1.三元运算
if条件成立的结果 if 条件 else 条件不成立的结果
例如:
a=20
b=10
c=a if a>b else b
print(c)
2.命名空间
- 全局命名空间:创建的存储“变量名与值的关系”的空间叫做全局命名空间
- 局部命名空间:在函数的运行中开辟的临时的空间叫做局部命名空间
- 内置命名空间:内置命名空间中存放了python解释器为我们提供的名字:input,print,str,list,tuple...它们都是我们熟悉的,拿过来就可以用的方法。

三种命名空间之间的加载顺序和取值顺序:
加载顺序:内置(程序运行前加载)-->全局(从上到下顺序加载进来的)-->局部(调用的时候加载)--->内置
取值:在局部调用:局部命名空间--->全局命名空间--->内置命名空间
站在全局范围找:全局----内置----局部
使用:
全局不能使用局部的
局部的可以使用全局的
3.作用域:就是作用范围
1.命名空间和作用域是分不开的
2.作用域分为两种:
全局作用域:全局命名空间与内置命名空间的名字都属于全局范围
在整个文件的任意位置都能被引用,全局有效
局部作用域:局部命名空间,只能在局部范围内生效
3.站在全局看:
使用名字的时候:如果全局有,用全局的
如果全局没有,用内置的
4.为什么要有作用域?
为了函数内的变量不会影响到全局
5.globals方法:查看全局作用域的名字【print(globals())】
locals方法:查看局部作用域的名字【print(locals())】

1 def func(): 2 a = 12 3 b = 20 4 print(locals()) 5 print(globals()) 6 7 func()
站在全局看,globals is locals
global关键字:强制转换为全局变量

1 # x=1 2 # def foo(): 3 # global x #强制转换x为全局变量 4 # x=10000000000 5 # print(x) 6 # foo() 7 # print(x) 8 # 这个方法尽量能少用就少用
nonlocal让内部函数中的变量在上一层函数中生效,外部必须有

1 # x=1 2 # def f1(): 3 # x=2 4 # def f2(): 5 # # x=3 6 # def f3(): 7 # # global x#修改全局的 8 # nonlocal x#修改局部的(当用nonlocal时,修改x=3为x=100000000,当x=3不存在时,修改x=2为100000000 ) 9 # # 必须在函数内部 10 # x=10000000000 11 # f3() 12 # print('f2内的打印',x) 13 # f2() 14 # print('f1内的打印', x) 15 # f1() 16 # # print(x)
4.函数的嵌套定义

1 def animal(): 2 def tiger(): 3 print('nark') 4 print('eat') 5 tiger() 6 animal()
5.作用域链

1 x=1 2 def heihei(): 3 x='h' 4 def inner(): 5 x='il' 6 def inner2(): 7 print(x) 8 inner2() 9 inner() 10 heihei()
6.函数名的本质:就是函数的内存地址

1 def func(): 2 print('func') 3 print(func)#指向了函数的内存地址
7.函数名可以用做函数的参数


1 def func(): 2 print('func') 3 4 def func2(f): 5 f() 6 print('func2') 7 func2(func)
函数名可以作为函数的返回值

return说明1
def func(): def func2(): print('func2') return func2 f2=func() f2() #func2=func() #func2()
2.
def f1(x):
print(x)
return '123'
def f2():
ret = f1('s') #f2调用f1函数
print(ret)
f2()
3.
def func():
def func2():
return 'a'
return func2 #函数名作为返回值
func2=func()
print(func2())
8.闭包:
闭包:1.闭 :内部的函数
2.包 :包含了对外部函数作用域中变量的引用
def hei():
x=20
def inner():
x=10 #如果x定义了,他就用自己的了,就实现不了闭包
print(x)

1 # 闭包的常用形式: 2 def hei(): 3 x=20 4 def inner(): 5 '''闭包函数''' 6 print(x) 7 return inner()
判断闭包函数的方法:__closure__

1 #输出的__closure__有cell元素 :是闭包函数 2 def func(): 3 name = 'eva' 4 def inner(): 5 print(name) 6 print(inner.__closure__) 7 return inner 8 9 f = func() 10 f() 11 12 13 #输出的__closure__为None :不是闭包函数 14 name = 'egon' 15 def func2(): 16 def inner(): 17 print(name) 18 print(inner.__closure__) 19 return inner 20 21 f2 = func2() 22 f2()
闭包获取网络应用

1 # from urllib.request import urlopen 2 # def index(url): 3 # def inner(): 4 # return urlopen(url).read() 5 # return inner 6 # u='http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/7156261.html#_label1' 7 # get = index(u) 8 # print(get())
9.总结
作用域:小范围的可以用大范围的,但是大范围的不能用小范围的
范围从大到小(图)
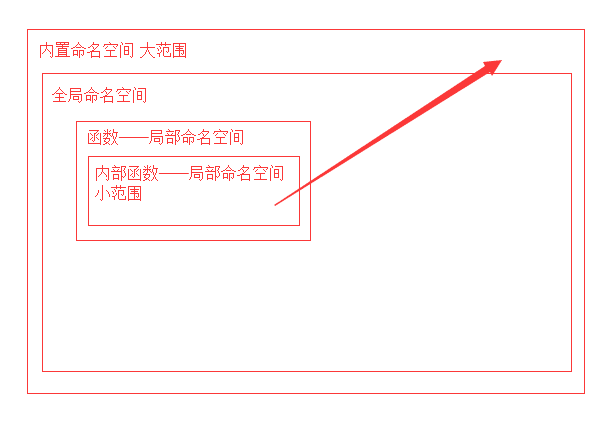
如果在小范围内,如果要用一个变量,是当前这个小范围有的,就用自己的
如果在小范围内没有,就用上一级的,上一级没有的,就用上上级的,以此类推
如果都没有,报错
10.思维导图