主要是分三种情况:
- 口胡一眼秒了,实现也很简单,随便写了写 / 懒得写
- 口胡一眼秒了,感觉不大会实现,于是去瞅了瞅别人的代码
- 没读懂题
A
直接模拟。
B
简单数学题 + 找规律,不过有点阅读理解
C
总感觉这题在哪做过,反正是简单题,把全局减法用标记存起来就好了。
D. Blue-Red Permutation
挺有意思的一个贪心,虽然也是简单题。注意到 Red 是可以变大的,那就让它尽量变大;Blue 是可以变小的,那就让它尽量变小。
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
int aa[MAXN];
std::vector<int> blues, reds;
std::string s;
void _main() {
cin >> n;
rep (i, 1, n) {
cin >> aa[i];
} cin >> s;
rep (i, 1, n) {
if (s[i - 1] == 'B') blues.push_back(aa[i]);
else reds.push_back(aa[i]);
}
bool ans = true;
std::sort(ALL(blues)); std::sort(ALL(reds));
// blue: decrease, place at 1 ~ siz(blue)
int ind = 1;
for (auto v : blues) {
if (v < ind) ans = false;
++ind;
}
// red: increase, place at siz(blue) + 1 ~ n
for (auto v : reds) {
if (v > ind) ans = false;
++ind;
}
cout << (ans ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
blues.clear(); reds.clear();
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
_main();
}
return 0;
}
E. Robot on the Board 1
很容易想到是记录上下左右当前最远扩展了多少,然后判一判就好了。
不过感觉自己有点思维固化,最开始的想法居然是先把所有操作走完,然后一个一个回退,没想到可以直接边走边判,超出了直接输出答案即可。
F. Robot on the Board 2
看到谷区没有题解于是就怒水了一发题解
从搜索说起
首先我们看到这个题目可以很自然地想到如何暴力:对于每一个格子从当前点出发进行搜索。
但是这个过程有很多步搜索是不必要的:从一个格子出发,最后停下来的位置是一定的,那么如果这个格子被搜过一遍了,我们还继续搜它干什么呢?直接用我们已经知道的信息不就好了吗?
于是我们考虑采用记忆化的思想:记录一个 dist[i][j] 表示从位置 (i, j) 出发能执行的最大指令数。
接下来从一个未搜过的起始点开始搜索,直到我们碰见一个之前走过的格子。这个结束有三种情况:
- 跳出地图边界
- 走到这次搜索走过的格子,也就是成环
- 走到以前搜索走过的格子
我们分别讨论一下:
跳出地图边界
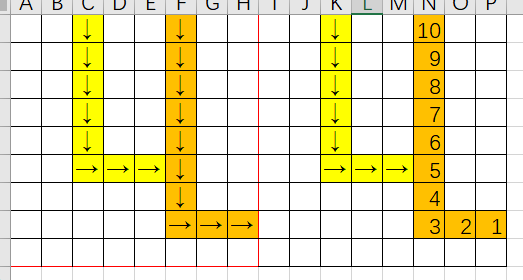
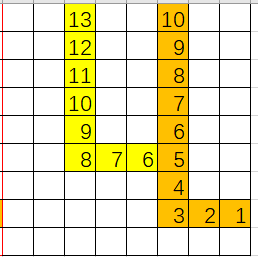
图是拿 Excel 画的
这种情况很简单,我们照着路径顺序逆着更新 dist 即可。
走出环
这种情况下,从环上的所有点出发,都能绕环走一圈,所以环上的点答案就是环长;环外的点就照着路径顺序逆着更新 dist。
走到以前走过的位置
可以发现,答案可以直接从我们之前走过的点继承过来的,照着路径顺序逆着更新 dist 即可。
代码实现
const int MAXN = 2000 + 10;
const std::string drr = "RLDU";
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
const int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int n, m;
char mat[MAXN][MAXN];
int dist[MAXN][MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN][MAXN];
void SearchGetPath(std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > &path, int &x, int &y) {
while (!(x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > m || vis[x][y])) {
// DEBUG(x); DEBUG(y);
vis[x][y] = true;
path.push_back({x, y});
int dr = (int) (drr.find(mat[x][y]));
x += dx[dr]; y += dy[dr];
}
}
void _main() {
cin >> n >> m;
rep (i, 1, n) cin >> (mat[i] + 1);
rep (x, 1, n) rep (y, 1, m) {
dist[x][y] = -1;
vis[x][y] = 0;
}
rep (x, 1, n) rep (y, 1, m) if (dist[x][y] == -1) {
int nx = x, ny = y; std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > path;
SearchGetPath(path, nx, ny);
if (nx < 1 || ny < 1 || nx > n || ny > m) {
// 跳出地图边界
path.push_back({nx, ny});
dist[nx][ny] = 0;
for (int i = (int) path.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
dist[path[i].fi][path[i].se] = dist[path[i + 1].fi][path[i + 1].se] + 1;
}
} else {
// 找环长
int circlesize = (int) (path.end() - std::find(ALL(path), std::make_pair(nx, ny)));
if (circlesize == 0) {
// 这不是环,是之前走过的路径
path.push_back({nx, ny});
for (int i = (int) path.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
dist[path[i].fi][path[i].se] = dist[path[i + 1].fi][path[i + 1].se] + 1;
}
continue;
}
int i = path.size() - 1;
int step = 1; // 一个小 trick,在环上的时候答案是 circlesize,在环外的时候答案就是 step
for (i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
dist[path[i].fi][path[i].se] = std::max(step, circlesize);
++step;
}
}
}
int ax = 0, ay = 0;
rep (i, 1, n) rep (j, 1, m) {
if (dist[i][j] > dist[ax][ay]) {
ax = i; ay = j;
}
}
cout << ax << ' ' << ay << ' ' << dist[ax][ay] << endl;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
_main();
}
return 0;
}
G. Banquet Preparations 1
本题还是有点阅读理解的。在看题解之前我一直没看懂题目到底在说什么,还以为是让试吃者的 balance 最小
题意就是让你求一组 (n) 个 (x_i),使得:
这个东西最小。
先化简一下式子:
其中每一个 (x_i) 都有一个范围限制:
左边是一个固定值,我们把它记为 (S);右边是一个一堆范围求和。是不是感觉好做一些了?
注意到一个性质:假如我们把所有 (x_i) 取到最小值的和记为 (L),取到最大值的和记为 (R),那么 (L leq sum x_i leq R),而且 (sum x_i) 可以取遍所有的 ([L, R])。这是初中的不等式知识,很好理解。
这个性质将题目转化为了:我们要在 ([L, R]) 中找到最接近 (lfloor frac{S}{2} floor) 的数。
此时这就是一道大水题了:对 (S, 2L, 2R) 分类讨论,
- (S leq 2L) 时直接将所有值取到最小;
- (2R leq S) 时直接将所有值取到最大;
- (S in [2L, 2R]) 时,如果 (S) 是偶数那么答案是 (0),否则是 (1)(因为一个奇数减一个偶数不可能是一个偶数),此时方案可以直接贪心的去取,先将所有的 (x) 保底取到最小值,然后将 (lfloor frac{S}{2} floor - L) 贪心地进行分配,如果当前能取最大值就尽量取最大值。
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
std::pair<lli, lli> dishes[MAXN];
std::pair<lli, lli> bounds[MAXN];
lli chosenx[MAXN];
void _main() {
n = read(); m = read();
lli s = 0;
lli suml = 0, sumr = 0;
rep (i, 1, n) {
lli a = read(); lli b = read();
dishes[i] = {a, b};
s += (a - b + m);
bounds[i].fi = std::max(m - b, 0ll);
bounds[i].se = std::min((lli) m, a);
suml += bounds[i].fi; sumr += bounds[i].se;
}
if (2ll * sumr <= s) {
printf("%lld
", s - 2ll * sumr);
rep (i, 1, n) {
lli x = bounds[i].se, y = m - x;
printf("%lld %lld
", x, y);
}
}
else if (s <= 2ll * suml) {
printf("%lld
", 2ll * suml - s);
rep (i, 1, n) {
lli x = bounds[i].fi, y = m - x;
printf("%lld %lld
", x, y);
}
}
else {
printf("%lld
", (s % 2));
lli ns = (s >> 1) - suml;
rep (i, 1, n) {
chosenx[i] = bounds[i].fi;
lli dtx = bounds[i].se - bounds[i].fi;
if (ns >= dtx) {
ns -= dtx; chosenx[i] += dtx;
} else {
chosenx[i] += ns; ns = 0;
}
}
lli checksum = 0;
rep (i, 1, n) {
printf("%lld %lld
", chosenx[i], m - chosenx[i]);
checksum += chosenx[i];
}
assert(std::abs(checksum * 2 - s) <= 1);
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("gout.out", "w", stdout);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T = read();
while (T --> 0) {
_main();
}
return 0;
}
H. Banquet Preparations 2
仍然是在看题解之后才看懂题意
不过这题我并没有看懂题解。。过几天再来填坑