Java第五次作业--面向对象高级特性(抽象类和接口)
(一)学习总结
1.在上周完成的思维导图基础上,补充本周的学习内容,对Java面向对象编程的知识点做一个全面的总结。
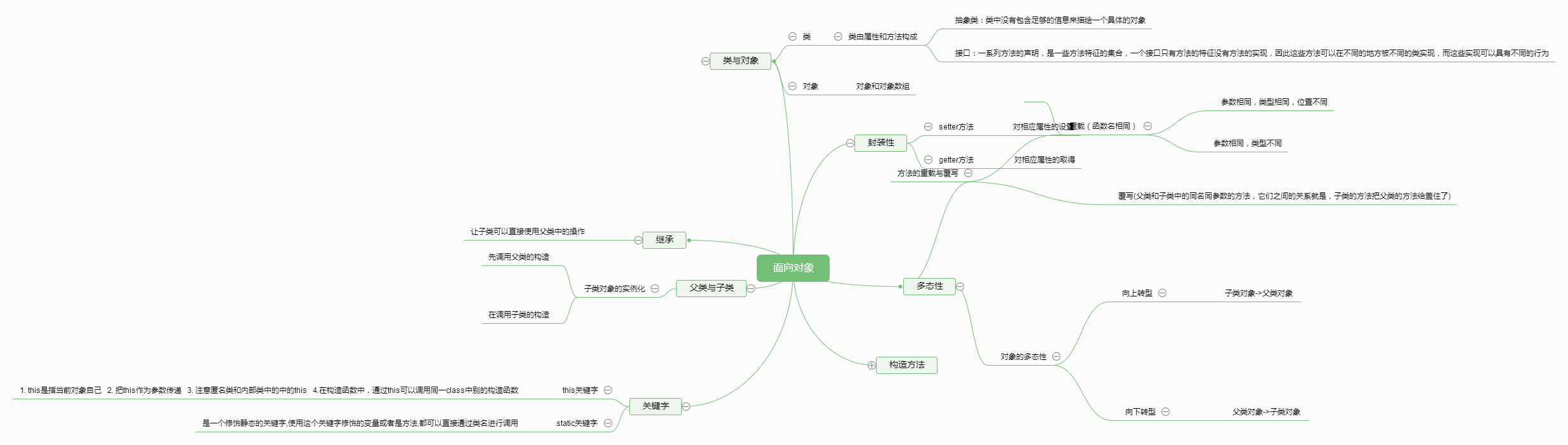
2.汽车租赁公司,出租汽车种类有客车、货车和皮卡三种,每辆汽车除了具有编号、名称、租金三个基本属性之外,客车有载客量,货车有载货量,皮卡则同时具有载客量和载货量。用面向对象编程思想分析上述问题,将其表示成合适的类、抽象类或接口,说明设计思路并画出类图。
- 设计思路:
设计两个接口:分别为载客(载客量方法)和载货(载货量方法)
设计一个汽车类的抽象方法,具有编号,名称,租金三种属性。
设计客车,货车,皮卡三种类继承抽象类
接口:客车->载客 货车->载货 皮卡->载客和载货 - 类图:
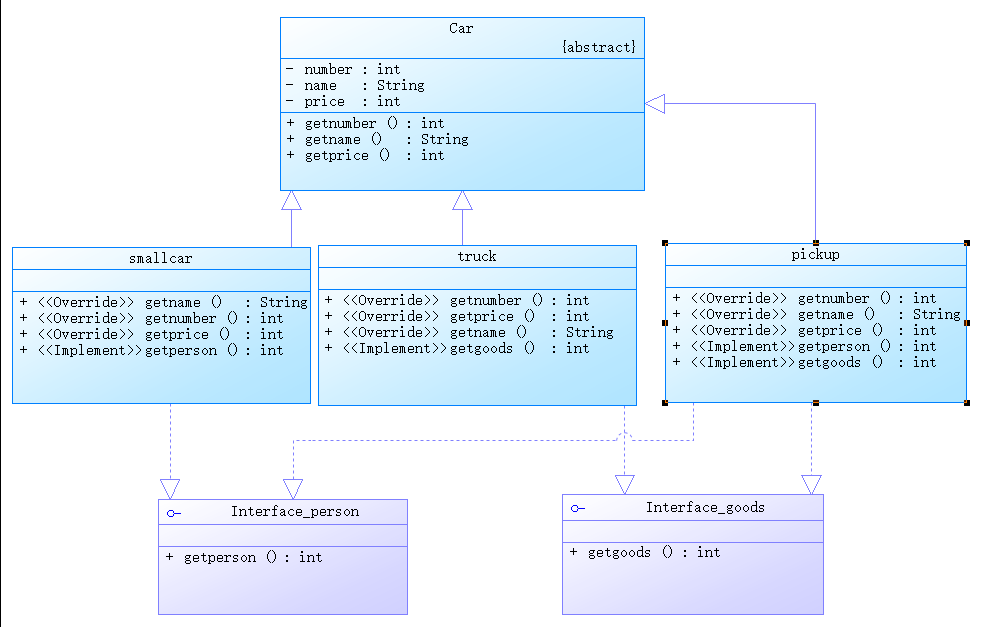
3.阅读下面程序,分析代码是否能编译通过,如果不能,说明原因,并进行改正。如果能,列出运行结果
interface Animal{
void breathe();
void run();
void eat();
}
class Dog implements Animal{
public void breathe(){
System.out.println("I'm breathing");
}
void eat(){
System.out.println("I'm eating");
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.breathe();
dog.eat();
}
}
不能通过,Dog类继承Animal接口,Dog类必须实现接口的抽象所有方法
修改后的代码为:
interface Animal{
void breathe();
void run();
void eat();
}
class Dog implements Animal{
public void breathe(){
System.out.println("I'm breathing");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("I'm eating");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("I'm running");
}
}
public class test04{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.breathe();
dog.eat();
dog.run();
}
}
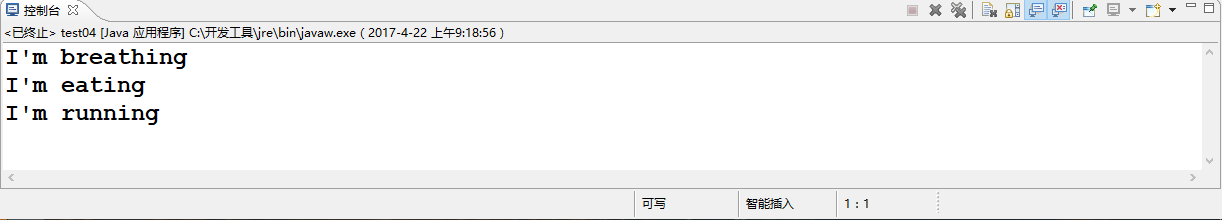
运行结果为:
4.运行下面的程序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] fruits = {"peach","banana","orange","apple"};
Arrays.sort(fruits);
for(int i = 0;i < fruits.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(fruits[i]);
}
}
}
程序输出的结果是升序排序的。查看String 类的源码,说明是如何实现的?如果现在希望对输出的结果进行降序排序,该如何处理?修改上述代码,实现按照字母顺序逆序排序。、
String类的源代码:
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
{
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** The offset is the first index of the storage that is used. */
private final int offset;
/** The count is the number of characters in the String. */
private final int count;
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
/**
* Class String is special cased within the Serialization Stream Protocol.
*
* A String instance is written initially into an ObjectOutputStream in the
* following format:
* <pre>
* <code>TC_STRING</code> (utf String)
* </pre>
* The String is written by method <code>DataOutput.writeUTF</code>.
* A new handle is generated to refer to all future references to the
* string instance within the stream.
*/
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
new ObjectStreamField[0];
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* an empty character sequence. Note that use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*/
public String() {
this.offset = 0;
this.count = 0;
this.value = new char[0];
}
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the
* newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an
* explicit copy of {@code original} is needed, use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*
* @param original
* A {@code String}
*/
public String(String original) {
int size = original.count;
char[] originalValue = original.value;
char[] v;
if (originalValue.length > size) {
// The array representing the String is bigger than the new
// String itself. Perhaps this constructor is being called
// in order to trim the baggage, so make a copy of the array.
int off = original.offset;
v = Arrays.copyOfRange(originalValue, off, off+size);
} else {
// The array representing the String is the same
// size as the String, so no point in making a copy.
v = originalValue;
}
this.offset = 0;
this.count = size;
this.value = v;
}
逆序排序:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] fruits = { "peach", "banana", "orange", "apple" };
Arrays.sort(fruits, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
char a = o1.charAt(0);
char b = o2.charAt(0);
if(o1.equals(o2)){
return 0;
}else if(a>b){
return -1;
}else{
return 1;
}
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {
System.out.println(fruits[i]);
}
}
}
(二)实验总结
1.某工厂生产各种音乐盒,客户无需知道音乐盒的制作过程,只需知道如何播放音乐盒即可。用简单工厂设计模式实现该过程:接口MusicBox具有方法play(),两个音乐盒类PianoBox,ViolinBox,MusicBoxFactory 产生MusicBox的实例。
-
程序设计思路:
建立MusicBox接口
建立PianoBox和ViolinBox两个类,继承MusicBox接口
建立Factory实现功能 -
实验问题分析:
问题1:如何用工厂方法优化代码
解决方案:class Factory { public static MusicBox getInstance (String className){ MusicBox f = null ; if("PianoBox".equals(className)){ f = new PianoBox(); } if("ViolinBox".equals(className)){ f = new ViolinBox(); } return f ; } }
2.修改第三次作业的第一题,使用java.util.Date类表示职工的生日和参加工作时间,并将职工信息按照生日大小排序后输出。(分别用comparable和comparator实现)
-
程序设计思路:
员工自动分配部门,所以排序时应该在部门中进行排序。
解决方法:将员工分成两个数组,再对其进行分别排序
实现代码:Employee [] E=new Employee [5];
Employee [] e=new Employee [5];
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<E.length;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"员工的信息");
System.out.println("输入员工号:");
int number=in.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入员工姓名");
String name=in.next();
System.out.println("输入员工性别");
String sex=in.next();
System.out.println("输入员工生日");
String str1=In.next();
birthday1[i]=sdf1.parse(str1);
System.out.println("输入员工工作日期");
String str2=In.next();
worktime1[i]=sdf1.parse(str2);
E[i]=new Employee(number,name,sex,birthday1[i],worktime1[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(E);
for(int i=0;i<e.length;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+6)+"员工的信息");
System.out.println("输入员工号:");
int number=in.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入员工姓名");
String name=in.next();
System.out.println("输入员工性别");
String sex=in.next();
System.out.println("输入员工生日");
String str1=In.next();
birthday2[i]=sdf1.parse(str1);
System.out.println("输入员工工作日期");
String str2=In.next();
worktime2[i]=sdf1.parse(str2);
e[i]=new Employee(number,name,sex,birthday2[i],worktime2[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(e);
3.在案例宠物商店的基础上,实现以下功能:
(1)展示所有宠物
(2)购买宠物
(3)显示购买清单
-
程序设计思路:
建立Pet接口
建立cat和dog两个类,继承Pet接口
用户选购的时候,根据编号,运用get方法的到相关宠物的信息 -
实验问题分析:
问题1:最后输出购物清单,无法一起输出
解决方案:设置一个数组接受用户购买的所有宠物的编号,在进行遍历,对其输出
实现代码:System.out.println("***************************************"); System.out.println(" 购物清单"); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ findcat(C[i],c); } for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ finddog(D[i],d); } System.out.println("共选购猫"+flagc+"只狗"+flagd+"只"); System.out.println("您购买宠物猫共花费了:"+catmoney+" 您购买宠物狗共花费了:"+dogmoney+" 您总共花费了:"+(dogmoney+catmoney));
(三)代码托管
- 码云commit历史截图