原创建时间:2018-05-12 10:58:56
第一道NOI的题目
洛谷 P1955 题解
题目描述
在实现程序自动分析的过程中,常常需要判定一些约束条件是否能被同时满足。
考虑一个约束满足问题的简化版本:假设x1,x2,x3...代表程序中出现的变量,给定n个形如xi=xj或xi≠xj的变量相等/不等的约束条件,请判定是否可以分别为每一个变量赋予恰当的值,使得上述所有约束条件同时被满足。例如,一个问题中的约束条件为:x1=x2,x2=x3,x3=x4,x4≠x1,这些约束条件显然是不可能同时被满足的,因此这个问题应判定为不可被满足。
现在给出一些约束满足问题,请分别对它们进行判定。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
从文件prog.in中读入数据。
输入文件的第1行包含1个正整数t,表示需要判定的问题个数。注意这些问题之间是相互独立的。
对于每个问题,包含若干行:
第1行包含1个正整数n,表示该问题中需要被满足的约束条件个数。接下来n行,每行包括3个整数i,j,e,描述1个相等/不等的约束条件,相邻整数之间用单个空格隔开。若e=1,则该约束条件为xi=xj;若e=0,则该约束条件为xi≠xj;
输出格式:
输出到文件 prog.out 中。
输出文件包括t行。
输出文件的第 k行输出一个字符串“ YES” 或者“ NO”(不包含引号,字母全部大写),“ YES” 表示输入中的第k个问题判定为可以被满足,“ NO” 表示不可被满足。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
2
2
1 2 1
1 2 0
2
1 2 1
2 1 1
输出 #1
NO
YES
输入 #2
2
3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 1 1
4
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 1
1 4 0
输出 #2
YES
NO
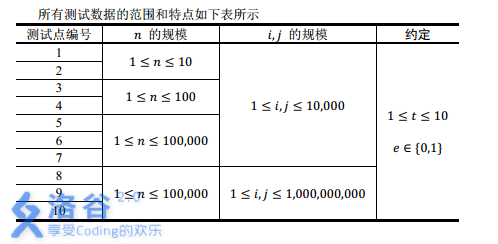
数据范围(图片来自洛谷)
解题思路
把题目中的「x1=x2」看做x1和x2在同一个集合里,「x1≠x2」看做x1和x2不在同一个集合里……
好了,显而易见这是道并查集的题目
读懂了题目,下手就很简单了
这里要注意:
「x1≠x2」是无法进行的操作(因为你不能强制他们不在同一个集合里!若非要实现,就又要维护一个数组),把它看成查询操作。
而且「x1=x2」类似的操作要先做,「x1≠x2」类似的操作要最后做(因为后者对集合没有影响,它是一个查询操作)
如果你遇到了类似这样的数据:
...
1 2 0
1 2 1
...
那么根据我们的思路, 「1 2 0」是一个查询操作,对集合没有影响,那么就相当于少了一个操作!
必须要先进行「x1=x2」类似的合并操作,再做「x1≠x2」类似的查询操作
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100000 + 10;
int U[MAXN], n, t;
int e[MAXN], e0[MAXN], x[MAXN], y[MAXN];
/* 快读 */
inline int getInt() {
int s = 0, x = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch > '9' || ch < '0') {
if (ch == '-') x = -x;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * x;
}
inline int Find(int x) {
if (U[x] == x) return x;
return U[x] = Find(U[x]);
}
inline void Union(int x, int y) {
x = Find(x), y = Find(y);
if (x == y) return;
U[x] = y;
return;
}
bool Main() {
n = getInt();
for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i) {
U[i] = i;
}
memset(e, 0, sizeof(e));
memset(x, 0, sizeof(x));
memset(y, 0, sizeof(y));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
x[i] = getInt(), y[i] = getInt(), e[i] = getInt();
}
int j = 1;
// 第一次做 「x1=y1」的合并操作
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int fe = e[i], fx = x[i], fy = y[i];
if (fe == 1) Union(fx, fy);
}
// 第二次做 「x1≠y1」的查询操作
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int fe = e[i], fx = x[i], fy = y[i];
if (fe == 0) {
if(Find(fx) == Find(fy)) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
t = getInt();
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
if (Main()) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}
离散化
简介
离散化,把无限空间中有限的个体映射到有限的空间中去,以此提高算法的时空效率。
通俗的说,离散化是在不改变数据相对大小的条件下,对数据进行相应的缩小。例如:
原数据:1,999,100000,15;处理后:1,3,4,2;
原数据:{100,200},{20,50000},{1,400};
处理后:{3,4},{2,6},{1,5};
对一堆数据进行离散化,
- 先排序 [ 推荐 std::sort() ](针对有序序列进行离散化)
- 删除重复元素(节省空间)
- 对数据进行索引(最终目的)
而其中我们要用到STL提供的pair来储存变量。pair提供一个包含两个数据成员的结构体模板,可以快速访问其中的元素,就像一个压缩包一样(
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#define Pair pair<ll,ll>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
const int MAXN = 600000 + 10;
int U[MAXN], n, t;
int e[MAXN], x[MAXN], y[MAXN];
Pair p[MAXN];
inline int getInt() {
int s = 0, x = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch > '9' || ch < '0') {
if (ch == '-') x = -x;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * x;
}
inline int Find(int x) {
if (U[x] == x) return x;
return U[x] = Find(U[x]);
}
inline void Union(int x, int y) {
x = Find(x), y = Find(y);
U[x] = y;
return;
}
bool stlCmp(Pair x, Pair y) {
return (x.first > y.first);
}
void Disc(Pair a[], int A[]) {
int tot = 0;
sort(a + 1, a + n*2 + 1, stlCmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n*2; ++i) {
if (i == 1 || a[i].first != a[i-1].first) tot++;
A[a[i].second] = tot;
}
}
bool Main() {
n = getInt();
for (int i = 0; i < 500010; ++i) {
U[i] = i;
}
memset(e, 0, sizeof(e));
memset(x, 0, sizeof(x));
memset(y, 0, sizeof(y));
memset(p, 0, sizeof(p));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int ax = getInt(), ay = getInt(), ae = getInt();
e[i] = ae;
p[i] = make_pair(ax, i);
p[i + n] = make_pair(ay, i+n);
}
Disc(p, x);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) y[i] = x[n + i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int fe = e[i], fx = x[i], fy = y[i];
if (fe == 1) Union(fx, fy);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int fe = e[i], fx = x[i], fy = y[i];
if (fe == 0) {
if(Find(fx) == Find(fy)) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
t = getInt();
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
if (Main()) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}