1. 本周学习总结
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容。

2. 书面作业
1. MySQL数据库基本操作
建立数据库,将自己的姓名、学号作为一条记录插入。(截图,需出现自己的学号、姓名)
在自己建立的数据库上执行常见SQL语句(截图)

2. 使用JDBC连接数据库与Statement
2.1 使用Statement操作数据库。(粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号)
2.2 使用JDBC操作数据库主要包含哪几个步骤?
-参考:实验任务书-题目2

2.1装载驱动,与数据库建立连接(Connection),向数据库发送SQL语句(Statement),获得和处理查询或更新语句返回的结果,关闭连接,释放资源。
3. PreparedStatement与参数化查询
3.1 使用PreparedStatement根据用户指定的查询条件进行查询。(粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号)
3.2 批量更新-批量插入1000个学生,统计整个操作所消耗的时间。对比普通方法插入与使用executeBatch方法所消耗的时间。(使用JUint4测试,需要出现时间对比截图)
3.1

3.2

运行:
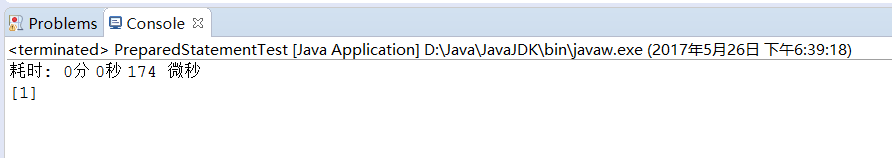
统计整个操作所消耗的时间174微秒,pStatement.executeBatch()输出1表示指示成功处理了命令,给出执行命令所影响数据库中行数的更新计数。
4. JDBCUtil与DAO
4.1 粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,并说明为什么要摘取这段代码。出现学号
4.2 使用DAO模式访问数据库有什么好处?
//201521123115
class StudentDao
{
public Connection conn = null;
public Statement statement = null;
public PreparedStatement pst=null;
public ResultSet rs=null;
private static String querySql ="select * from lin";
public StudentDao() {
try {
Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public boolean add(Student stu)
{
boolean flag=true;
String sql= "insert into lin (Name,ID) values(?,?)";
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,stu.name);
pst.setInt(2,stu.id);
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==0){
flag=false;
}
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
pst.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {}
}
return flag;
}
public boolean delete(Student stu)
{
boolean flag=true;
String sql="delete from user where id=?";
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1,stu.id);
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==0){
flag=false;
}
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
pst.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {}
}
return flag;
}
public boolean update(Student stu)
{
boolean flag=true;
String sql="update lin set Name=? where ID=?";
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,stu.name);
pst.setInt(2,stu.id);
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==0){
flag=false;
}
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
pst.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {}
}
return flag;
}
public List
{
List
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(querySql);
rs=pst.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
students.add(new Student(rs.getString("Name"),rs.getInt("ID")));
}
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
rs.close();
pst.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {}
}
return students;
}
public Student findById(int id)
{
Student stu=new Student();
String sql="SELECT * FROM lin where id=?";
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1,id);
rs=pst.executeQuery();
stu.name=rs.getString("Name");
stu.id=rs.getInt("ID");
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
rs.close();
pst.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {}
}
return stu;
}
public List
{
String sql="SELECT * FROM lin where Name like "?%"";
List
try{
pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,name);
rs=pst.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
students.add(new Student(rs.getString("Name"),rs.getInt("ID")));
}
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try{
rs.close();
pst.close();
}catch (SQLException e){}
}
return students;
}
DAO(Data Access Object):数据存取对象,位于业务逻辑和持久化数据之间,能够实现对持久化数据的访问
分工比较细,为了方便后期维护,使程序更加健壮。
5. 使用数据库改造购物车系统
5.1 使用数据库改造以前的购物车系统(应有图形界面)。如果以前为完成购物车系统,可编写基于数据库的学生管理系统。包括对学生的增删改查,要求使用。
5.2 相比较使用文件,使用数据库存储与管理数据有何不一样?
5.2答:数据库可以存储大量的信息;数据库管理方便,可以用sql操作,对大量数据易于增,删,改,查,极大减少了工作量;数据库比普通的存储方式安全,一般的数据库都有备份数据的功能和相应的命令可以实现它。
3. 码云
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
