1.原理
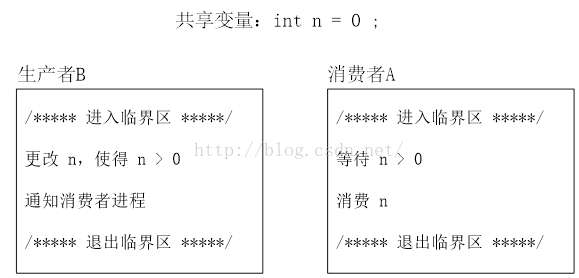
假设有两个线程同时访问一个全局变量 n,这个全局变量的初始值等于0。
Int n = 0 ;
消费者线程 A 进入临界区,访问 n,A 必须等到 n 大于 0 才能接着往下执行,如果 n== 0,那么 A 将一直等待。
还有一个生产者线程 B,B 进入临界区,修改 n 的值,使得 n >0,当 n > 0 时,B 通知等待 n > 0 的消费者线程A。A 被 B 通知之后就可以接着往下执行了。
以上情况造成死锁:
当 A 进入临界区时,其他线程不能进入临界区,意味着 B 没有机会去修改 n, n 的值一直为 0,不满足A 继续执行的条件(n > 0),A 只能一直等待。
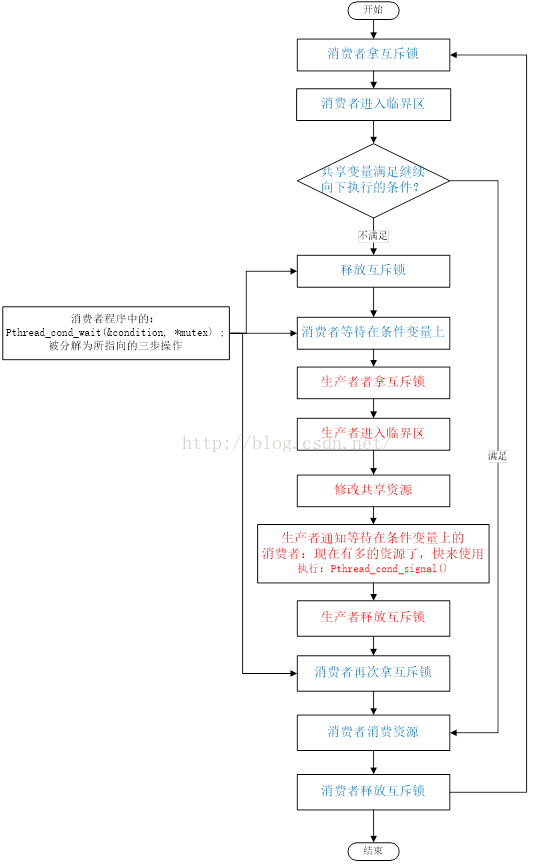
消费者进程拿到互斥锁 --> 进入临界区 --> 发现共享资源 n 不满足继续执行的条件(n> 0) --> 等待 n > 0
消费者进程占有互斥锁 --> 生产者进程无法进入临界区 --> 无法修改 n 的值 --> 生产者等待消费者释放互斥锁
解决死锁的方案就是采用条件变量。
通常情况下,对共享资源(比如 n)保护要用到锁操作,当一个进程进入临界区时会拿到互斥锁(lock 操作),然后其他进程拿不到互斥锁,也就无法进入临界区,因此当进程进入临界区,发现共享资源不满足继续向下执行的条件(n > 0)时,就应该释放锁,让其他进程修改共享资源,以满足自己所需的执行条件。
消费者进入临界区 --> 共享变量不满足继续向下执行的条件 --> 消费者等待在条件变量 --> 释放互斥锁 --> 生产者进入临界区 --> 修改条件变量 --> 生产者通知消费者:现在有多的资源了,快来使用 --> 消费者再次拿互斥锁 --> 消费资源 --> 释放互斥锁。如果有多个消费者进程等待在条件变量上,就可以形成等待队列。
生产者和消费者模型中互斥锁和条件变量的使用流程图如下,其中蓝色代表消费者的执行流,红色是生产者的执行流。
2.使用方法
条件变量的使用主要有以下五个函数:
/* 初始化一个条件变量 */
int pthread_cond_init (pthread_cond_t* cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);
/* 销毁一个条件变量 */
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t* cond);
/* 令一个消费者等待在条件变量上 */
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t* cond);
/* 生产者通知等待在条件变量上的消费者 */
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t* cond);
/* 生产者向消费者广播消息 */
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t* cond);
消费者等待条件的伪代码:
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 拿到互斥锁,进入临界区
while( 条件为假)
pthread_cond_wait(cond, mutex); // 令进程等待在条件变量上
修改条件
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 释放互斥锁
生产者通知消费者的伪代码:
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 拿到互斥锁,进入临界区
设置条件为真
pthread_cond_signal(cond); // 通知等待在条件变量上的消费者
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 释放互斥锁
以下是示例程序,演示了互斥锁和条件变量配合使用方法,由于是在Linux下写的程序,所以注释全是英文的。
condition_test.c:
/***************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 2016 chengonghao
* All rights reserved.
*
* chengonghao@yeah.net
***************************************************************/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define CONSUMERS_COUNT 2
#define PRODUCERS_COUNT 1
pthread_mutex_t g_mutex ;
pthread_cond_t g_cond ;
pthread_t g_thread[CONSUMERS_COUNT + PRODUCERS_COUNT] ;
int share_variable = 0 ;// this is the share variable, shared by consumer and producer
void* consumer( void* arg )
{
int num = (int)arg ;
while ( 1 )
{
/******* critical section begin *******/
pthread_mutex_lock( &g_mutex ) ;
// if share_variable == 0, means consumer shell stop here
while ( share_variable == 0 )
{
printf( "consumer %d begin wait a condition...
", num ) ;
// put a thread blocked ont a condition variable( here is g_cond),
// and unlock the mutex( here is g_mutex )
pthread_cond_wait( &g_cond, &g_mutex ) ;
}
// here means n != 0 and consumer can goes on
// consumer consumed shared variable, so the number of shared variable shell minus
printf( "consumer %d end wait a condition...
", num ) ;
printf( "consumer %d begin consume product
", num ) ;
-- share_variable ;
pthread_mutex_unlock( &g_mutex ) ;
/******** critial section end *********/
sleep( 1 ) ;
}
return NULL ;
}
void* producer( void* arg )
{
int num = (int)arg ;
while ( 1 )
{
/******* critical section begin *******/
pthread_mutex_lock( &g_mutex ) ;
// produce a shared variable
printf( "producer %d begin produce product...
", num ) ;
++ share_variable ;
printf( "producer %d end produce product...
", num ) ;
// unblock threads blocked on a condition variable( here is g_cond )
pthread_cond_signal( &g_cond ) ;
printf( "producer %d notified consumer by condition variable...
", num ) ;
pthread_mutex_unlock( &g_mutex ) ;
/******** critial section end *********/
sleep( 5 ) ;
}
return 1 ;
}
int main( void )
{
// initiate mutex
pthread_mutex_init( &g_mutex, NULL ) ;
// initiate condition
pthread_cond_init( &g_cond, NULL ) ;
// initiate consumer threads
for ( int i = 0; i < CONSUMERS_COUNT; ++ i )
{
pthread_create( &g_thread[i], NULL, consumer, (void*)i ) ;
}
sleep( 1 ) ;
// initiate producer threads
for ( int i = 0; i < PRODUCERS_COUNT; ++ i )
{
pthread_create( &g_thread[i], NULL, producer, (void*)i ) ;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < CONSUMERS_COUNT + PRODUCERS_COUNT; ++ i )
{
pthread_join( g_thread[i], NULL ) ;
}
pthread_mutex_destroy( &g_mutex ) ;
pthread_cond_destroy( &g_cond ) ;
}
编译程序:
cgh@ubuntu:~/condition_test$ gcc condition_test.c -o test –lpthread
运行程序:
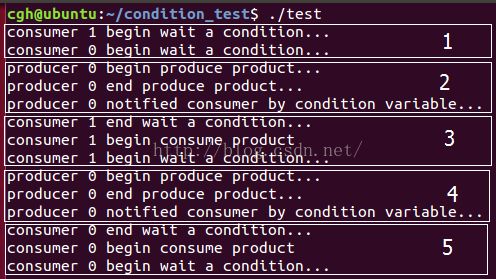
1. 第一个框,消费者 1 和0 发现share_variable == 0,于是先后等待在条件变量上;
2. 第二个框,生产者 0 开始生产共享变量,即 ++ share_variable,然后通知等待在条件变量上的消费者;
3. 第三个框,消费者 1 被生产者唤醒,开始消费共享变量,即– share_variable;
4. 第四个框,生产者 0 继续生产共享变量,++ share_variable,然后通知等待在条件变量上的消费者;
5. 第五个框,消费者 0 被唤醒,开始消费共享变量,即– share_variable;
以此类推,以上描述简化了拿锁和释放锁的过程,可以结合上面的流程图来理解代码。
---------------------
作者:chengonghao
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/chengonghao/article/details/51779279
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!