一、粘包/拆包概念
TCP是一个“流”协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一长串二进制数据。TCP作为传输层协议并不不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行数据包的划分,所以在业务上认为是一个完整的包,可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也有可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP粘包和拆包问题。
一般所谓的TCP粘包是在一次接收数据不能完全地体现一个完整的消息数据。TCP通讯为何存在粘包呢?主要原因是TCP是以流的方式来处理数据,再加上网络上MTU的往往小于在应用处理的消息数据,所以就会引发一次接收的数据无法满足消息的需要,导致粘包的存在。处理粘包的唯一方法就是制定应用层的数据通讯协议,通过协议来规范现有接收的数据是否满足消息数据的需要。
现在假设客户端向服务端连续发送了两个数据包,用packet1和packet2来表示,那么服务端收到的数据可以分为三种,现列举如下:
第一种情况:
接收端正常收到两个数据包,即没有发生拆包和粘包的现象,此种情况不在本文的讨论范围内。
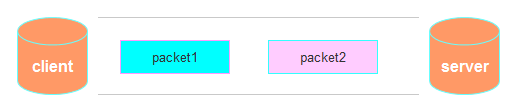
第二种情况:
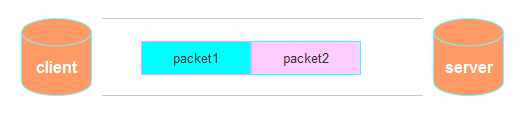
接收端只收到一个数据包,由于TCP是不会出现丢包的,所以这一个数据包中包含了发送端发送的两个数据包的信息,这种现象即为粘包。这种情况由于接收端不知道这两个数据包的界限,所以对于接收端来说很难处理。
第三种情况:
这种情况有两种表现形式,如下图。接收端收到了两个数据包,但是这两个数据包要么是不完整的,要么就是多出来一块,这种情况即发生了拆包和粘包。这两种情况如果不加特殊处理,对于接收端同样是不好处理的。
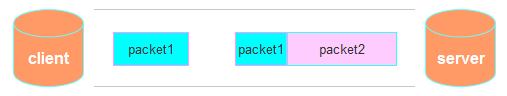
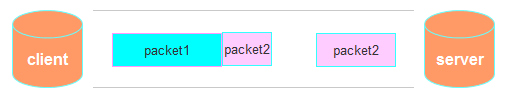
二、粘包问题的解决策略
- 消息定长,报文大小固定长度,不够空格补全,发送和接收方遵循相同的约定,这样即使粘包了通过接收方编程实现获取定长报文也能区分。
- 包尾添加特殊分隔符,例如每条报文结束都添加回车换行符(例如FTP协议)或者指定特殊字符作为报文分隔符,接收方通过特殊分隔符切分报文区分。
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示信息的总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段
三、Netty粘包和拆包解决方案
Netty提供了多个解码器,可以进行分包的操作,分别是:
LineBasedFrameDecoder
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(添加特殊分隔符报文来分包)
FixedLengthFrameDecoder(使用定长的报文来分包)
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
四、TCP粘包和拆包实例演示
首先编写服务端
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class). childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } }
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.UUID; public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { byte[] buffer = new byte[msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(buffer); String message = new String(buffer, Charset.forName("utf-8")); System.out.println("服务端接收到的消息内容:"+message); System.out.println("服务端接收的消息数量:"+(++this.count)); ByteBuf responseByteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(UUID.randomUUID().toString(),Charset.forName("utf-8")); ctx.writeAndFlush(responseByteBuf); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
然后编写客户端
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; public class MyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new MyClientInitializer()); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost",8899).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler()); } }
package com.spring.netty.handler; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("send from client ", Charset.forName("utf-8")); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { byte[] buffer = new byte[msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(buffer); String message = new String(buffer,Charset.forName("utf-8")); System.out.println("客户端接收到的消息内容:"+message); System.out.println("客户端接收到的消息数量:"+(++this.count)); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
分别运行服务端和客户端查看运行效果
服务端效果:
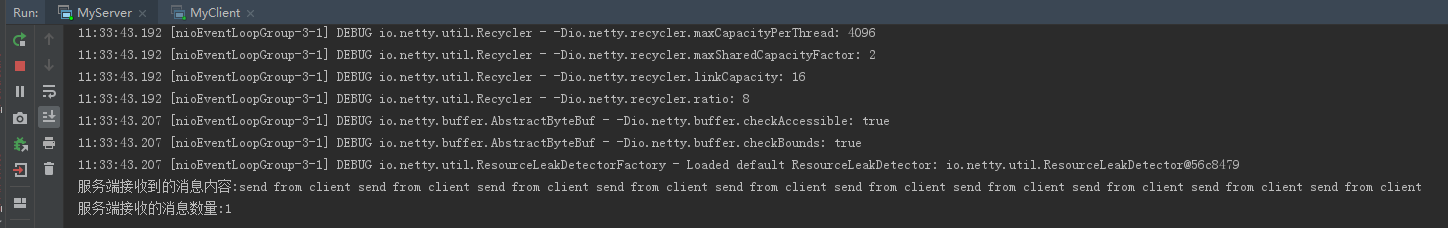
客户端效果:
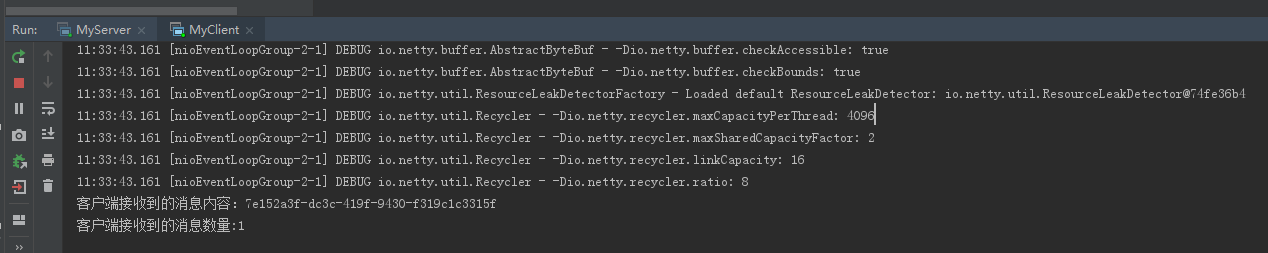
本节我们介绍了TCP粘包拆包的现象及做了个实例演示,下节我们来介绍在Netty中如何解决粘包拆包问题。