二叉树是很常用的一种数据结构。但是在使用它之前,得先构造一棵二叉树,下面这篇文章记录一下如何构造一棵二叉排序树 和 完全二叉树。
一,给定一组整数,请构造一棵二叉排序树
比如:2,4,5,1,3

构造二叉排序树,采用了递归方式来构造。
1 //根据数组 arr 中的元素构造一棵二叉排序树 2 public void buildTree(int[] arr){ 3 for (int node : arr) { 4 insert(node); 5 } 6 } 7 8 private void insert(int ele){ 9 root = insert(root, ele); 10 } 11 12 private BinaryNode insert(BinaryNode root, int ele){ 13 //递归的结束条件.base condition 14 if(root == null) 15 return new BinaryNode(ele); 16 17 if(root.ele > ele) 18 root.left = insert(root.left, ele); 19 else if(root.ele < ele) 20 root.right = insert(root.right, ele); 21 else 22 root.left = insert(root.left, ele); 23 24 return root;//若某结点的左右孩子不空,在后续的递归调用中该结点的左右指针是不会变的. 25 }
二,给定一组整数,请按照从上到下,从左到右的顺序构造一棵二叉树(其实就是完全二叉树)
比如:2,4,5,1,3
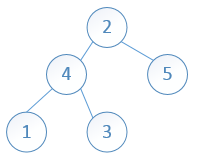
构造一棵完全二叉树,其实这个过程与“二叉树的按层打印非常相似”。因此,需要一个队列保存“下一个待构造的结点”。
当某个结点的左右孩子都已经构造完毕时(next==2),从队列中取出下一个结点,并开始构造它的左右孩子。
1 public void buildCompleteTree(int[] nodes){ 2 Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryNode>(); 3 root = new BinaryNode(nodes[0]); 4 BinaryNode currentNode = null; 5 6 // queue.offer(root); 7 int next = 0;//标记当前结点的左右孩子是否已经构造完毕,当next为2时表示当前结点的左右孩子已经构造完毕 8 currentNode = root;//保存当前正在"构造"的结点 9 int count = 1;//记录数组中的已经构造的元素 10 while(count < nodes.length){ 11 if(next == 2)//某结点的左右孩子已经构造好了,该结点才能够 出队列 12 { 13 currentNode = queue.poll(); 14 next = 0; 15 } 16 if(currentNode.left == null && count < nodes.length)//完全二叉树,先构造左孩子 17 { 18 currentNode.left = new BinaryNode(nodes[count++]); 19 queue.offer(currentNode.left); 20 next++; 21 } 22 if(currentNode.right == null && count < nodes.length)//再构造右孩子 23 { 24 currentNode.right = new BinaryNode(nodes[count++]); 25 queue.offer(currentNode.right); 26 next++; 27 } 28 } 29 }
三,完整代码实现

import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class MyBinarySearchTree { private class BinaryNode{ BinaryNode left; BinaryNode right; int ele; public BinaryNode(int ele) { this.ele = ele; } } private BinaryNode root;//根节点 //根据数组 arr 中的元素构造一棵二叉排序树 public void buildTree(int[] arr){ for (int node : arr) { insert(node); } } private void insert(int ele){ root = insert(root, ele); } private BinaryNode insert(BinaryNode root, int ele){ //递归的结束条件.base condition if(root == null) return new BinaryNode(ele); if(root.ele > ele) root.left = insert(root.left, ele); else if(root.ele < ele) root.right = insert(root.right, ele); else root.left = insert(root.left, ele); return root;//若某结点的左右孩子不空,在后续的递归调用中该结点的左右指针是不会变的. } public void printTreeLineByLine(BinaryNode root){ Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new LinkedList<MyBinarySearchTree.BinaryNode>(); int current = 1;//当前层未打印的结点个数 int next = 0;//下一层待打印的结点个数 queue.offer(root); BinaryNode currentNode; while(!queue.isEmpty()) { currentNode = queue.poll(); current--; System.out.print(currentNode.ele + " ");//打印当前节点 if(currentNode.left != null) { queue.offer(currentNode.left); next++; } if(currentNode.right != null) { queue.offer(currentNode.right); next++; } if(current == 0)//表示本行所有的结点已经打印完了 { System.out.println();//打印下一行 current = next; next = 0; } } } public void buildCompleteTree(int[] nodes){ Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new LinkedList<BinaryNode>(); root = new BinaryNode(nodes[0]); BinaryNode currentNode = null; // queue.offer(root); int next = 0;//标记当前结点的左右孩子是否已经构造完毕 currentNode = root;//保存当前正在"构造"的结点 int count = 1;//记录数组中的已经构造的元素 while(count < nodes.length){ if(next == 2)//某结点的左右孩子已经构造好了 { currentNode = queue.poll(); next = 0; } if(currentNode.left == null && count < nodes.length) { currentNode.left = new BinaryNode(nodes[count++]); queue.offer(currentNode.left); next++; } if(currentNode.right == null && count < nodes.length) { currentNode.right = new BinaryNode(nodes[count++]); queue.offer(currentNode.right); next++; } } } //test public static void main(String[] args) { MyBinarySearchTree bst = new MyBinarySearchTree(); int[] arr = {2,4,5,1,3}; // bst.buildTree(arr); // bst.printTreeLineByLine(bst.root); System.out.println("----------------"); bst.buildCompleteTree(arr); bst.printTreeLineByLine(bst.root); } }
原文地址:博客园hapjin http://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/5738354.html
