一、CSS选择器
1.基本选择器
标签选择器可以选中所有的标签元素,比如div,ul,li,p 等等,不管标签藏的多深,都能选中,选中的是所有的,而不是某一个,所以说"共性"而不是特性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>高级选择器</title>
<style>
h4{
background: green;
}
.active{
font-size: 22px;
}
h4.active{
color:red;
}
li.active{
background: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li >
<a href="#">1</a>
</li>
<li class="active">
<a href="#">2</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">3</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">4</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

注意:li标签是以一行为显示的
2.高级选择器
说明:高级选择器又分为:后代选择器、子代选择器、并集选择器、交集选择器
# 选中id
同一个页面中id不能重复。
任何的标签都可以设置id
id命名规范 要以字母 可以有数字 下划线 - 大小写严格区分 aa和AA是两个不一样的属性值
示例:
<div class="father">
<div class="item">
<div class="a">
<p>内容</p>
</div>
</div>
<p>内容</p>
<div class="a">
<p>另一个内容</p>
</div>
<a href="#">哈哈</a>
</div>
<p>另一个内容</p>
<h4 class="active">我是一个4级标签</h4>

属性选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style>
label[for]{
color: red;
}
input[type='text']{
background-color: red;
}
label[for^='vip']{
color: blue;
}
label[for*='i']{
color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 属性选择器仅限于在表单控件中 -->
<form>
<label for="username">用户名</label>
<label for="vip">vip</label>
<label for="vvip">vvip</label>
<input type="text">
<input type="password">
</form>
</body>
</html>
后代选择器
使用空格表示后代选择器。顾名思义,父元素的后代(包括儿子,孙子,重孙子)

.container p{
color: red;
}
.container .item p{
color: yellow;
}
子代选择器
使用>表示子代选择器。比如div>p,仅仅表示的是当前div元素选中的子代(不包含孙子....)元素p。

.container>p{
color: yellowgreen;
}
并集选择器
多个选择器之间使用逗号隔开。表示选中的页面中的多个标签。一些共性的元素,可以使用并集选择器

/*并集选择器*/ h3,a{ color: #008000; text-decoration: none; }
交集选择器
使用.表示交集选择器。第一个标签必须是标签选择器,第二个标签必须是类选择器 语法:div.active
比如有一个<h4 class='active'></h4>这样的标签。

h4{ 100px; font-size: 14px; } .active{ color: red; text-decoration: underline; } /* 交集选择器 */ h4.active{ background: #00BFFF; }
它表示两者选中之后元素共有的特性。
伪类选择器
伪类选择器一般会用在超链接a标签中,使用a标签的伪类选择器,我们一定要遵循"爱恨准则"

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .box ul li.item a:link{ color: red; } .box ul li.item a:visited{ color: yellow; } .box ul li.item a:hover{ color: green; font-size: 30px; } .box ul li.item a:active{ color: pink; background-color: #000; } span{ display: block; 200px; height: 200px; background-color: yellow; } span:hover{ display: block; 200px; height: 200px; background-color: yellow; } span:hover{ color: red; cursor: pointer; background-color: #000; font-size: 30px; } input{ 300px; height: 200px; } ul>li{ height: 100px; background-color: red; } /* 行内标签: a span 1、在一行内显示 2、不能设置宽高 3、宽高 是内容的宽高 行内块 1.在一行内显示 2.可以设置宽高 块级标签 div p ul li 1、独占一行 2、可以设置标签宽高 3、如果不设置宽高,默认body100%宽度 */ </style> </head> <body> <span>哈哈哈</span> <input type="text"> <input type="password"> <ul> <li>111</li> </ul> <div class="box"> <ul> <li class="item"> <a href="#">超链接</a> </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> /*ul>li{ list-style: none; }*/ ul li:first-child{ color: red; } ul li:last-child{ color: red; } ul li:nth-child(3){ color: blue; } ul li:nth-child(n){ color: yellow; } ul li:nth-child(3n+1){ color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li>冯波1</li> <li>冯波2</li> <li>冯波3</li> <li>冯波4</li> <li>冯波5</li> <li>冯波6</li> <li>冯波7</li> <li>冯波8</li> </ul> </body> </html>
CSS3的选择器nth-child()
/*选中第一个元素*/
div ul li:first-child{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
/*选中最后一个元素*/
div ul li:last-child{
font-size: 20px;
color: yellow;
}
/*选中当前指定的元素 数值从1开始*/
div ul li:nth-child(3){
font-size: 30px;
color: purple;
}
/*n表示选中所有,这里面必须是n, 从0开始的 0的时候表示没有选中*/
div ul li:nth-child(n){
font-size: 40px;
color: red;
}
/*偶数*/
div ul li:nth-child(2n){
font-size: 50px;
color: gold;
}
/*奇数*/
div ul li:nth-child(2n-1){
font-size: 50px;
color: yellow;
}
/*隔几换色 隔行换色
隔4换色 就是5n+1,隔3换色就是4n+1
*/
div ul li:nth-child(5n+1){
font-size: 50px;
color: red;
}

/*设置第一个首字母的样式*/ p:first-letter{ color: red; font-size: 30px; } /* 在....之前 添加内容 这个属性使用不是很频繁 了解 使用此伪元素选择器一定要结合content属性*/ p:before{ content:'alex'; } /*在....之后 添加内容,使用非常频繁 通常与咱们后面要讲到布局 有很大的关联(清除浮动)*/ p:after{ content:'&'; color: red; font-size: 40px; }
CSS的两大特性:继承性和层叠性
继承性
面向对象语言都会存在继承的概念,在面向对象语言中,继承的特点:继承了父类的属性和方法。那么我们现在主要研究css,css就是在设置属性的。不会牵扯到方法的层面。
继承:给父级设置一些属性,子级继承了父级的该属性,这就是我们的css中的继承。
记住:有一些属性是可以继承下来 : color 、 font-*、 text-*、line-* 。主要是文本级的标签元素。
但是像一些盒子元素属性,定位的元素(浮动,绝对定位,固定定位)不能继承。
层叠性
层叠性: 权重的标签覆盖掉了权重小的标签,说白了 ,就是被干掉了
权重: 谁的权重大,浏览器就会显示谁的属性
谁的权重大? 非常简单就是小学的数数。
数:id的数量 class的数量 标签的数量,顺序不能乱
/*1 0 0 */显示红色
#box{
color: red;
}
/*0 1 0*/
.container{
color: yellow;
}
/*0 0 1*/
p{
color: purple;
}
继承性
有一些属性是可以继承下来 : color 、 font-*、 text-*、line-* 。主要是文本级的标签元素。但是像一些盒子元素属性,定位的元素(浮动,绝对定位,固定定位)不能继承。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>继承性</title> <style> p{ color: blue; background-color: transparent; } div{ color: red; font-size: 40px; background: green; 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p>John</p> </div> </body> </html>

层叠性

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>层叠性</title> <style> #box{ color: green; } .container{ color: yellow; } p{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <p id="box" class="container"> 赵云是什么颜色 </p> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>层叠性</title> <style> #box #box2 p{ color: red; } #box1 #box2 .wrap3 p{ color: green; } #box1 #box2 #box3 p{ color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box1" class="wrap1"> <div id="box2" class="wrap2"> <di id="box3" class="wrap3"> <p>再来猜猜我是什么颜色?</p> </di> </div> </div> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> #box2 .wrap3 p{ color: yellow; } #box1 .wrap2 p{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 当权重一样的 后来者居中 --> <div id='box1' class="wrap1"> <div id="box2" class="wrap2"> <div id="box3" class="wrap3"> <p>再来猜猜我是什么颜色?</p> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>

权重深入
说明:
1.先看标签元素有没有被选中,如果选中了,就数数 (id,class,标签的数量) 谁的权重大 就显示谁的属性。权重一样大,后来者居上
2.如果没有被选中标签元素,权重为0。
如果属性都是被继承下来的 权重都是0 。权重都是0:"就近原则" : 谁描述的近,就显示谁的属性
3.继承来的,描述的一样近,数权重
4.继承来的,描述的一样近,权重一样,后来者居上

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>权重深入</title> 6 <style> 7 #box1.wrap2{ 8 color: red; 9 } 10 #box2.wrap3{ 11 color: yellow; 12 } 13 #box1 .wrap3{ 14 color: red; 15 } 16 #box1 .wrap2 .wrap3{ 17 color: red !important; /*设置优先级无限大*/ 18 } 19 .wrap1 #box2 .wrap3{ 20 color: green; 21 } 22 </style> 23 </head> 24 <body> 25 <div id = 'box1' class="wrap1"> 26 <div id="box2" class="wrap2"> 27 <div id="box3" class="wrap3"> 28 <p style="color: yellow">再来猜猜我是什么颜色?</p> 29 </div> 30 </div> 31 </div> 32 </body> 33 </html>

第一种现象:当权重相同时,以后来设置的属性为准,前提一定要权重相同
#box2 .wrap3 p{
color: yellow;
}
#box1 .wrap2 p{
color: red;
}
我们会发现此时显示的是红色的。
第二种现象: 第一个选择器没有选中内层标签,那么它是通过继承来设置的属性,那么它的权重为0。第二个选择器选中了内层标签,有权重。
所以 继承来的元素 权重为0。跟选中的元素没有可比性。
#box1 #box2 .wrap3{
color: red;
}
#box2 .wrap3 p{
color: green;
}
我们会发现此时显示的是绿色的。
第三种现象:如果都是继承来的属性,谁描述的近,显示谁的属性。'就近原则'
#box1 #box2 .wrap3{
color: red;
}
.wrap1 #box2{
color: green;
}
!important 的使用。
!important:设置权重为无限大
!important 不影响继承来的权重,只影响选中的元素。不要随便使用!important,因为使用它会影响页面的布局
盒模型
在CSS中,"box model"这一术语是用来设计和布局时使用,然后在网页中基本上都会显示一些方方正正的盒子。我们称为这种盒子叫盒模型。
盒模型有两种:标准模型和IE模型。我们在这里重点讲标准模型。
盒模型示意图

盒模型的属性
width:内容的宽度
height: 内容的高度
padding:内边距,边框到内容的距离
border: 边框,就是指的盒子的宽度
margin:外边距,盒子边框到附近最近盒子的距离
如果让你做一个宽高402*402的盒子,您如何来设计呢?
答案有上万种,甚至上一种。
盒模型的计算
如果一个盒子设置了padding,border,width,height,margin(咱们先不要设置margin,margin有坑,后面课程会讲解)
盒子的真实宽度=width+2*padding+2*border
盒子的真实宽度=height+2*padding+2*border
那么在这里要注意看了。标准盒模型,width不等于盒子真实的宽度。
另外如果要保持盒子真实的宽度,那么加padding就一定要减width,减padding就一定要加width。真实高度一样设置。
padding
padding:就是内边距的意思,它是边框到内容之间的距离
另外padding的区域是有背景颜色的。并且背景颜色和内容的颜色一样。也就是说background-color这个属性将填充所有的border以内的区域
padding的设置
padding有四个方向,分别描述4个方向的padding。
描述的方法有两种
1、写小属性,分别设置不同方向的padding
padding-top: 30px; padding-right: 30px; padding-bottom: 30px; padding-left: 30px;
2、写综合属性,用空格隔开
/*上 右 下 左*/
padding: 20px 30px 40px 50px ;
/*上 左右 下*/
padding: 20px 30px 40px;
/* 上下 左右*/
padding: 20px 30px;
/*上下左右*/
padding: 20px;
一些标签默认有padding
比如ul标签,有默认的padding-left值。
那么我们一般在做站的时候,是要清除页面标签中默认的padding和margin。以便于我们更好的去调整元素的位置。
我们现在初学可以使用通配符选择器
*{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
But,这种方法效率不高。
所以我们要使用并集选择器来选中页面中应有的标签(不同背,因为有人已经给咱们写好了这些清除默认的样式表,reset.css)
边框
border:边框的意思,描述盒子的边框
边框有三个要素: 粗细 线性样式 颜色
border: solid
如果颜色不写,默认是黑色。如果粗细不写,不显示边框。如果只写线性样式,默认的有上下左右 3px的宽度,实体样式,并且黑色的边框。
按照3要素来写border
border- 3px; border-style: solid; border-color: red; /* border- 5px 10px; border-style: solid dotted double dashed; border-color: red green yellow; */
按照方向划分
border-top-color: red; border-top-style: solid; border-right- 10px; border-right-color: red; border-right-style: solid; border-bottom- 10px; border-bottom-color: red; border-bottom-style: solid; border-left- 10px; border-left-color: red; border-left-style:solid;
上面12条语句,相当于 bordr: 10px solid red;
另外还可以这样:
border-top: 10px solid red; border-right: 10px solid red; border-bottom: 10px solid red; border-left: 10pxb solid red;
border:none;
border:0;
表示border没有设置样式。
使用border来制作小三角
/*小三角 箭头指向下方*/
div{
0;
height: 0;
border-bottom: 20px solid red;
border-left: 20px solid transparent;
border-right: 20px solid transparent;
}
margin
margin:外边距的意思。表示边框到最近盒子的距离。
/*表示四个方向的外边距离为20px*/ margin: 20px; /*表示盒子向下移动了30px*/ margin-top: 30px; /*表示盒子向右移动了50px*/ margin-left: 50px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
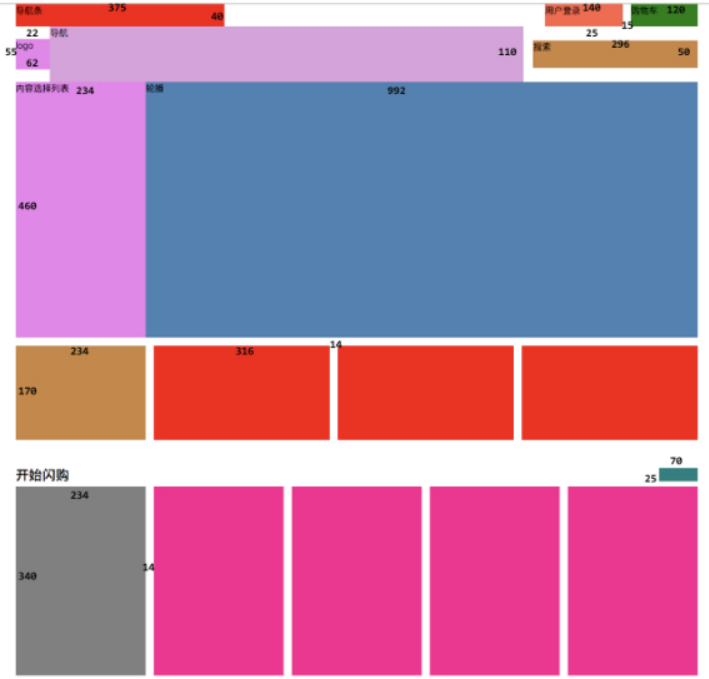
下面演示,做小米官网的简单布局图
先看设计图

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
ul{
list-style: none;
}
/*导航栏的样式*/
.nav{
1226px;
height: 40px;
/**/
margin: 0 auto;
}
.nav .navt{
375px;
height: 40px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
}
.nav .car{
120px;
height: 40px;
background-color: green;
float: right;
margin-left: 15px;
}
.nav .login{
140px;
height: 40px;
background-color: pink;
float: right;
}
.wrap{
1226px;
height: 110px;
/*background: #666;*/
margin: 0 auto;
}
.wrap .logo{
62px;
height: 55px;
background-color: purple;
float: left;
margin-top: 22px;
}
.wrap .nav2{
850px;
height: 110px;
background: pink;
float: left;
}
.wrap .search{
296px;
height: 50px;
float: right;
background-color: purple;
margin-top: 30px;
}
ul{
1226px;
height: 300px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
ul li{
float: left;
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color:red;
margin-left: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="nav">
<div class="navt"></div>
<div class="car"></div>
<div class="login"></div>
</div>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="logo"></div>
<div class="nav2"></div>
<div class="search"></div>
</div>
<!--<ul>-->
<!--<li>1</li>-->
<!--<li>2</li>-->
<!--</ul>-->
</body>
</html>
网页效果:

今日作业:
完成设计图剩余部分
