一,使用OLS拟合
import pandas as pd import statsmodels.api as sm # 数据的导入 data = pd.read_table("E:\python\part 2\017\TRD_Index.txt",sep=' ') # 目标数据的提取 # 根据 行标签 提取数据 sh_data = data[data['Indexcd']==1] sz_data = data[data.Indexcd==399106] # 提取 列 数据 sh_ret = sh_data.Retindex sz_ret = sz_data['Retindex'] # 索引一致化 # print(sh_ret.index) # print(sz_ret.index) sz_ret.index = sh_ret.index # 构造回归模型 model = sm.OLS(sh_ret,sm.add_constant(sz_ret)).fit() print(model.summary())
模型结果:
OLS Regression Results ============================================================================== Dep. Variable: Retindex R-squared: 0.825 Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.825 Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 5698. Date: Thu, 14 Dec 2017 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00 Time: 19:11:39 Log-Likelihood: 4520.3 No. Observations: 1211 AIC: -9037. Df Residuals: 1209 BIC: -9026. Df Model: 1 Covariance Type: nonrobust ============================================================================== coef std err t P>|t| [95.0% Conf. Int.] ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ const -0.0003 0.000 -1.747 0.081 -0.001 3.58e-05 Retindex 0.7603 0.010 75.487 0.000 0.741 0.780 ============================================================================== Omnibus: 154.029 Durbin-Watson: 1.821 Prob(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 382.039 Skew: 0.701 Prob(JB): 1.10e-83 Kurtosis: 5.367 Cond. No. 60.5 ============================================================================== Warnings: [1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified. Process finished with exit code 0
- 可以得出R的平方为:0.825,可以解释82.5%的方差。
- 截距项为-0.0003,p值为0.081,无法通过通过置信度为0.05的检验,可以推断该模型不含截距项,即为0.
- 斜率为0.7603,通过检验,显著不为0.
- 模型为:sh_ret = -0.0003 + 0.7603 sz_ret + e
绘图比较:
# 绘图 # 原始数据和拟合数据的对比 plt.scatter(sz_ret.values,sh_ret.values,color='b') plt.plot(sz_ret.values,model.fittedvalues,color='r') plt.show()

拟合检验:
# 拟合检验 # 拟合值和残余项的检验(随机分布) plt.scatter(model.fittedvalues,model.resid,color = 'g') plt.xlabel('nihezhi',size =20) plt.ylabel('cancha',size=20) plt.show() # 拟合值和残余项的检验(水平的宽度一致的条带) plt.scatter(model.fittedvalues,model.resid**2,color = 'g') plt.xlabel('nihezhi',size =20) plt.ylabel('cancha',size=20) plt.show() # 正态性检验 # sm.qqplot(model.resid_pearson,stats.norm,line='45')
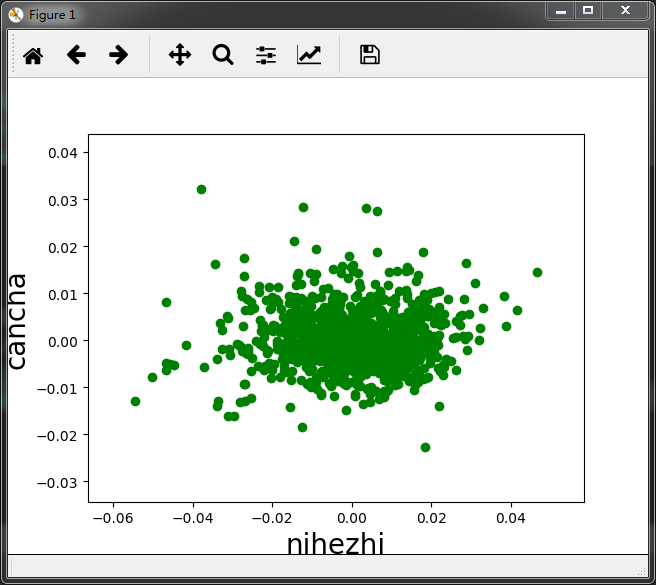
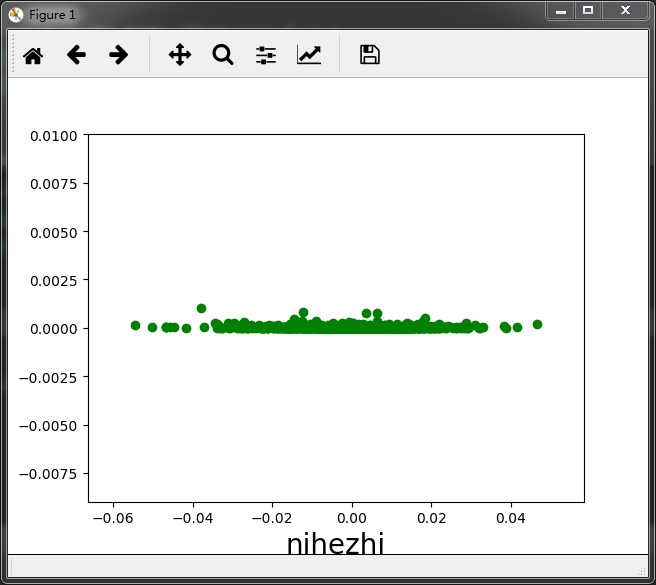
二,使用np的多项式拟合。
import pandas as pd import statsmodels.api as sm import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 数据的导入 data = pd.read_table("E:\python\part 2\017\TRD_Index.txt",sep=' ') # 目标数据的提取 # 根据 行标签 提取数据 sh_data = data[data['Indexcd']==1] sz_data = data[data.Indexcd==399106] # 提取 列 数据 sh_ret = sh_data.Retindex sz_ret = sz_data['Retindex'] # 索引一致化 # print(sh_ret.index) # print(sz_ret.index) sz_ret.index = sh_ret.index # 回归拟合 reg = np.polyfit(sz_ret.values,sh_ret.values,deg=1) print(reg) # 查看模型的参数 reg_fc = np.poly1d(reg) print(reg_fc) # 查看回归方程 # 查看拟合值 ry = np.polyval(reg,sz_ret.values) print(ry[:5]) # 绘图 plt.scatter(sz_ret.values,sh_ret.values,color="b") plt.plot(sz_ret.values,ry,color='r') plt.show()
对比OLS拟合可以看出:
- 拟合方程相同。
- 绘制的图形也是相同的。
- OLS拟合的结果更为专业。