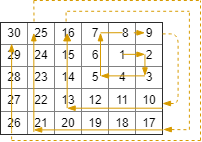
On a 2 dimensional grid with
Rrows andCcolumns, we start at(r0, c0)facing east.Here, the north-west corner of the grid is at the first row and column, and the south-east corner of the grid is at the last row and column.
Now, we walk in a clockwise spiral shape to visit every position in this grid.
Whenever we would move outside the boundary of the grid, we continue our walk outside the grid (but may return to the grid boundary later.)
Eventually, we reach all
R * Cspaces of the grid.Return a list of coordinates representing the positions of the grid in the order they were visited.
Example 1:
Input: R = 1, C = 4, r0 = 0, c0 = 0 Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]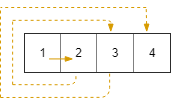
Example 2:
Input: R = 5, C = 6, r0 = 1, c0 = 4 Output: [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
Note:
1 <= R <= 1001 <= C <= 1000 <= r0 < R0 <= c0 < C
Approach #1: Math. [Java] [21ms]
class Solution {
int numOfGrids = 1;
public int[][] spiralMatrixIII(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
int total = R * C;
int steps = 0;
int changeLen = 0;
int len = 0;
int x = r0;
int y = c0;
List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Set<String> seen = new HashSet<>();
String[] dirs = {"right", "down", "left", "up"};
String key = x + " " + y;
seen.add(key);
ans.add(new int[] {x, y});
while (numOfGrids < total) {
int cur = steps % 4;
if (changeLen % 2 == 0) len++;
if (dirs[cur].equals("right")) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
y = y + 1;
key = x + " " + y;
if (x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C && !seen.contains(key)) {
seen.add(key);
ans.add(new int[] {x, y});
numOfGrids++;
}
}
} else if (dirs[cur].equals("down")) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
x = x + 1;
key = x + " " + y;
if (x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C && !seen.contains(key)) {
seen.add(key);
ans.add(new int[] {x, y});
numOfGrids++;
}
}
} else if (dirs[cur].equals("up")) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
x = x - 1;
key = x + " " + y;
if (x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C && !seen.contains(key)) {
seen.add(key);
ans.add(new int[] {x, y});
numOfGrids++;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
y = y - 1;
key = x + " " + y;
if (x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C && !seen.contains(key)) {
seen.add(key);
ans.add(new int[] {x, y});
numOfGrids++;
}
}
}
steps++;
changeLen++;
}
int[][] ret = new int[ans.size()][2];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
ret[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return ret;
}
}
Approach #2: Math. [Java] [3ms]
class Solution {
int i=0;
public int[][] spiralMatrixIII(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
int x = r0, y = c0, len=1;
int[][] res= new int[R*C][2];
while(i < R*C) {
for(int k=0; k<len; k++) add(res, x, y++, R, C);
for(int k=0; k<len; k++) add(res, x++, y, R, C);
len ++;
for(int k=0; k<len; k++) add(res, x, y--, R, C);
for(int k=0; k<len; k++) add(res, x--, y, R, C);
len++;
}
return res;
}
void add(int[][] res, int x, int y, int R, int C) {
if (x >= R || x < 0 || y >= C || y < 0) return;
res[i] = new int[]{x, y};
i++;
}
}