瞬间移动
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 263 Accepted Submission(s): 143
Problem Description
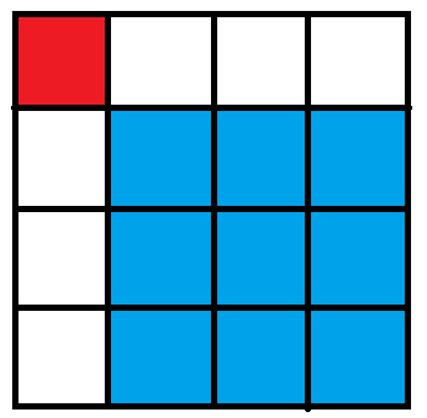
有一个无限大的矩形,初始时你在左上角(即第一行第一列),每次你都可以选择一个右下方格子,并瞬移过去(如从下图中的红色格子能直接瞬移到蓝色格子),求到第n行第m列的格子有几种方案,答案对1000000007取模。

Input
多组测试数据。
两个整数n,m(2≤n,m≤100000)
两个整数n,m(2≤n,m≤100000)
Output
一个整数表示答案
Sample Input
4 5
Sample Output
10
Source
题解:斜着看可以看出来其实是个杨辉三角,就是C(n + m - 4, m - 2);杨辉三角可以用逆元写;
代码:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; const int MOD = 1000000007; typedef __int64 LL; LL P[200010]; void init(){ P[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= 200000; i++){ P[i] = P[i - 1] * i % MOD; } } LL quick_mul(LL a, LL n){ LL ans = 1; while(n){ if(n & 1){ ans *= a; ans %= MOD; } n >>= 1; a *= a; a %= MOD; } return ans % MOD; } LL C(int n, int m){ LL a = P[n]; LL b = P[m] * P[n - m]%MOD; LL p = quick_mul(b, MOD - 2); return a * p % MOD; } int main(){ init(); int n, m; while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){ printf("%I64d ", C(n + m - 4, m - 2)); } return 0; }
还有两种必定超时的方法:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 1010; int dp[MAXN][MAXN]; int main(){ int n, m; while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){ memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){ for(int j = 2; j <= m; j++){ for(int p = 1; p < i; p++){ for(int k = 1; k < j; k++){ dp[i][j] += dp[p][k]; } } } } printf("%d ", dp[n][m]); } return 0; }
记忆化搜索;
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 1010; int dp[MAXN][MAXN]; int dfs(int x, int y){ if(x <= 0 || y <= 0) return 0; if(dp[x][y]) return dp[x][y]; for(int i = 1; i < x; i++){ for(int j = 1; j < y; j++){ dp[x][y] += dfs(i, j); } } return dp[x][y]; } int main(){ int n, m; while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){ dp[1][1] = 1; printf("%d ", dfs(n, m)); } return 0; }