问题:
给定n个地点,以及地点之间的航班和费用。
求从src到dst,中转最多k次以内,花费最少的费用。
Example 1: Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]] src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 Output: 200 Explanation: The graph looks like this: The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 1 stop costs 200, as marked red in the picture. Example 2: Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]] src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 Output: 500 Explanation: The graph looks like this: The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 0 stop costs 500, as marked blue in the picture. Constraints: The number of nodes n will be in range [1, 100], with nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. The size of flights will be in range [0, n * (n - 1) / 2]. The format of each flight will be (src, dst, price). The price of each flight will be in the range [1, 10000]. k is in the range of [0, n - 1]. There will not be any duplicated flights or self cycles.
example 1:
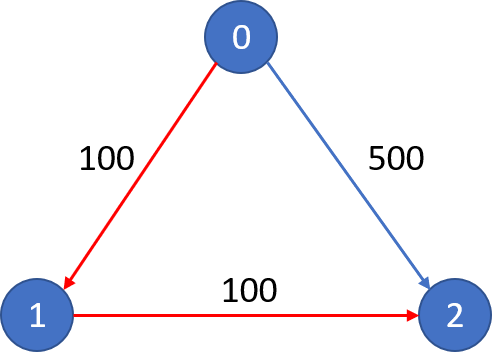
example 2:

解法一:BFS
将从src到node i的cost存入queue。
{node i, cost}
由于题目限制中转站点数 k
因此需要对queue的遍历,通过层次区分。
⚠️ 注意:在层次区分的问题中,不能使用优先队列 priority_queue,由于其会打乱节点的层次顺序。
使用dist数组保存,src到每个节点的最小距离。
在 k 层以内,按层,随时更新该距离 为最小。
⚠️ 注意:queue的遍历,不能因为遍历到dst节点就停止,由于之后还可能存在花费更少的路径,只是中转需要更多的情况。
因此到达 k 层遍历之前,要一直遍历queue,直到queue遍历结束。
若dist[dst]==INT_MAX, 则没有src->dst的路径。返回-1,否则返回dist[dst]
代码参考:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { 4 int res=-1; 5 if(src==dst) return 0; 6 vector<vector<vector<int>>> graph(n,vector<vector<int>>()); 7 for(vector<int>& flt:flights) { 8 graph[flt[0]].push_back({flt[1],flt[2]}); 9 //printf("graph[%d]_insert:{%d,%d} ", flt[0], flt[1], flt[2]); 10 } 11 queue<pair<int,int>> q;//stop, cost 12 vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX); 13 q.push({0,src}); 14 dist[src] = 0; 15 int cur_s, cur_cost; 16 int count = 0; 17 while(!q.empty()) { 18 int sz = q.size(); 19 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 20 cur_cost = q.front().first; 21 cur_s = q.front().second; 22 q.pop(); 23 //until k steps, can't return. 24 //cause there maybe a less cost way which may spend more steps. 25 //if(cur_s==dst) return min(dist[dst], cur_cost); 26 //printf("cur_s:%d cur_cost:%d ", cur_s, cur_cost); 27 for(auto next:graph[cur_s]) { 28 //printf("graph[%d] ", cur_s); 29 //printf("next[0]:%d, next[1]:%d ", next[0], next[1]); 30 if(dist[next[0]] > cur_cost+next[1]) { 31 //printf("INSERT next[0]:%d, cur_cost+next[1]:%d+%d ", next[0], cur_cost,next[1]); 32 dist[next[0]] = cur_cost+next[1]; 33 q.push({dist[next[0]], next[0]}); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 if(count>=K) return dist[dst]==INT_MAX?-1:dist[dst]; 38 //printf("count:%d ", count); 39 count++; 40 } 41 return dist[dst]==INT_MAX?-1:dist[dst]; 42 } 43 };
解法二:优先队列 priority_queue
上述解法中,解释了层级相关的问题,不能使用优先队列,
但如果将层级关系作为变量,保存至queue中,在K以内的所有情况,cost的更新(选取最短距离)都是不限于层级关系的,
满足K以内的情况,才保存在queue中进行处理,即可规避该问题。
使用了优先队列,那么可保证先处理的一定是距离最短的节点,
若先找到dst,即可返回。
代码参考:
1 typedef tuple<int, int, int> ti; 2 class Solution { 3 public: 4 int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) { 5 if(src==dst) return 0; 6 vector<vector<vector<int>>> graph(n); 7 for(vector<int>& flt:flights) { 8 graph[flt[0]].push_back({flt[1],flt[2]}); 9 } 10 priority_queue<ti, vector<ti>, greater<ti>> q;//cost,stop,K(level) 11 q.push({0,src, K+1}); 12 int cur_s, cur_cost, cur_k; 13 while(!q.empty()) { 14 auto [cur_cost, cur_s, cur_k] = q.top(); 15 q.pop(); 16 if(cur_s==dst) return cur_cost; 17 if(!cur_k) continue;//level > K, invalid route 18 for(auto next:graph[cur_s]) { 19 q.push({cur_cost+next[1], next[0], cur_k-1}); 20 } 21 } 22 return -1; 23 } 24 };