1,堆作为优先级队列的应用
对于普通队列而言,具有的性质为FIFO,只要实现在队头删除元素,在队尾插入元素即可。因此,这种队列的优先级可视为按 时间到达 的顺序来衡量优先级的。到达得越早,优先级越高,就优先出队列被调度。
更一般地,元素 不能单纯地按时间到来的先后来分优先级(或者说插入的顺序),在这种情形下,使用堆更容易表达优先级队列。
Sometimes the processing order of the items in a queue needs to be based on characteristics of those items,
rather than just the order they are created or added to the queue.
2,堆的两个性质:①结构性质--堆从结构上看是一颗完全二叉树。然而,从物理存储上看,堆的实现基本上是使用一个一维数组存储堆中所有的结点。②ordering property---这是由堆的定义决定的,如大顶堆:根结点的值要大于左右孩子的值。
由于堆具有这两个性质,故在对堆进行操作时,如插入操作、删除操作……都需要维护好这两个性质,因此:这也是为什么堆的插入、删除操作经常需要进行向上调整和向下调整,这就是为了维护堆的 ordering property。
3,建堆时间复杂度的分析
在数据结构--堆的实现(上)中,分析了建堆的两种方法,时间复杂度一种为O(nlogn),一种为O(n)。现在仔细分析如下:
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Sort { 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{ 7 Scanner sc = new Scanner(new File("inputfile"));//read heap's element from inputfile 8 int n = sc.nextInt();//first line in the file gives number of integers to be read 9 ArrayMaxHeap<Integer> sortHeap = new ArrayMaxHeap<Integer>(n); 10 //build heap 11 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 12 sortHeap.add(sc.nextInt());//O(nlogn) 13 14 //sort phase 15 while(!sortHeap.isEmpty()) 16 System.out.println(sortHeap.removeMax()); 17 } 18 }
在上面for循环中的建堆操作中,添加堆中的第一个元素时,完全二叉树高度为1,调用add方法进行堆调整的最坏情况需要 Log1 时间。添加第二个元素时,完全二叉树高度为2,进行堆调整的最坏情况需要 log2 时间……添加第 i 个元素时,最坏需要 logi 时间进行堆调整。故将 n 个元素添加到堆中需要时间:
log1 + log2 + log3 + …… + log(n-1) + logn = log(1*2*3……*n) = log n!
n! = (n/e)nsqrt(2n*pi)
故 O(logn!) = O(nlogn)
同理,也可分析下 while 循环中的堆排序。removeMax()的时间复杂度为logn,n为当前堆中元素的个数。故堆排序的时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
从这里可以看出,此种建堆的方法是调用堆定义的接口来实现的。即调用 堆的接口add()来实现。
另一种建堆的方式则是直接操作堆的底层存储---一维数组 来建堆。此方法建堆的时间复杂度为O(n)
1 Integer[] arr = new Integer[4];arr[0] = 20;arr[1] = 40;arr[2] = 30;arr[3] = 10; 2 ArrayMaxHeap<Integer> heap2 = new ArrayMaxHeap<Integer>(arr); 3 4 public ArrayMaxHeap(T[] entries){ 5 heap = (T[]) new Comparable[entries.length + 1];//how to use generic array... 6 lastIndex = entries.length; 7 for(int index = 0; index < entries.length; index++) 8 { 9 heap[index + 1] = entries[index];//第0号位置不存放元素 10 System.out.println(heap[index + 1]); 11 } 12 for(int index = lastIndex / 2; index >= 1; index--) 13 reheap(index);//从最后一个非叶结点到根结点调用reheap进行堆调整操作 14 }
在第12行的for循环中,从最后一个非叶结点(lastIndex/2)开始,直接调用reheap()操作Integer数组。
private void reheap(int rootIndex){ boolean done = false;//标记堆调整是否完成 T orphan = heap[rootIndex]; int largeChildIndex = 2 * rootIndex;//默认左孩子的值较大 //堆调整基于以largeChildIndex为根的子树进行 while(!done && (largeChildIndex <= lastIndex)){ //largeChildIndex 标记rootIndex的左右孩子中较大的孩子 int leftChildIndex = largeChildIndex;//默认左孩子的值较大 int rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1; //右孩子也存在,比较左右孩子 if(rightChildIndex <= lastIndex && (heap[largeChildIndex].compareTo(heap[rightChildIndex] )< 0)) largeChildIndex = rightChildIndex; if(orphan.compareTo(heap[largeChildIndex]) < 0){ heap[rootIndex] = heap[largeChildIndex]; rootIndex = largeChildIndex; largeChildIndex = 2 * rootIndex;//总是默认左孩子的值较大 } else//以rootIndex为根的子树已经构成堆了 done = true; } heap[rootIndex] = orphan; }
reheap的伪代码如下:
input:array A[0...n-1] output: max heap in A[0...n-1] x = n/2 - 1 while(x>=0) v=value at x siftdown(v) x=x-1 endwhile
时间复杂度为O(n)的分析:
假设堆的高度为 h,当reheap某个结点时,需要对 以该结点为根 的子树进行向下的调整。向下调整时根结点有两次比较(与左右孩子的比较)。
因此,假设某结点在第 i 层,0<= i <h,该结点一共需要 2(h-i)次比较。(最后一层叶结点是不需要比较的,因为建堆是从非叶结点开始)
由于是完全二叉树,故第 i 层的结点个数为 2i
总比较次数为:除去最后一层叶子结点外,其它层的所有的结点的比较次数之和.设总比较次数为S
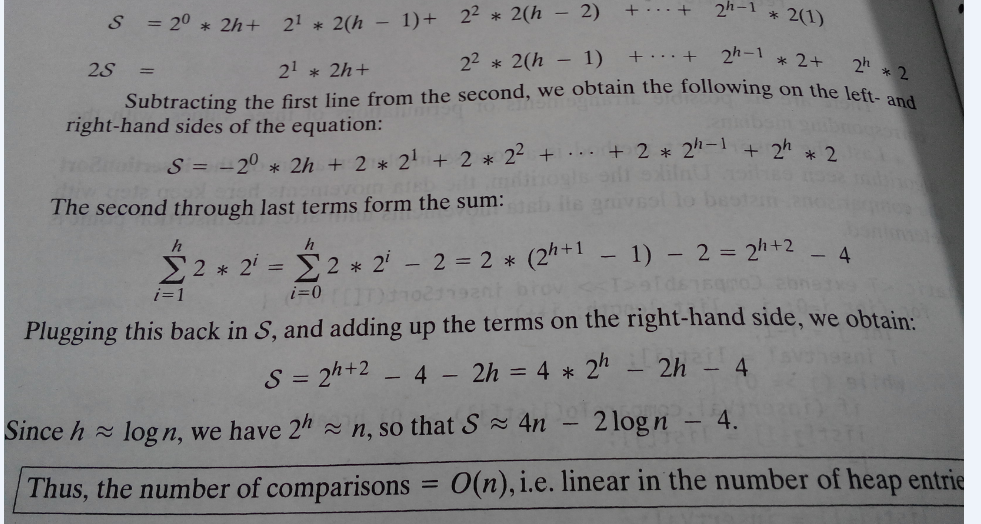
因此,终于明白这种建堆方法的时间复杂度为O(n)了。