 29 30 // 提供一个静态的公有方法,直接返回 SingletonInstance.INSTANCE 31 public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() { 32 return SingletonInstance.INSTANCE; 33 } 34 }
优缺点说明:
-
这种方式采用了类装载的机制来保证初始化实例时只有一个线程
-
静态内部类方式在Singleton类被装载时并不会立即实例化,而是在需要实例化时,调用getInstance方法,才会装载 SingletonInstance 类,从而完成 Singleton 的实例化
-
类的静态属性只会在第一次加载类的时候初始化,所以在这里,JVM帮助我们保证了线程的安全性,在类进行初始化时,别的线程是无法进入的。
-
优点:避免了线程不安全,利用静态内部类特点实现延迟加载,效率高
-
结论:推荐使用
枚举
代码示例:
1 package com.atguigu.singleton.type8; 2 3 public class SingletonTest08 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Singleton instance = Singleton.INSTANCE; 7 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.INSTANCE; 8 // true 9 System.out.println(instance == instance2); 10 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()); 11 System.out.println(instance2.hashCode()); 12 instance.sayOK(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // 使用枚举,可以实现单例,推荐 17 enum Singleton { 18 19 // 属性 20 INSTANCE; 21 22 public void sayOK() { 23 System.out.println("ok~"); 24 } 25 }
优缺点说明:
-
这借助JDK1.5中添加的枚举来实现单例模式。不仅能避免多线程同步问题,而且还能防止反序列化重新创建新的对象
-
这种方式是EffectiveJava作者JoshBloch提倡的方式
-
结论:推荐使用
单例模式在 JDK 应用的源码分析
-
我们JDK中,java.lang.Runtime就是经典的单例模式(饿汉式)
-
代码分析+Debug源码+代码说明
单例模式注意事项和细节说明
-
单例模式保证了系统内存中该类只存在一个对象,节省了系统资源,对于一些需要频繁创建销毁的对象,使用单例模式可以提高系统性能
-
当想实例化一个单例类的时候,必须要记住使用相应的获取对象的方法,而不是使用new
-
单例模式使用的场景:需要频繁的进行创建和销毁的对象、创建对象时耗时过多或耗费资源过多(即:重量级对象),但又经常用到的对象、工具类对象、频繁访问数据库或文件的对象(比如数据源、session 工厂等)
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq784515681/article/details/105261444
参考:http://c.biancheng.net/view/1338.html
