一.WebSocket协议是什么?
WebSocket 是 HTML5 开始提供的一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通讯的协议。
二.那为什么我们要用WebSocket协议呢?
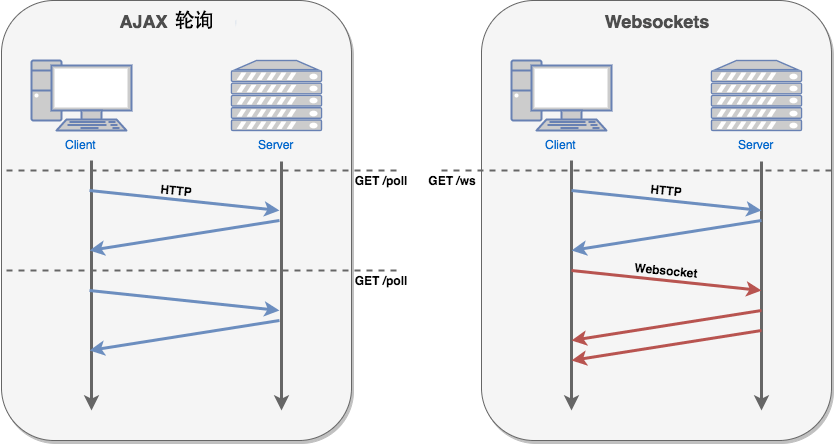
了解计算机网络协议的人,应该都知道:HTTP 协议是一种无状态的、无连接的、单向的应用层协议。它采用了请求/响应模型。通信请求只能由客户端发起,服务端对请求做出应答处理。
这种通信模型有一个弊端:HTTP 协议无法实现服务器主动向客户端发起消息。
因此,为了解决这种弊端,WebSocket就被人们发明出来了。
WebSocket 连接允许客户端和服务器之间进行全双工通信,以便任一方都可以通过建立的连接将数据推送到另一端。WebSocket 只需要建立一次连接,就可以一直保持连接状态。这相比于轮询方式的不停建立连接显然效率要大大提高。
这样,HTML5 定义的 WebSocket 协议,能更好的节省服务器资源和带宽,并且能够更实时地进行通讯。
效果如图:(图片来源于菜鸟教程)
三.客户端API
以下 API 用于创建 WebSocket 对象。
var websocket = new WebSocket("wss://www.xxxxx.cn/xxxxxx/websocket/");
以上代码中的参数地址, 指定连接的 URL。
四.WebSocket事件
以下是 WebSocket 对象的相关事件。假定我们使用了以上代码创建了 websocket对象:
| open | websocket.onopen | 连接建立时触发 |
| message | websocket.onmessage | 客户端接收服务端数据时触发 |
| error | websocket.onerror | 通信发生错误时触发 |
| close | websocket.onclose | 连接关闭时触发 |
五.WebSocket方法
以下是 WebSocket 对象的相关方法。假定我们使用了以上代码创建了 websocket对象:
| send() | websocket.send() | 使用连接发送数据 |
| close() | websocket.close() | 关闭连接 |
六.那WebSocket该怎么写呢?
目前大部分浏览器支持 WebSocket() 接口,你可以在以下浏览器中尝试实例: Chrome, Mozilla, Opera 和 Safari。
举个例子,记得博主另外一篇ajax的文章中,有人提问:如何利用jquery直接序列化提取表单的内容并通过ajax提交上去?
那么就按这个问题来做衍生:
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>骑马行天下小demo</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
//方法
function WebSocketTest()
{
//
if ("WebSocket" in window)
{
alert("您的浏览器支持 WebSocket!");
// 打开一个 websocket
var websocket = new WebSocket("wss://www.xxxxx.cn/xxxxx/websocket/");
websocket .onopen = function()
{
var txt = JSON.stringify($('#myform').serializeJSON());
var txtObject = JSON.parse(txt); //转换为json对象
//获取用户ID
var userId = getCookie("sellerId");
txtObject.userId = userId;
//出生城市
var arr = new Array();
arr[0] = txtObject.testCity;
arr[1] = txtObject.testProvince;
arr[2] = txtObject.testArea;
txtObject.birthCity = arr;
delete txtObject.testCity;
delete txtObject.testProvince;
delete txtObject.testArea;
var birth = txtObject.birthYear + "-" + ((txtObject.birthMonth) > 9 ? txtObject.birthMonth : "0" + txtObject.birthMonth) + "-" + ((txtObject.birthDay) >9 ? txtObject.birthDay : "0" + txtObject.birthDay); //拼接年月日
txtObject.birthDate = birth;
//删除年月日
delete txtObject.birthYear;
delete txtObject.birthMonth;
delete txtObject.birthDay;
var datas = JSON.stringify(txtObject); //转化为字符串
// Web Socket 已连接上,使用 send() 方法发送数据
websocket.send(datas); //发送数据给服务器
alert("数据发送中...");
};
websocket.onmessage = function(txt)
{
var failname= txt.data;
alert("数据已接收...");
};
//监听窗口关闭事件,当窗口关闭时,主动去关闭websocket连接,防止连接还没断开就关闭窗口,server端会抛异常。
window.onbeforeunload = function() {
websocket.close();
};
websocket.onclose = function()
{
// 关闭 websocket
websocket.close();
alert("连接已关闭...");
};
}
else
{
// 浏览器不支持 WebSocket
alert("您的浏览器不支持 WebSocket!");
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="sse">
<a href="javascript:WebSocketTest()">运行 WebSocket</a>
<form action="" method="get" id="myform">
<!--中间内容我就隐藏了,就是一些表单控件-->
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
如上:我们调用 .serializeJSON() 方法来序列化form表单的数据成JS对象,所以我们需要引入一个jquery.serializejson.js库;
代码如下:
(function (factory) { if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) { // AMD. Register as an anonymous module. define(['jquery'], factory); } else if (typeof exports === 'object') { // Node/CommonJS var jQuery = require('jquery'); module.exports = factory(jQuery); } else { // Browser globals (zepto supported) factory(window.jQuery || window.Zepto || window.$); // Zepto supported on browsers as well } }(function ($) { "use strict"; // jQuery('form').serializeJSON() $.fn.serializeJSON = function (options) { var f, $form, opts, formAsArray, serializedObject, name, value, parsedValue, _obj, nameWithNoType, type, keys, skipFalsy; f = $.serializeJSON; $form = this; // NOTE: the set of matched elements is most likely a form, but it could also be a group of inputs opts = f.setupOpts(options); // calculate values for options {parseNumbers, parseBoolens, parseNulls, ...} with defaults // Use native `serializeArray` function to get an array of {name, value} objects. formAsArray = $form.serializeArray(); f.readCheckboxUncheckedValues(formAsArray, opts, $form); // add objects to the array from unchecked checkboxes if needed // Convert the formAsArray into a serializedObject with nested keys serializedObject = {}; $.each(formAsArray, function (i, obj) { name = obj.name; // original input name value = obj.value; // input value _obj = f.extractTypeAndNameWithNoType(name); nameWithNoType = _obj.nameWithNoType; // input name with no type (i.e. "foo:string" => "foo") type = _obj.type; // type defined from the input name in :type colon notation if (!type) type = f.attrFromInputWithName($form, name, 'data-value-type'); f.validateType(name, type, opts); // make sure that the type is one of the valid types if defined if (type !== 'skip') { // ignore inputs with type 'skip' keys = f.splitInputNameIntoKeysArray(nameWithNoType); parsedValue = f.parseValue(value, name, type, opts); // convert to string, number, boolean, null or customType skipFalsy = !parsedValue && f.shouldSkipFalsy($form, name, nameWithNoType, type, opts); // ignore falsy inputs if specified if (!skipFalsy) { f.deepSet(serializedObject, keys, parsedValue, opts); } } }); return serializedObject; }; $.serializeJSON = { defaultOptions: { checkboxUncheckedValue: undefined, // to include that value for unchecked checkboxes (instead of ignoring them) parseNumbers: false, // convert values like "1", "-2.33" to 1, -2.33 parseBooleans: false, // convert "true", "false" to true, false parseNulls: false, // convert "null" to null parseAll: false, // all of the above parseWithFunction: null, // to use custom parser, a function like: function(val){ return parsed_val; } skipFalsyValuesForTypes: [], // skip serialization of falsy values for listed value types skipFalsyValuesForFields: [], // skip serialization of falsy values for listed field names customTypes: {}, // override defaultTypes defaultTypes: { "string": function(str) { return String(str); }, "number": function(str) { return Number(str); }, "boolean": function(str) { var falses = ["false", "null", "undefined", "", "0"]; return falses.indexOf(str) === -1; }, "null": function(str) { var falses = ["false", "null", "undefined", "", "0"]; return falses.indexOf(str) === -1 ? str : null; }, "array": function(str) { return JSON.parse(str); }, "object": function(str) { return JSON.parse(str); }, "auto": function(str) { return $.serializeJSON.parseValue(str, null, null, {parseNumbers: true, parseBooleans: true, parseNulls: true}); }, // try again with something like "parseAll" "skip": null // skip is a special type that makes it easy to ignore elements }, useIntKeysAsArrayIndex: false // name="foo[2]" value="v" => {foo: [null, null, "v"]}, instead of {foo: ["2": "v"]} }, // Merge option defaults into the options setupOpts: function(options) { var opt, validOpts, defaultOptions, optWithDefault, parseAll, f; f = $.serializeJSON; if (options == null) { options = {}; } // options ||= {} defaultOptions = f.defaultOptions || {}; // defaultOptions // Make sure that the user didn't misspell an option validOpts = ['checkboxUncheckedValue', 'parseNumbers', 'parseBooleans', 'parseNulls', 'parseAll', 'parseWithFunction', 'skipFalsyValuesForTypes', 'skipFalsyValuesForFields', 'customTypes', 'defaultTypes', 'useIntKeysAsArrayIndex']; // re-define because the user may override the defaultOptions for (opt in options) { if (validOpts.indexOf(opt) === -1) { throw new Error("serializeJSON ERROR: invalid option '" + opt + "'. Please use one of " + validOpts.join(', ')); } } // Helper to get the default value for this option if none is specified by the user optWithDefault = function(key) { return (options[key] !== false) && (options[key] !== '') && (options[key] || defaultOptions[key]); }; // Return computed options (opts to be used in the rest of the script) parseAll = optWithDefault('parseAll'); return { checkboxUncheckedValue: optWithDefault('checkboxUncheckedValue'), parseNumbers: parseAll || optWithDefault('parseNumbers'), parseBooleans: parseAll || optWithDefault('parseBooleans'), parseNulls: parseAll || optWithDefault('parseNulls'), parseWithFunction: optWithDefault('parseWithFunction'), skipFalsyValuesForTypes: optWithDefault('skipFalsyValuesForTypes'), skipFalsyValuesForFields: optWithDefault('skipFalsyValuesForFields'), typeFunctions: $.extend({}, optWithDefault('defaultTypes'), optWithDefault('customTypes')), useIntKeysAsArrayIndex: optWithDefault('useIntKeysAsArrayIndex') }; }, // Given a string, apply the type or the relevant "parse" options, to return the parsed value parseValue: function(valStr, inputName, type, opts) { var f, parsedVal; f = $.serializeJSON; parsedVal = valStr; // if no parsing is needed, the returned value will be the same if (opts.typeFunctions && type && opts.typeFunctions[type]) { // use a type if available parsedVal = opts.typeFunctions[type](valStr); } else if (opts.parseNumbers && f.isNumeric(valStr)) { // auto: number parsedVal = Number(valStr); } else if (opts.parseBooleans && (valStr === "true" || valStr === "false")) { // auto: boolean parsedVal = (valStr === "true"); } else if (opts.parseNulls && valStr == "null") { // auto: null parsedVal = null; } else if (opts.typeFunctions && opts.typeFunctions["string"]) { // make sure to apply :string type if it was re-defined parsedVal = opts.typeFunctions["string"](valStr); } // Custom parse function: apply after parsing options, unless there's an explicit type. if (opts.parseWithFunction && !type) { parsedVal = opts.parseWithFunction(parsedVal, inputName); } return parsedVal; }, isObject: function(obj) { return obj === Object(obj); }, // is it an Object? isUndefined: function(obj) { return obj === void 0; }, // safe check for undefined values isValidArrayIndex: function(val) { return /^[0-9]+$/.test(String(val)); }, // 1,2,3,4 ... are valid array indexes isNumeric: function(obj) { return obj - parseFloat(obj) >= 0; }, // taken from jQuery.isNumeric implementation. Not using jQuery.isNumeric to support old jQuery and Zepto versions optionKeys: function(obj) { if (Object.keys) { return Object.keys(obj); } else { var key, keys = []; for(key in obj){ keys.push(key); } return keys;} }, // polyfill Object.keys to get option keys in IE<9 readCheckboxUncheckedValues: function (formAsArray, opts, $form) { var selector, $uncheckedCheckboxes, $el, uncheckedValue, f, name; if (opts == null) { opts = {}; } f = $.serializeJSON; selector = 'input[type=checkbox][name]:not(:checked):not([disabled])'; $uncheckedCheckboxes = $form.find(selector).add($form.filter(selector)); $uncheckedCheckboxes.each(function (i, el) { // Check data attr first, then the option $el = $(el); uncheckedValue = $el.attr('data-unchecked-value'); if (uncheckedValue == null) { uncheckedValue = opts.checkboxUncheckedValue; } // If there's an uncheckedValue, push it into the serialized formAsArray if (uncheckedValue != null) { if (el.name && el.name.indexOf("[][") !== -1) { // identify a non-supported throw new Error("serializeJSON ERROR: checkbox unchecked values are not supported on nested arrays of objects like '"+el.name+"'. See https://github.com/marioizquierdo/jquery.serializeJSON/issues/67"); } formAsArray.push({name: el.name, value: uncheckedValue}); } }); }, extractTypeAndNameWithNoType: function(name) { var match; if (match = name.match(/(.*):([^:]+)$/)) { return {nameWithNoType: match[1], type: match[2]}; } else { return {nameWithNoType: name, type: null}; } }, shouldSkipFalsy: function($form, name, nameWithNoType, type, opts) { var f = $.serializeJSON; var skipFromDataAttr = f.attrFromInputWithName($form, name, 'data-skip-falsy'); if (skipFromDataAttr != null) { return skipFromDataAttr !== 'false'; // any value is true, except if explicitly using 'false' } var optForFields = opts.skipFalsyValuesForFields; if (optForFields && (optForFields.indexOf(nameWithNoType) !== -1 || optForFields.indexOf(name) !== -1)) { return true; } var optForTypes = opts.skipFalsyValuesForTypes; if (type == null) type = 'string'; // assume fields with no type are targeted as string if (optForTypes && optForTypes.indexOf(type) !== -1) { return true } return false; }, attrFromInputWithName: function($form, name, attrName) { var escapedName, selector, $input, attrValue; escapedName = name.replace(/(:|.|[|]|s)/g,'\$1'); // every non-standard character need to be escaped by \ selector = '[name="' + escapedName + '"]'; $input = $form.find(selector).add($form.filter(selector)); // NOTE: this returns only the first $input element if multiple are matched with the same name (i.e. an "array[]"). So, arrays with different element types specified through the data-value-type attr is not supported. return $input.attr(attrName); }, // Raise an error if the type is not recognized. validateType: function(name, type, opts) { var validTypes, f; f = $.serializeJSON; validTypes = f.optionKeys(opts ? opts.typeFunctions : f.defaultOptions.defaultTypes); if (!type || validTypes.indexOf(type) !== -1) { return true; } else { throw new Error("serializeJSON ERROR: Invalid type " + type + " found in input name '" + name + "', please use one of " + validTypes.join(', ')); } }, splitInputNameIntoKeysArray: function(nameWithNoType) { var keys, f; f = $.serializeJSON; keys = nameWithNoType.split('['); // split string into array keys = $.map(keys, function (key) { return key.replace(/]/g, ''); }); // remove closing brackets if (keys[0] === '') { keys.shift(); } // ensure no opening bracket ("[foo][inn]" should be same as "foo[inn]") return keys; }, deepSet: function (o, keys, value, opts) { var key, nextKey, tail, lastIdx, lastVal, f; if (opts == null) { opts = {}; } f = $.serializeJSON; if (f.isUndefined(o)) { throw new Error("ArgumentError: param 'o' expected to be an object or array, found undefined"); } if (!keys || keys.length === 0) { throw new Error("ArgumentError: param 'keys' expected to be an array with least one element"); } key = keys[0]; // Only one key, then it's not a deepSet, just assign the value. if (keys.length === 1) { if (key === '') { o.push(value); // '' is used to push values into the array (assume o is an array) } else { o[key] = value; // other keys can be used as object keys or array indexes } // With more keys is a deepSet. Apply recursively. } else { nextKey = keys[1]; if (key === '') { lastIdx = o.length - 1; // asume o is array lastVal = o[lastIdx]; if (f.isObject(lastVal) && (f.isUndefined(lastVal[nextKey]) || keys.length > 2)) { // if nextKey is not present in the last object element, or there are more keys to deep set key = lastIdx; // then set the new value in the same object element } else { key = lastIdx + 1; // otherwise, point to set the next index in the array } } // '' is used to push values into the array "array[]" if (nextKey === '') { if (f.isUndefined(o[key]) || !$.isArray(o[key])) { o[key] = []; // define (or override) as array to push values } } else { if (opts.useIntKeysAsArrayIndex && f.isValidArrayIndex(nextKey)) { // if 1, 2, 3 ... then use an array, where nextKey is the index if (f.isUndefined(o[key]) || !$.isArray(o[key])) { o[key] = []; // define (or override) as array, to insert values using int keys as array indexes } } else { // for anything else, use an object, where nextKey is going to be the attribute name if (f.isUndefined(o[key]) || !f.isObject(o[key])) { o[key] = {}; // define (or override) as object, to set nested properties } } } // Recursively set the inner object tail = keys.slice(1); f.deepSet(o[key], tail, value, opts); } } }; }));
七.总结
共同加油,共同进步,有什么问题欢迎在下方留言或者私信我,提出好问题的,我可能会在下一次博文中,写一篇关于该问题的知识点,谢谢!