1. 进程链、进程扇 图示

所谓进程链就是父进程创建一个子进程,创建的子进程再次创建出一个属于自己的子进程,这样依次往下循环。
所谓的进程扇就是一个父进程创建出多个子进程。
2. 进程链
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork ");
}else if(pid > 0){
break;
}
sleep(3);
}
printf("pid: %d, ppid: %d
",
getpid(), getppid());
while(1);
return 0;
}
编译运行:
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇# gcc fork_list.c
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇# ./a.out
pid: 9957, ppid: 9905 // 一旦执行./a.out,这条语句就会立马打印。
pid: 9958, ppid: 9957 // 延时3秒后,main进程的子进程执行到该打印语句。
pid: 9959, ppid: 9958 // 延时3秒后,main进程的孙进程执行到该打印语句。
pid: 9960, ppid: 9959
pid: 9962, ppid: 9960
pid: 9963, ppid: 9962
^C
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇#
实验截图:

3. 进程扇
实验1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
printf("before fork : pid: %d, ppid: %d
",
getpid(), getppid());
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork ");
}else if(0 == pid){
break;
}
}
printf("pid: %d, ppid: %d
",
getpid(), getppid());
while(1);
return 0;
}
编译运行:
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
9904 pts/12 00:00:00 su
9905 pts/12 00:00:00 bash
10074 pts/12 00:00:00 ps
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇#
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇# gcc fork_list.c
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇# ./a.out
before fork : pid: 10087, ppid: 9905
pid: 10089, ppid: 10087
pid: 10088, ppid: 10087
pid: 10087, ppid: 9905
pid: 10091, ppid: 10087
pid: 10090, ppid: 10087
pid: 10092, ppid: 10087
^C
root@lmw-virtual-machine:/home/lmw/MINE/Linux_C_exercise/fork/进程链和进程扇#
实验截图:
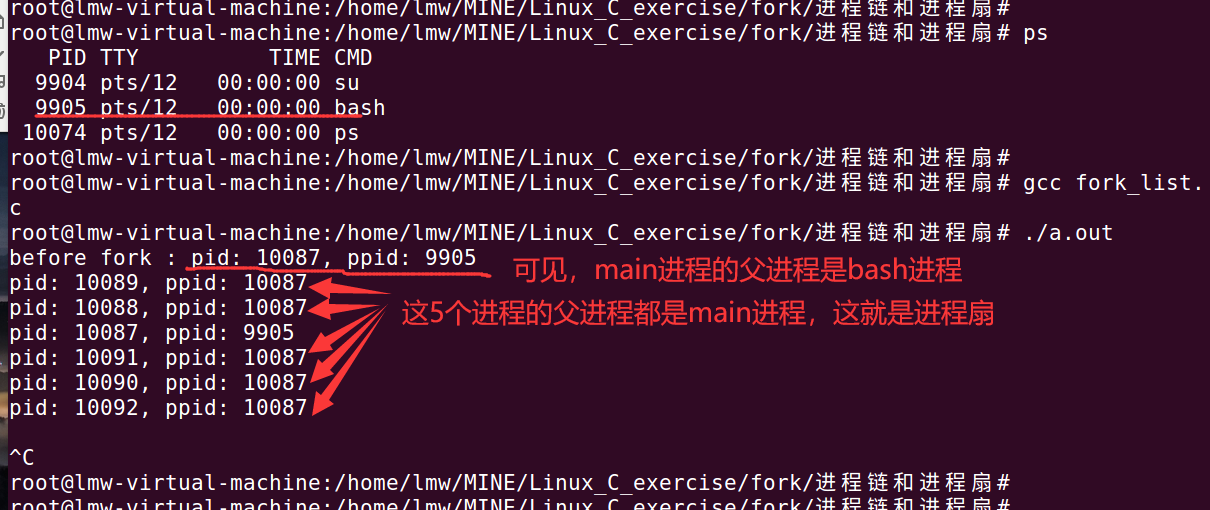
分析:
main进程 fork 5 个进程后, 一共就有了6个进程,
这6个进程具体是谁先执行到最后一条printf代码,这是不一定的,由CPU统一调度。
实验2
在实验1的基础上,修改为:设置main进程是首个执行到最后一条printf语句的进程。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
printf("before fork : pid: %d, ppid: %d
",
getpid(), getppid());
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
perror("fork ");
}else if(0 == pid){
sleep(3);
break;
}
}
printf("pid: %d, ppid: %d
",
getpid(), getppid());
while(1);
return 0;
}
编译运行:
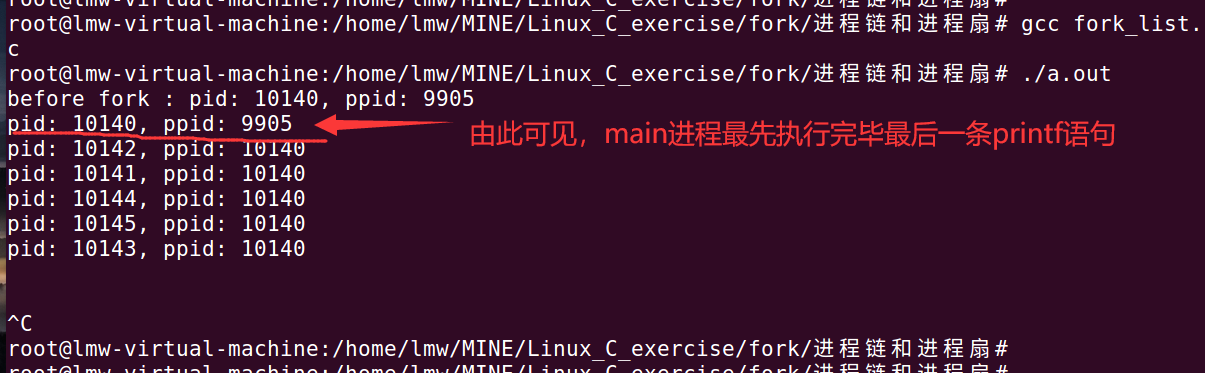
思路分析:
main进程fork出来的子进程们都会sleep 3 秒, 而main进程只需要飞速执行完毕5次fork(所花时间相对sleep 3秒可以忽略不计), 就可以执行到最后一条printf打印语句。
.