昨天学习到对应的知识图谱在networkx的构建,在此先前的代码上,添加一部分的代码,用来完成静态知识的提取。
通过昨天的代码,已经有了基础的节点的增删功能,现在再添加对于节点之间关系的判断,还有一些简单的自然语言的处理如下。
因为现在的关系并没有知识提取的功能,我们现在来添加一些回答的规则用来让回答有一些逻辑的问题。
import difflib
#判断A,B字符间的相似度
def get_str_equal_rate(A,B):
return difflib.SequenceMatcher(None, A, B).quick_ratio()
#获得邻接节点之间的关系,0无连通,1单向连通,2反向连通,3双向连通
def get_nodes_relation(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node1,node2,relation="relation"):
throught_over=False
throught_unti=False
try:
temp=digraph[node1][node2][relation]
if temp:
throught_over=True
except Exception:
throught_over=False
try:
temp=digraph[node2][node1][relation]
if temp:
throught_unti=True
except Exception:
throught_unti=False
if(throught_over and throught_unti):
if(digraph[node2][node1][relation]==digraph[node1][node2][relation]):
return 4
else:
return 3
elif throught_unti:
return 2
elif throught_over:
return 1
else:
return 0
#原子信息处理
def nlp_atom_handle(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node1,node2,relation="relation"):
ptype = get_nodes_relation(digraph, node1, node2, relation)
if (ptype == 4):
return "是" + str(node2) + "的" + str(digraph[node1][node2][relation])
elif (ptype == 3):
return str(digraph[node1][node2][relation]) + str(node2) + ";" + str(node2) + str(
digraph[node2][node1][relation]) + str(node1)
elif (ptype == 2):
return str(node2) + str(digraph[node2][node1][relation]) + str(node1)
elif (ptype == 1):
return str(digraph[node1][node2][relation]) + str(node2)
#处理长距离节点关系
def nlp_nodes(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node1,node2,relation="relation"):
try:
path=nx.dijkstra_path(G, node1, node2, weight='weight')
result=str(node1)
for i in range(len(path)-1):
result+=nlp_atom_handle(digraph,path[i],path[i+1],relation)
if(i!=len(path)-2):
result+=","
else:
result+="。"
except Exception:
result = str(node1)+"和"+str(node2)+"没有任何关系。"
return result
#单节点释义(What)
def nlp_node(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node1,relation="relation"):
try:
result=str(node1)+"("+str(digraph.nodes[node1]['attribute'])+")"
path=[one for one in digraph.neighbors(node1)]
for i in range(len(path)):
result += nlp_atom_handle(digraph, node1, path[i], relation)
if (i != len(path) - 1):
result += ","
result += "。"
prepath=path
path = [one for one in digraph.predecessors(node1) if one not in prepath]
for i in range(len(path)):
result += nlp_atom_handle(digraph, node1, path[i], relation)
if (i != len(path) - 1):
result += ","
else:
result += "。"
except Exception:
result="知识图谱中不存在"+str(node1)
return result
#根据节点的关系得到对应节点列表
def get_relation_nodes(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node,info,relation="relation"):
pnodelist=[]
web=digraph[node]
for one in web:
if web[one][relation]==info:
pnodelist.append(one)
return pnodelist
#得到属性为info的邻居节点
def get_neighbors_attribute_nodes(digraph: nx.DiGraph,node,info):
nlist=[one for one in digraph.successors(node)]
result=[]
for one in nlist:
if digraph.nodes[one]['attribute']==info:
result.append(one)
return result
添加完上述对语言进行处理的一些简单函数之后,我们继续添加对应的节点关系,同时让其回答一些问题看看效果
再次基础上添加电影节点 阿凡达和复仇者联盟,并设定小四喜欢看阿凡达
#知识图谱知识提取测试
#根据知识图谱得到小四和小五的关系
print("小四和小五有什么关系?",nlp_nodes(G, "小四", "小五"))
#释义腾讯节点
print("腾讯是什么?",nlp_node(G,"腾讯"))
#释义张三节点
print("张三是什么?",nlp_node(G,"张三"))
#在知识图谱中添加电影节点,并且设置小四喜欢看阿凡达
add_node_attribute(G,['阿凡达','复仇者联盟'],'电影')
print("所有的节点属性:",get_nodes_attribute(G))
add_edge(G,"小四","阿凡达","喜欢看")
#释义小四节点
print("小四是什么?",nlp_node(G,"小四"))
#释义阿凡达节点
print("阿凡达是什么?",nlp_node(G,"阿凡达"))
print("李四的朋友有?",get_relation_nodes(G,"李四",'朋友'))
print("张三有关的公司有?",get_neighbors_attribute_nodes(G,"张三","公司"))
运行上述代码之后,运行的结果如下所示

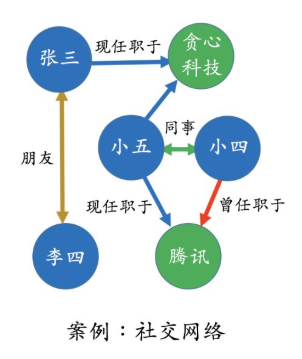
运行结果如上。(在图的基础上添加了小四喜欢看阿凡达)
可以看到对应的知识已经能够被简单地进行回答了。但是现在还是处于静态方面的文档,如果我想设定一个动态问答呢?如广东的天气现在如何?很明显,这个时候就需要用到对应的函数对应的关系了。