1. 循环显示图像的原理
循环显示有些类似于循环链表,最后一个结点的下一个结点又是第1个结点。循环显示图像也可以模拟这一点。
也许细心的读者从上一节实现的ImageAdapter类中会发现些什么。对!就是getView方法中的position参数和getCount方法的关系。position参数的值是不可能超过getCount方法返回的值的,也就是说,position参数值的范围是0 至 getCount() - 1。
如果这时Gallery组件正好显示到最后一个图像,position参数值正好为getCount() - 1。那么我们如何再让Gallery显示下一个图像呢?也就是说让position参数值再增1,对!将getCount()方法的返回值也增1。
那么这里还有一个问题,如果position参数值无限地增加,就意味着resIds数组要不断地增大,这样会大大消耗系统的资源。
想到这,就需要解决两个问题:
- 既要position不断地增加,又让resIds数组中保存的图像资源ID是有限的,该怎么做呢?
- getCount()方法返回值大小设定
对于getCount()方法非常好解决,可以让getCount方法返回一个很大的数,例如,Integer.MAX_VALUE。这时position参数值就可以随着Gallery组件的图像不断向前移动而增大。现在resIds数组只有15个元素,如果position的值超过数组边界,要想继续循环取得数组中的元素(也就是说,当position的值是15时,取resIds数组的第0个元素,是16时取第1个元素),最简单的方法就是取余,代码如下:
resIds[position % resIds.length]
针对上面的分析,在本节对ImageAdapter类做了如下两个改进:
(1)使getCount方法返回一个很大的值。建议返回Integer.MAX_VALUE。
(2)在getView方法中通过取余来循环取得resIds数组中的图像资源ID。
通过上面两点改进,可以使图像列表在向右移动时会循环显示图像。当然,这种方法从本质上说只是伪循环,也就是说,如果真把图像移动到getCount方法返回的值那里,那也就显示到最后一个图像的。不过在这里getCount方法返回的是Integer.MAX_VALUE,这个值超过了20亿,除非有人真想把图像移动到第20亿的位置,否则Gallery组件看着就是一个循环显示图像的组件。
2. Gallery组件实现循环显示图像的案例
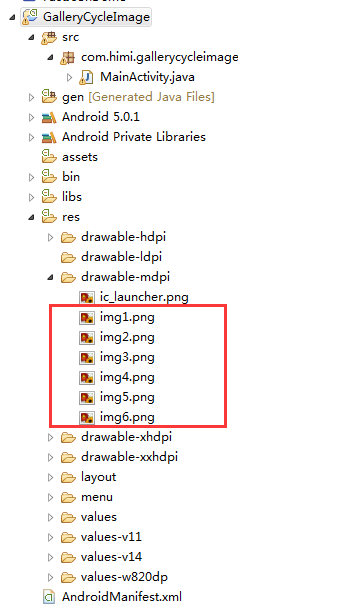
(1)新建一个Android工程,工程目录如下:
(2)首先我们来到主布局文件之中,如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 4 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <Gallery 8 android:id="@+id/gallery" 9 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:layout_marginTop="30dp" /> 12 13 <ImageSwitcher 14 android:id="@+id/imageswitcher" 15 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_marginTop="30dp" /> 18 19 </LinearLayout>
(2)接着我们来到MainActivity,如下:
1 package com.himi.gallerycycleimage; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.content.Context; 5 import android.content.res.TypedArray; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.View; 8 import android.view.ViewGroup; 9 import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils; 10 import android.widget.AdapterView; 11 import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener; 12 import android.widget.BaseAdapter; 13 import android.widget.Gallery; 14 import android.widget.Gallery.LayoutParams; 15 import android.widget.ImageSwitcher; 16 import android.widget.ImageView; 17 import android.widget.ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory; 18 19 public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnItemSelectedListener, ViewFactory { 20 private Gallery gallery; 21 private ImageSwitcher imageSwitcher; 22 private ImageAdapter imageAdapter; 23 private int[] resIds = new int[] { R.drawable.img1, R.drawable.img2, R.drawable.img3, R.drawable.img4, 24 R.drawable.img5, R.drawable.img6 }; 25 26 @Override 27 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 28 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 29 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 30 31 gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gallery); 32 imageAdapter = new ImageAdapter(this); 33 gallery.setAdapter(imageAdapter); 34 gallery.setOnItemSelectedListener(this); 35 36 imageSwitcher = (ImageSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.imageswitcher); 37 // 设置ImageSwitcher组件的工厂对象 38 imageSwitcher.setFactory(this); 39 // 设置ImageSwitcher组件显示图像的动画效果 40 imageSwitcher.setInAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, android.R.anim.fade_in)); 41 imageSwitcher.setOutAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, android.R.anim.fade_out)); 42 } 43 44 public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter { 45 int mGalleryItemBackground; 46 private Context mContext; 47 48 public ImageAdapter(Context context) { 49 mContext = context; 50 TypedArray typedArray = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery); 51 mGalleryItemBackground = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0); 52 } 53 54 // 第1点改进,返回一个很大的值,例如,Integer.MAX_VALUE 55 public int getCount() { 56 return Integer.MAX_VALUE; 57 } 58 59 public Object getItem(int position) { 60 return position; 61 } 62 63 public long getItemId(int position) { 64 return position; 65 } 66 67 public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { 68 ImageView imageView = new ImageView(mContext); 69 // 第2点改进,通过取余来循环取得resIds数组中的图像资源ID 70 imageView.setImageResource(resIds[position % resIds.length]); 71 imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY); 72 imageView.setLayoutParams(new Gallery.LayoutParams(163, 106)); 73 imageView.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground); 74 return imageView; 75 } 76 } 77 78 @Override 79 public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { 80 // 选中Gallery中某个图像时,在ImageSwitcher组件中放大显示该图像 81 imageSwitcher.setImageResource(resIds[position % resIds.length]); 82 } 83 84 @Override 85 public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) { 86 } 87 88 // ImageSwitcher组件需要这个方法来创建一个View对象(一般为ImageView对象) 89 // 来显示图像 90 public View makeView() { 91 ImageView imageView = new ImageView(this); 92 imageView.setBackgroundColor(0xFF000000); 93 imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_CENTER); 94 imageView.setLayoutParams(new ImageSwitcher.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT)); 95 return imageView; 96 } 97 98 }
与此同时,在上面的ImageAdapter类的构造方法中获得了Gallery组件的属性信息。这些信息被定义在resvaluesattrs.xml文件中,代码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <resources> 3 <declare-styleable name="Gallery"> 4 <attr name="android:galleryItemBackground" /> 5 </declare-styleable> 6 </resources>
上面的属性信息用于设置Gallery的背景风格。
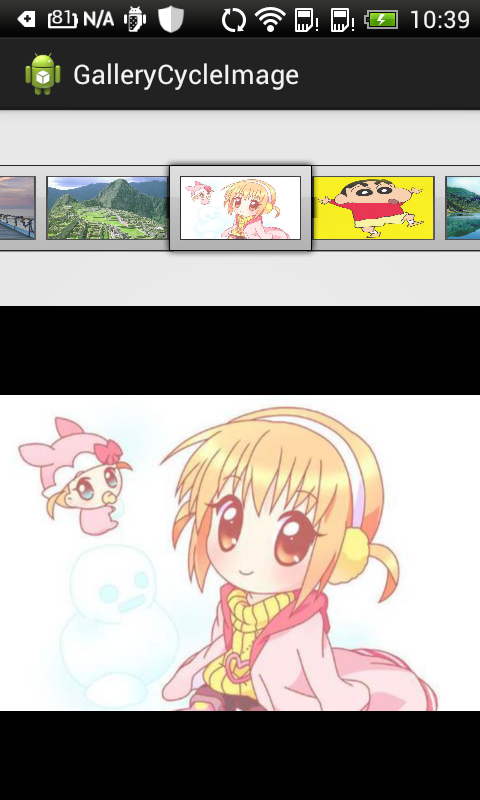
(3)布署程序到手机上如下:
- 应用程序初次启动

- 滑动一下