1. atexit函数: 用于登记用户自定义的进程终止函数,这样会覆盖系统默认提供的标准终止函数

我们自定义的进程终止函数并非在所有进程终止的情况下都会被调用,是否会被调用与进程的终止方式有关。
下图展示了不同的进程终止方式的区别:
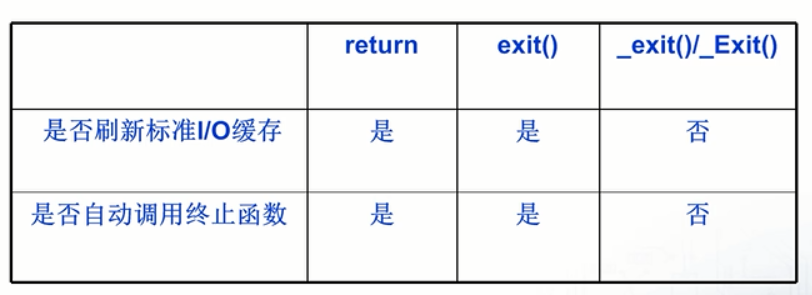
_exit或者_EXIT不会负责调用进程终止函数,也不会刷新缓存。而exit和关键字return会调用进程终止函数,也会刷新缓存。
2. 进程的启动和退出方式 框图详解
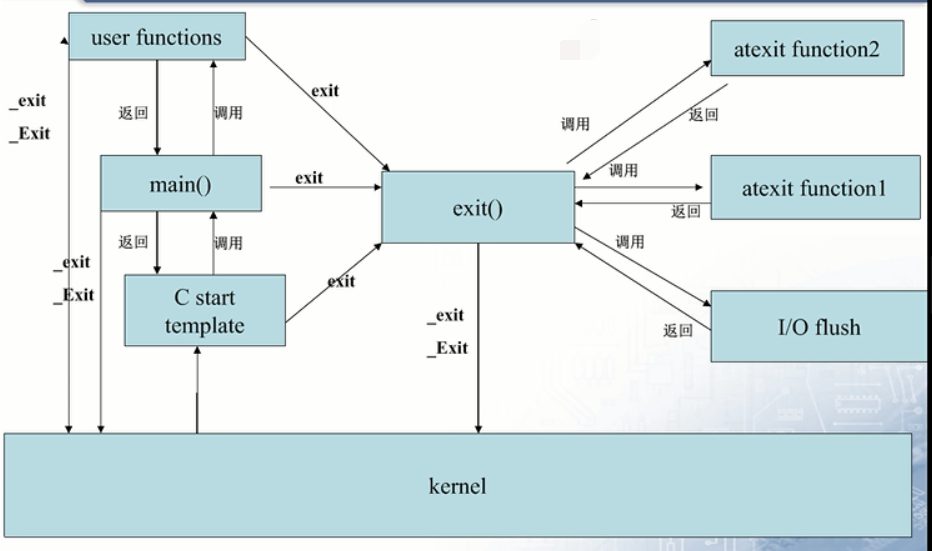
上图中虽然没有提return, 补充下: 使用return和exit的效果是一样的。
3. 实践出真知
实验1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void term_func1(void){
printf("term_func1
");
}
void term_func2(void){
printf("term_func2
");
}
void term_func3(void){
printf("term_func3
");
}
int main(){
atexit(term_func1);
atexit(term_func2);
atexit(term_func3);
return 0;
}
编译运行 :
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程终止# gcc process_end.c
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程终止# ./a.out term_func3
term_func2
term_func1
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程终止#
结论: 登记的多个进程终止函数执行顺序是以栈的方式执行,先登记的后执行。
实验2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void term_func1(void){
printf("term_func1
");
}
void term_func2(void){
printf("term_func2
");
}
void term_func3(void){
printf("term_func3
");
}
int main(int argc, char**argv){
atexit(term_func1);
atexit(term_func2);
atexit(term_func3);
FILE* fp = fopen("file.txt", "wb+");
// 对于wb+,如果文件不存在则会创建,如果文件存在则会覆盖写入。
fprintf(fp, "hello this is a test");
if(!strcmp(argv[1], "exit"))
exit(0);
else if(!strcmp(argv[1], "_exit"))
_exit(0);
else if(!strcmp(argv[1], "_Exit"))
_Exit(0);
else if(!strcmp(argv[1], "return"))
return 0;
else
printf("your input Error!
");
return 0;
}
编译运行 :
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# ./a.out exit
term_func3
term_func2
term_func1
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# cat file.txt
hello this is a testroot@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# ./a.out return
term_func3
term_func2
term_func1
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# cat file.txt
hello this is a testroot@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# ./a.out _exit
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止# cat file.txt
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/for
k/进程终止#
结论: 本实验使用到的fprintf是标准C库里的进行IO操作的函数,是带缓存的,这里不是写标准输入或输出(行缓存),也不是标准错误(无缓存),而是写普通的文件,是全缓存方式。
全缓存方式,刷新缓存的时机是:
1,调用fclose 2. 调用刷新缓存函数fflush sync等 3. 缓存满了
4. 程序退出, 但是对程序退出的方式有要求, 即:
程序退出时使用_exit或者_EXIT不会负责调用进程终止函数,也不会刷新缓存。而使用exit和关键字return会调用进程终止函数,同时也会刷新缓存。
.