阅读书籍: Android开发艺术探索 Android开发进阶从小工到专家
对线程池原理的简单理解:
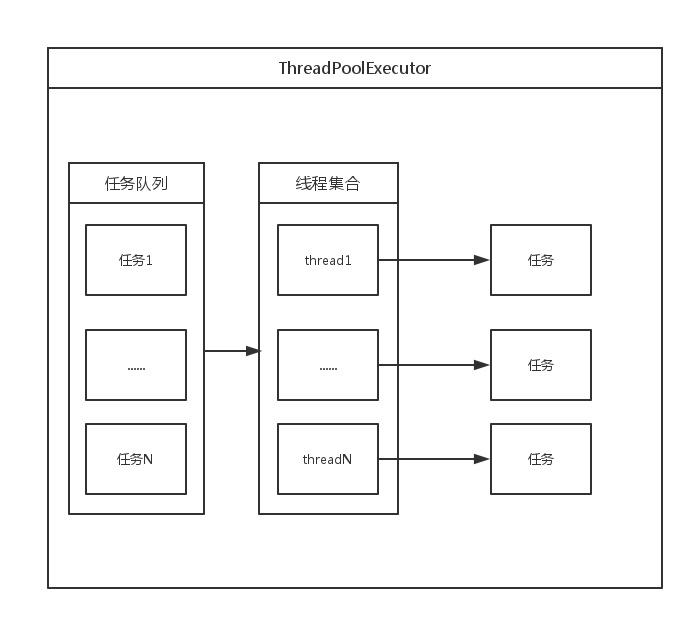
创建多个线程并且进行管理,提交的任务会被线程池指派给其中的线程进行执行,通过线程池的统一调度和管理使得多线程的使用更简单,高效.
使用线程池的优势:
1.重用线程池中的线程,避免因为线程的创建和销毁所带来的性能开销.
2.能有效控制线程池的最大并发数,避免大量的线程之间因互相抢占系统资源而导致的阻塞现象.
3.能够对线程进行简单的管理,并提供定时执行以及指定间隔循环执行等功能.
ThreadPoolExecutor
Android中的线程池都是直接或者间接通过配置ThreadPoolExecutor来实现的,通过不同的参数可以创建不同的线程池.
ThreadPoolExecutor类中有四个构造方法,下面是比较常用的一个.
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory)
corePoolSize
线程池的核心线程数,默认情况下,核心线程会在线程池中一直存活,即使他们处于闲置状态.可以通过设置ThreadPoolExecutor的allowCoreThreadTimeOut属性为true,这样闲置的核心线程在等待新任务到来时会有超时策略,这个时间间隔由keepAliveTime所指定.
maximumPoolSize
线程池所能容纳的最大线程数,当活动线程数达到这个数值后,后续的新任务将会被阻塞.
keepAliveTime
非核心线程闲置时的超时时长,闲置超过这个时长,非核心线程就会被回收.当ThreadPoolExecutor的allowCoreThreadTimeOut属性设置为true时,keepAliveTime同样会作用于核心线程.
unit
用于指定keepAliveTime参数的时间单位,这是一个枚举,例如TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS等.
workQueue
线程池中的任务队列,通过线程池的execute方法提交的Runnable对象会存储在这个参数中.
threadFactory
线程工厂,为线程池提供创建新线程的功能.ThreadFactory是一个接口,它只有一个方法: Thread newThread(Runnable r).
除了以上这些参数外,还有一个不常用的参数RejectedExecutionHandler handler.当线程池无法执行新任务时(这可能是由于任务队列已满或者是无法成功执行任务),会调用handler的rejectedExecution方法来通知调用者,默认情况下该方法会直接抛出一个RejectedExecutionException.(该参数不常用)
ThreadPoolExecutor执行任务时,大致遵循如下规则:
(1)如果线程池中的线程数量未达到核心线程数,那么会直接启动一个核心线程来执行任务.
(2)如果线程池中的线程数量已经达到或者超过核心线程的数量,那么任务会被插到任务队列中排队等待执行.
(3)如果在步骤2中无法将任务插入到任务队列中(这往往是由于任务队列已满),这个时候如果线程数量未达到线程池规定的最大值,那么会立刻启动一个非核心线程来执行任务.
(4)如果步骤3中线程数量已经达到线程池规定的最大值,那么就拒绝执行此任务,ThreadPoolExecutor会调用RejectedExecutionHandler的RejectedExecution方法来通知调用者.
线程池的分类
从线程池的功能特性上来说,Android的线程池主要分为四类,这4类线程池可以通过Executors所提供的工厂方法来得到.
FixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点:
从参数中可以看到FixedThreadPool中只有核心线程并且这些核心线程没有超时机制,任务队列也是没有大小限制的.
FixedThreadPool线程数量固定,当线程处于空闲状态时,它们并不会被回收,除非线程池被关闭了.当所有的线程都处于活动状态时,新任务都会处于等待状态,直到有线程空闲出来.
由于只有核心线程并且这些核心线程不会被回收,这意味着它能够更加快速地响应外界的请求.
使用场景:
对于Android平台,由于资源有限,最常使用的就是通过Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int size)来启动固定数量的线程池
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
fixedThreadPool(3);
}
private static void fixedThreadPool(int size) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(size);
for (int i = 0;i < MAX; i++) {
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.i("MainActivity","执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
执行结果:
03-31 16:03:01.016 25903-25934/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-1
03-31 16:03:01.016 25903-25935/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-2
03-31 16:03:01.016 25903-25936/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-3
03-31 16:03:03.016 25903-25934/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-1
03-31 16:03:03.016 25903-25935/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-2
03-31 16:03:03.016 25903-25936/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-3
03-31 16:03:05.016 25903-25935/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-2
03-31 16:03:05.016 25903-25934/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-1
03-31 16:03:05.016 25903-25936/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-3
03-31 16:03:07.016 25903-25935/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-2
从结果中可以看到,每隔2s有三个线程同时运行,而且是相同的三个线程.
CachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点
从参数中可以看出,它是一种线程数量不定的线程池,而且没有核心线程,只有非核心线程,并且最大线程数为Integer.MAX_VALUE(由于Integer.MAX_VALUE是一个很大的数(0x7FFFFFFF),实际上就相当于最大线程数可以任意大).有60s超时机制,当整个线程池都处于闲置状态时,线程池中的线程都会超时而被停止,这个时候几乎不占用任何系统资源.
使用场景
从CachedThreadPool的特性来看,这类线程池比较适合执行大量的耗时较少的任务.(以空间换时间)
//省略onCreate函数
private static void cachedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0;i < MAX; i++) {
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.i("MainActivity","执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
执行结果:
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6791/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-7
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6785/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-1
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6787/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-3
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6788/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-4
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6789/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-5
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6790/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-6
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6786/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-2
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6792/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-8
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6793/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-9
03-31 16:48:47.776 6757-6794/com.example.janiszhang.threadpooldemo I/MainActivity: 执行线程: pool-1-thread-10
从结果来看,每次调用execute,(在没有空闲线程可用情况下)就会立即启动一个线程,所有任务几乎在同时完成.
ScheduledThreadPool
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
特点及使用场景:
从参数列表可以看出,它的核心线程数是固定的,非核心线程数没有限制.
这类线程池主要用于执行定时任务和具有固定周期的重复任务.
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4);
//2000ms后执行command
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.i("MainActivity", "执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
},2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//延迟10ms后,每隔1000ms执行一次command
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.i("MainActivity", "执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
},10,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
SingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
特点与使用场景:
这类线程池内部只有一个核心线程,它确保所有的任务都在同一个线程中按顺序执行.SingleThreadExecutor的意义在于统一所有的外界任务到一个线程中,这使得在这些任务之间不需要处理线程同步的问题.
线程池的最佳大小
线程池的最佳大小取决于可用处理器的数目以及工作队列中的任务性质.
若在一个具有N个处理器的系统上只有一个工作队列,其中全部是计算性质的任务,在线程池具有N或N+1个线程时一般会获得最大的CPU利用率.
对于那些可能需要等待I/O完成的任务,需要线程池的大小超过可用处理器的数目,因为并不是所有线程都一直在工作.