1 TCP为何会有粘包半包?
1.1 粘包
发送方每次写入数据 < 套接字缓冲区大小
接收方读取套接字缓冲区数据不够及时
1.2 半包
发送方写入数据 > 套接字缓冲区大小
发送的数据大于协议的MTU ( Maximum Transmission Unit,最大传输单元),必须拆包
而且
一个发送可能被多次接收,多个发送可能被一次接收
一个发送可能占用多个传输包,多个发送可能公用一个传输包
本质是因为 TCP 是流式协议,消息无边界。
而UDP就像快递,虽然一次运输多个,但每个包都有边界,一个个签收
所以无此类问题。
清楚了问题产生的本质,那么就知道如何避免了,即确定消息的边界
解决方案
1、使用自定义协议,来实现TCP的粘包/拆包问题
2、使用protobuf 协议,可以看前一篇记录
Netty ByteBuf
ByteBuf的基本结构
ByteBuf由一段地址空间,一个read index和一个write index组成。两个index分别记录读写进度,省去了NIO中ByteBuffer手动调用flip和clear的烦恼。
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes |
| | (CONTENT) | |
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| | | |
0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity
通过上图可以很好的理解ByteBuf的数据划分。writer index到capacity之间的部分是空闲区域,可以写入数据;reader index到writer index之间是已经写过还未读取的可读数据;0到reader index是已读过可以释放的区域。
三个index之间的关系是:reader index <= writer index <= capacity
存储空间
ByteBuf根据其数据存储空间不同有可以分为三种:基于JVM堆内的,基于直接内存的和组合的。
堆内受JVM垃圾收集器的管辖,使用上相对安全一些,不用每次手动释放。弊端是GC是会影响性能的;还有就是内存的拷贝带来的性能损耗(JVM进程到Socket)。
直接内存则不受JVM的管辖,省去了向JVM拷贝数据的麻烦。但是坏处就是别忘了释放内存,否则就会发生内存泄露。相比于堆内存,直接内存的的分配速度也比较慢。
最佳实践:在IO通信的线程中的读写Buffer使用DirectBuffer(省去内存拷贝的成本),在后端业务消息的处理使用HeapBuffer(不用担心内存泄露)。
通过hasArray检查一个ByteBuf heap based还是direct buffer。
创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf提供了两个工具类来创建ByteBuf,分别是支持池化的Pooled和普通的Unpooled。Pooled缓存了ByteBuf的实例,提高性能并且减少内存碎片。它使用Jemalloc来高效的分配内存。
如果在Channel中我们可以通过channel.alloc()来拿到ByteBufAllocator,具体它使用Pool还是Unpool,Directed还是Heap取决于程序的配置。
索引的标记与恢复
markReaderIndex和resetReaderIndex是一个成对的操作。markReaderIndex可以打一个标记,调用resetReaderIndex可以把readerIndex重置到原来打标记的位置。
空间释放
discardReadByte可以把读过的空间释放,这时buffer的readerIndex置为0,可写空间和writerIndex也会相应的改变。discardReadBytes在内存紧张的时候使用用,但是调用该方法会伴随buffer的内存整理的。这是一个expensive的操作。
clear是把readerIndex和writerIndex重置到0。但是,它不会进行内存整理,新写入的内容会覆盖掉原有的内容。
参考案例
1定义协议
https://www.cnblogs.com/sidesky/p/6913109.html
2代码
常量
协议格式
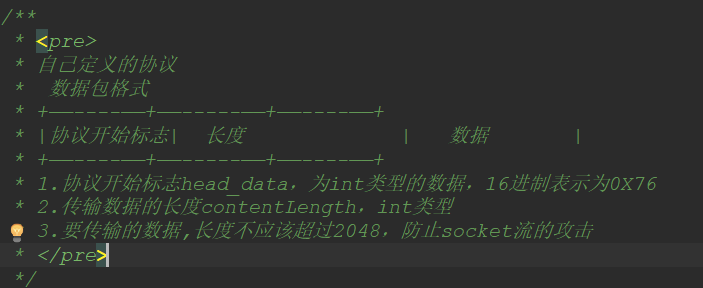
协议类
SmartCarProtocol
package com.netty.protobuf; import com.netty.config.ConstantValue; import java.util.Arrays; /** * <pre> * 自己定义的协议 * 数据包格式 * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 | * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76 * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型 * 3.要传输的数据 * </pre> */ public class SmartCarProtocol { /** * 消息的开头的信息标志 */ private int head_data = ConstantValue.HEAD_DATA; /** * 消息的长度 */ private int contentLength; /** * 消息的内容 */ private byte[] content; /** * 用于初始化,SmartCarProtocol * * @param contentLength * 协议里面,消息数据的长度 * @param content * 协议里面,消息的数据 */ public SmartCarProtocol(int contentLength, byte[] content) { this.contentLength = contentLength; this.content = content; } public int getHead_data() { return head_data; } public int getContentLength() { return contentLength; } public void setContentLength(int contentLength) { this.contentLength = contentLength; } public byte[] getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(byte[] content) { this.content = content; } @Override public String toString() { return "SmartCarProtocol [head_data=" + head_data + ", contentLength=" + contentLength + ", content=" + Arrays.toString(content) + "]"; } }
编码器
package com.netty.protobuf; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder; /** * <pre> * 自己定义的协议 * 数据包格式 * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 | * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76 * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型 * 3.要传输的数据 * </pre> */ public class SmartCarEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<SmartCarProtocol> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, SmartCarProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { // 写入消息SmartCar的具体内容 // 1.写入消息的开头的信息标志(int类型) out.writeInt(msg.getHead_data()); // 2.写入消息的长度(int 类型) out.writeInt(msg.getContentLength()); // 3.写入消息的内容(byte[]类型) out.writeBytes(msg.getContent()); } }
解码器
package com.netty.protobuf; import com.netty.config.ConstantValue; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder; import java.util.List; /** * <pre> * 自己定义的协议 * 数据包格式 * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 | * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+ * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76 * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型 * 3.要传输的数据,长度不应该超过2048,防止socket流的攻击 * </pre> */ public class SmartCarDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { /** * <pre> * 协议开始的标准head_data,int类型,占据4个字节. * 表示数据的长度contentLength,int类型,占据4个字节. * </pre> */ public final int BASE_LENGTH = 4 + 4; @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer, List<Object> out) throws Exception { // 可读长度必须大于基本长度 if (buffer.readableBytes() >= BASE_LENGTH) { // 记录包头开始的index int beginReader; while (true) { // 获取包头开始的index beginReader = buffer.readerIndex(); // 标记包头开始的index buffer.markReaderIndex(); // 读到了协议的开始标志,结束while循环 if (buffer.readInt() == ConstantValue.HEAD_DATA) { break; } // 未读到包头,略过一个字节 // 每次略过,一个字节,去读取,包头信息的开始标记 buffer.resetReaderIndex(); buffer.readByte(); // 当略过,一个字节之后, // 数据包的长度,又变得不满足 // 此时,应该结束。等待后面的数据到达 if (buffer.readableBytes() < BASE_LENGTH) { return; } } // 消息的长度 int length = buffer.readInt(); // 判断请求数据包数据是否到齐 if (buffer.readableBytes() < length) { // 还原读指针 buffer.readerIndex(beginReader); return; } // 读取data数据 byte[] data = new byte[length]; buffer.readBytes(data); SmartCarProtocol protocol = new SmartCarProtocol(data.length, data); out.add(protocol); } } }
客户端
//传输自定义协议数据 pipeline.addLast(new SmartCarEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new SmartCarDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new ClientChannelHandler());
服务端
//传输自定义协议数据 pipeline.addLast(new SmartCarEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new SmartCarDecoder()); //自定义Handler pipeline.addLast(new ServerChannelHandler());
客户端发送数据
//传输自定义协议数据 @Async public String sendMsgSmartCarProtocol(Msg msg){ // 发送SmartCar协议的消息 // 要发送的信息 String data = GsonUtil.GsonString(msg); Channel channel = channelContainer.getChannel(); String socketString = channel.localAddress().toString(); // 获得要发送信息的字节数组 byte[] content = data.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()); // 要发送信息的长度 int contentLength = content.length; SmartCarProtocol protocol = new SmartCarProtocol(contentLength, content); channel.writeAndFlush(protocol); return socketString; }
服务端接收数据
private String beat = "hello"; private int count = 0; @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object obj) throws Exception { //传输自定义协议数据 // 用于获取客户端发来的数据信息 SmartCarProtocol body = (SmartCarProtocol) obj; byte[] content = body.getContent(); if(beat.equals(new String(content))){ System.out.println("Server接受的客户端的信息 :"+ new String(body.getContent())); // 会写数据给客户端 String str = "ok"; byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()); SmartCarProtocol response = new SmartCarProtocol(bytes.length, bytes); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); }else{ count ++; System.out.println("Server接受的客户端的信息 :"+count+","+ new String(body.getContent())); } //传输字符窜数据 // String socketString = ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString(); // if(beat.equals(obj.toString())){ // ctx.writeAndFlush("ok"); // }else{ // System.out.println("client:"+socketString+":"+obj.toString()); // } //传输实体类数据 // MessageProto.Message message = (MessageProto.Message) obj; // String socketString = ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString(); // if(beat.equals(message.getContent())){ // System.out.println("client:"+socketString+":"+message.getContent()); // MessageProto.Message pong = MessageProto.Message.newBuilder().setContent("ok").build(); // ctx.writeAndFlush(pong); // }else { // count ++; // System.out.println("服务端接收客户端"+socketString+"的数据:"); // System.out.println(count+","+message.getId()+","+message.getContent()); // String content = message.getContent(); // System.out.println(content); // Msg msg = GsonUtil.GsonToBean(content, Msg.class); // msg.setRemoteaddress(socketString); // TaskService taskService = SpringUtil.getBean(TaskService.class); // taskService.insertMsg(msg); // } }
以上测试代码,仅供参考