核心是使用RestController关键字
一。返回单个实体类
1.创建实体类
package com.example.helloworld; public class User { private int id; private String username; private String password; public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } }
2.编写Controller代码
package com.example.helloworld; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloWorldController { @GetMapping("/helloworld") String helloWorld() { return "hello world"; } @RequestMapping("getUser") public User getUser() { User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("hello spring boot"); user.setPassword("123456"); return user; } }
测试:
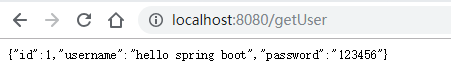
二。返回List
@RequestMapping("getUserList")
public List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setUsername("hello spring boot" + i);
user.setPassword("123456");
userList.add(user);
}
return userList;
}
测试:
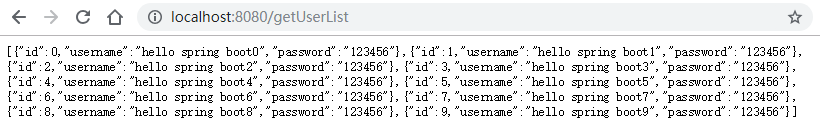
三。返回Map
@RequestMapping("getUserMap")
public Map<String, User> getUserMap() {
Map<String, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setUsername("hello spring boot" + i);
user.setPassword("123456");
userMap.put(i + "", user);
}
return userMap;
}
测试:

Over ...