参考:https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/di-ling-zhang-bi-du-xi-lie/bfs-kuang-jia
问题:
求从【0000】四位密码锁初始状态,最少经过几步,能找到给定目标秘密target
另,其中若转到给定deadends的密码,则永远打不开锁,因此需要避开这些密码。
Example 1: Input: deadends = ["0201","0101","0102","1212","2002"], target = "0202" Output: 6 Explanation: A sequence of valid moves would be "0000" -> "1000" -> "1100" -> "1200" -> "1201" -> "1202" -> "0202". Note that a sequence like "0000" -> "0001" -> "0002" -> "0102" -> "0202" would be invalid, because the wheels of the lock become stuck after the display becomes the dead end "0102". Example 2: Input: deadends = ["8888"], target = "0009" Output: 1 Explanation: We can turn the last wheel in reverse to move from "0000" -> "0009". Example 3: Input: deadends = ["8887","8889","8878","8898","8788","8988","7888","9888"], target = "8888" Output: -1 Explanation: We can't reach the target without getting stuck. Example 4: Input: deadends = ["0000"], target = "8888" Output: -1 Constraints: 1 <= deadends.length <= 500 deadends[i].length == 4 target.length == 4 target will not be in the list deadends. target and deadends[i] consist of digits only.
解法:BFS(广度优先搜索)
- queue:q:存储每层尝试的节点
- set:visited:存储已经访问过的节点,避免重复访问,形成死循环
框架过程:
- INIT:将start节点加入q和visited中,开始处理尝试q中的所有节点
- (q不为空的情况下,还有层次未尝试)对于每一层尝试
- INIT:获取当前层q.size,用来界定层次+1
- 对每一层的所有节点:
- 判断是否为target?是->return step,否->继续
- 将当前节点cur的所有邻接节点都加入q和visited中。
- 条件:这些邻接节点不在visited中(即未曾访问过)
- 每层所有节点判定完毕,step++。
- 最后都没有找到target的话,即无法找到。
对本问题:
q:储存所有下一步的密码可能。(向上拨一位,向下拨一位,各4位,则共有8中可能)
visited:已经判断过的密码。
⭐️ 特:deadends,若当前判断的密码是deadends中的密码,则放弃尝试,continue到下一个密码的尝试。
代码参考:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 //getAdjacentNode 4 void pushAdjacentNode(queue<string>& q, unordered_set<string>& visited, string s) { 5 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { 6 string up = plusOne(s, i); 7 if(visited.count(up)==0) { 8 q.push(up); 9 visited.insert(up); 10 } 11 string down = minusOne(s, i); 12 if(visited.count(down)==0) { 13 q.push(down); 14 visited.insert(down); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 string plusOne(string s, int pos) { 19 if(s[pos]=='9') s[pos]='0'; 20 else s[pos]++; 21 return s; 22 } 23 string minusOne(string s, int pos) { 24 if(s[pos]=='0') s[pos]='9'; 25 else s[pos]--; 26 return s; 27 } 28 int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) { 29 queue<string> q; 30 unordered_set<string> visited; 31 unordered_set<string> dead(deadends.begin(), deadends.end()); 32 int res = 0; 33 q.push("0000"); 34 visited.insert("0000"); 35 36 while(!q.empty()) { 37 int sz = q.size(); 38 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 39 string cur = q.front(); 40 q.pop(); 41 if(dead.count(cur) != 0) continue; 42 if(cur == target) { 43 return res; 44 } 45 pushAdjacentNode(q, visited, cur); 46 } 47 res++; 48 } 49 return -1; 50 } 51 };
解法:Bidirectional BFS(双向 广度优先搜索)
条件:已知target目标节点+初始节点。(只知道初始节点时,只能用单向 BFS)
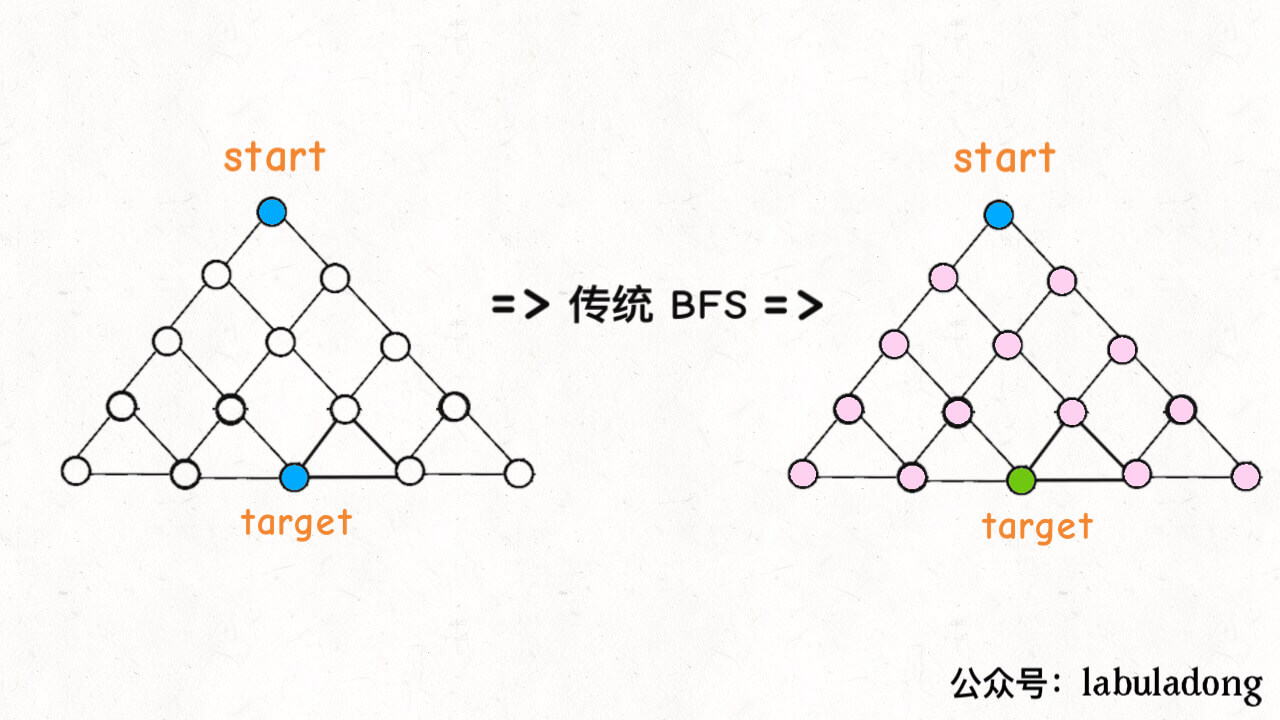
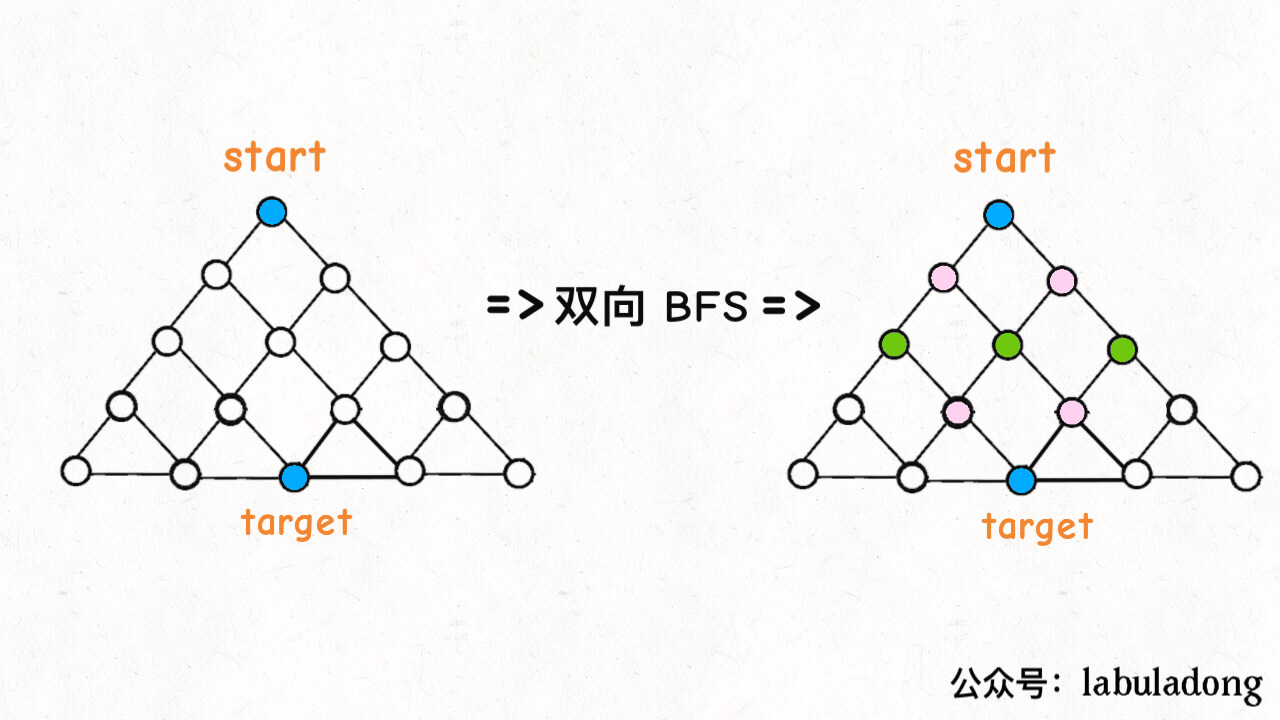
时间复杂度一样,只是双向BFS从两侧遍历,缩小了半棵树的搜索。
实现:
| 改变内容 | 单向BFS | 双向BFS |
| 遍历对象 | queue q(start向下) | unordered_set q1(start向下),q2(target向上) |
| ⚠️ visited添加时机 | ⭕️ 加入q的同时 | ⭕️ 马上使用visited之前(由于每次加入visit的节点,实际是为下下一次check对象准备的<不能妨碍下一次check>) |
| 每层遍历新增邻接节点 | 插入q中 | 插入每层遍历新作临时set tmp中 |
| 判断是否找到 | cur==target? | q2.count(cur)!=0? 反向搜索set中是否存在正向搜索的当前节点? |
| 每层判断结束 | 层数+1,step++ |
除层数+1外,设置下次循环搜索对象为p2(当前的反向),tmp为下次循环搜索的p2,丢弃当前搜索完的p1 |
♻️ 优化:使得每次的搜索对象p1的长度最短(遍历次数尽可能少),即当p1.size()>p2.size()则调换swap(p1,p2)。
代码参考:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 //getAdjacentNode 4 void pushAdjacentNode(unordered_set<string>& q, unordered_set<string>& visited, string s) { 5 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { 6 string up = plusOne(s, i); 7 if(visited.count(up)==0) { 8 q.insert(up); 9 //visited.insert(up); 10 } 11 string down = minusOne(s, i); 12 if(visited.count(down)==0) { 13 q.insert(down); 14 //visited.insert(down); 15 //delay the timing to flag cur visited. 16 //cause this visited node is of the next next check obj, not the next check obj. 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 string plusOne(string s, int pos) { 21 if(s[pos]=='9') s[pos]='0'; 22 else s[pos]++; 23 return s; 24 } 25 string minusOne(string s, int pos) { 26 if(s[pos]=='0') s[pos]='9'; 27 else s[pos]--; 28 return s; 29 } 30 int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) { 31 unordered_set<string> q1; 32 unordered_set<string> q2; 33 unordered_set<string> visited; 34 unordered_set<string> dead(deadends.begin(), deadends.end()); 35 int res = 0; 36 q1.insert("0000"); 37 q2.insert(target); 38 //visited.insert("0000"); 39 //visited.insert(target); 40 41 while(!q1.empty() && !q2.empty()) { 42 unordered_set<string> tmp; 43 if(q1.size()>q2.size()) { 44 swap(q1, q2); 45 } 46 int sz = q1.size(); 47 for(string cur : q1) { 48 if(dead.count(cur) != 0) continue; 49 //if(cur == target) { 50 if(q2.count(cur) != 0) { 51 return res; 52 } 53 visited.insert(cur);//put in visited directly before using visited set. 54 pushAdjacentNode(tmp, visited, cur); 55 } 56 res++; 57 //q1 checked over, discard it. 58 //and q2 will be the next check object, 59 //tmp is the new object waiting like q2 position. 60 q1 = q2; 61 q2 = tmp; 62 } 63 return -1; 64 } 65 };